Android自定义属性
我们在学习Android开发时,时不时避免不了要自己定义控件,才能满足我们的需求。而自定义控件的时候,就必须设置控件的属性,所有今天我来整理下自定义属性的几种方法:
方法一:通过命名空间去获得属性的值
自定义控件属性文件:/res/values/attrs.xml
参考文件:..\adt-bundle-windows-x86_64-20131030\sdk\platforms\android-19\data\res\values\attrs.xml
attrs.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<resources>
<!-- 定义一个属性的集合,名字叫MyAttrsView,名字建议起的有意义 -->
<declare-styleable name="MyAttrsView">
<!-- 定义一个reference类型的属性,名字叫my_bg -->
<attr name="my_bg" format="reference" />
<!-- 定义一个string类型的属性,名字叫my_name -->
<attr name="my_name" format="string" />
<!-- 定义一个string类型的属性,名字叫my_age -->
<attr name="my_age" format="string" />
</declare-styleable>
</resources>activity_main.xml
<RelativeLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
xmlns:xbmu="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/cn.xbmu.myattrsview"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent">
<cn.xbmu.myattrsview.MyAttrsView
xbmu:my_bg="@drawable/ic_launcher"
xbmu:my_name="my_name_myattrsview"
xbmu:my_age="18"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="@string/hello_world" />
</RelativeLayout>
注意:
自定义命名空间:
xmlns:xxxx="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/<当前软件的包名>"
例如:
xmlns:xbmu="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/cn.xbmu.myattrsview"
MyAttrsView.java
package cn.xbmu.myattrsview;
import android.content.Context;
import android.util.AttributeSet;
import android.view.View;
public class MyAttrsView extends View {
// 需要设置自定义样式的时候用到
public MyAttrsView(Context context, AttributeSet attrs, int defStyle) {
super(context, attrs, defStyle);
}
// 在布局文件中实例化,Android系统规定的
public MyAttrsView(Context context, AttributeSet attrs) {
super(context, attrs);
// 1.根据命名空间去得到属性
String my_bg = attrs.getAttributeValue(
"http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/cn.xbmu.myattrsview",
"my_bg");
String my_name = attrs.getAttributeValue(
"http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/cn.xbmu.myattrsview",
"my_name");
String my_age = attrs.getAttributeValue(
"http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/cn.xbmu.myattrsview",
"my_age");
System.out.println("my_bg:" + my_bg + ",my_name:" + my_name
+ ",my_age:" + my_age);
}
// 在代码中实例化
public MyAttrsView(Context context) {
super(context);
}
}
运行效果:
![]()
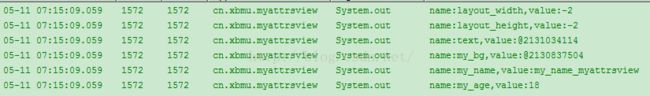
方法二:遍历得到所有属性
MyAttrsView.java
package cn.xbmu.myattrsview;
import android.content.Context;
import android.util.AttributeSet;
import android.view.View;
public class MyAttrsView extends View {
// 需要设置自定义样式的时候用到
public MyAttrsView(Context context, AttributeSet attrs, int defStyle) {
super(context, attrs, defStyle);
}
// 在布局文件中实例化,Android系统规定的
public MyAttrsView(Context context, AttributeSet attrs) {
super(context, attrs);
//2.遍历所有属性
int count = attrs.getAttributeCount();
for(int i=0;i<count;i++){
String name = attrs.getAttributeName(i);
String value = attrs.getAttributeValue(i);
System.out.println("name:"+name+",value:"+value);
}
}
// 在代码中实例化
public MyAttrsView(Context context) {
super(context);
}
}
运行效果:
方法三:用系统工具去取属性,并且区分开来
MyAttrsView.java
package cn.xbmu.myattrsview;
import android.content.Context;
import android.content.res.TypedArray;
import android.graphics.Bitmap;
import android.graphics.Canvas;
import android.graphics.Color;
import android.graphics.Paint;
import android.graphics.drawable.BitmapDrawable;
import android.graphics.drawable.Drawable;
import android.util.AttributeSet;
import android.view.View;
public class MyAttrsView extends View {
private String myName;//名称
private String myAge;//年龄
private Bitmap bitmapBg;//图标背景
private Paint paint = null;
// 需要设置自定义样式的时候用到
public MyAttrsView(Context context, AttributeSet attrs, int defStyle) {
super(context, attrs, defStyle);
}
// 在布局文件中实例化,Android系统规定的
public MyAttrsView(Context context, AttributeSet attrs) {
super(context, attrs);
paint = new Paint();
paint.setColor(Color.BLUE);
//设置抗锯齿
paint.setAntiAlias(true);
// 3.使用系统工具去取属性,并且区分出来
TypedArray typedArray = context.obtainStyledAttributes(attrs,
R.styleable.MyAttrsView);
int indexCount = typedArray.getIndexCount();
for (int i = 0; i < indexCount; i++) {
// 得到属性的id
int id = typedArray.getIndex(i);
switch (id) {
case R.styleable.MyAttrsView_my_name:
myName = typedArray.getString(id);
break;
case R.styleable.MyAttrsView_my_age:
myAge = typedArray.getString(id);
break;
case R.styleable.MyAttrsView_my_bg:
Drawable bg = typedArray.getDrawable(id);
//转换成bitmap
BitmapDrawable drawable = (BitmapDrawable) bg;
bitmapBg = drawable.getBitmap();
break;
default:
break;
}
}
}
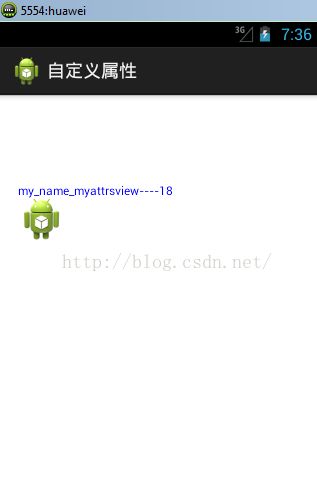
@Override
protected void onDraw(Canvas canvas) {
super.onDraw(canvas);
canvas.drawText(myName+"----"+myAge, 20, 100, paint);
canvas.drawBitmap(bitmapBg, 20, 100, paint);
}
// 在代码中实例化
public MyAttrsView(Context context) {
super(context);
}
}
运行效果: