HDU-2489 Minimal Ratio Tree(最小生成树[Prim])
Minimal Ratio Tree
Time Limit : 2000/1000ms (Java/Other) Memory Limit : 32768/32768K (Java/Other)
Problem Description
For a tree, which nodes and edges are all weighted, the ratio of it is calculated according to the
following equation.
which is a sub-graph of the original graph, with m nodes and whose ratio is the smallest among
all the trees of m nodes in the graph.
Input
Input contains multiple test cases. The first line of each test case contains two integers
n (2<=n<=15) and m (2<=m<=n), which stands for the number of nodes in the graph and the
number of nodes in the minimal ratio tree. Two zeros end the input. The next line contains n
numbers which stand for the weight of each node. The following n lines contain a diagonally
symmetrical n×n connectivity matrix with each element shows the weight of the edge connecting
one node with another. Of course, the diagonal will be all 0, since there is no edge connecting
a node with itself.
All the weights of both nodes and edges (except for the ones on the diagonal of the matrix)
All the weights of both nodes and edges (except for the ones on the diagonal of the matrix)
are integers and in the range of [1, 100].
The figure below illustrates the first test case in sample input. Node 1 and Node 3 form
The figure below illustrates the first test case in sample input. Node 1 and Node 3 form
Output
For each test case output one line contains a sequence of the m nodes which constructs
the minimal ratio tree. Nodes should be arranged in ascending order. If there are several
such sequences, pick the one which has the smallest node number; if there's a tie, look
at the second smallest node number, etc. Please note that the nodes are numbered from 1 .
Sample Input
3 2 30 20 10 0 6 2 6 0 3 2 3 0 2 2 1 1 0 2 2 0 0 0
Sample Output
1 3 1 2
好多次都能想到正解,但是不敢去写,还是需要勇于尝试,不断地尝试才能有更多的理解。
数据范围很小,枚举每一种点的组合情况即可。
#include <cstdio>
#include <cstring>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std;
const double EPS=0.000001;
int ans,sume,sumv;
int n,u,m,w[17],g[17][17];
int ori,cnt,vis,dis[17],pre;
double minr,tmp;
void Prim() {
int i,j;
memset(dis,0x3f,sizeof(dis));
vis=ori,sume=sumv=0;
for(i=1;i<=n;++i)
if((vis&(1<<i))==0) {
dis[i]=0;
break;
}
for(j=1;j<=m;++j) {
u=0;
for(i=1;i<=n;++i)
if(!(vis&(1<<i))&&dis[u]>dis[i])
u=i;
vis|=1<<u;
sume+=dis[u];
sumv+=w[u];
for(i=1;i<=n;++i)
dis[i]=min(dis[i],g[u][i]);
}
if(minr-EPS>(tmp=double(sume)/sumv)) {
minr=tmp;
ans=ori;
}
}
void DFS(int i) {
if(cnt==pre) {
Prim();
return ;
}
if(i>n)
return ;
DFS(i+1);
++cnt;
ori|=1<<i;
DFS(i+1);
--cnt;
ori&=~(1<<i);
}
int main() {
int i,j;
while(scanf("%d%d",&n,&m),n||m) {
for(i=1;i<=n;++i)
scanf("%d",&w[i]);
for(i=1;i<=n;++i)
for(j=1;j<=n;++j)
scanf("%d",&g[i][j]);
minr=999999999;
ori=cnt=0;
pre=n-m;
DFS(1);
for(i=1;i<=n;++i)
if(!(ans&(1<<i))) {
printf("%d",i++);
break;
}
for(;i<=n;++i)
if(!(ans&(1<<i)))
printf(" %d",i);
printf("\n");
}
return 0;
}
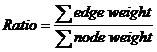
![HDU-2489 Minimal Ratio Tree(最小生成树[Prim])_第1张图片](http://img.e-com-net.com/image/info5/18a07e93c5eb4b859ec95b557c083160.jpg)