Zoj1051 A New Growth Industry
Zoj1051 A New Growth Industry
A biologist experimenting with DNA modification of bacteria has found a way to make bacterial colonies sensitive to the
surrounding population density. By changing the DNA, he is able to "program" the bacteria to respond to the varying densities in their immediate neighborhood.
The culture dish is a square, divided into 400 smaller squares (20x20). Population in each small square is measured on a four point scale (from 0 to 3). The DNA information is represented as an array D, indexed from 0 to 15, of integer values and is interpreted as follows:
In any given culture dish square, let K be the sum of that square's density and the densities of the four squares immediately to the left, right, above and below that square (squares outside the dish are considered to have density 0). Then, by the next day, that dish square's density will change by D[K] (which may be a positive, negative, or zero value). The total density cannot, however, exceed 3 nor drop below 0.
Now, clearly, some DNA programs cause all the bacteria to die off (e.g., [-3, -3, ..., -3]). Others result in immediate population explosions (e.g., [3,3,3, ..., 3]), and others are just plain boring (e.g., [0, 0, ... 0]). The biologist is interested in how some of the less obvious DNA programs might behave.
Write a program to simulate the culture growth, reading in the number of days to be simulated, the DNA rules, and the initial population densities of the dish.
Input Format:
Input to this program consists of three parts:
1. The first line will contain a single integer denoting the number of days to be simulated.
2. The second line will contain the DNA rule D as 16 integer values, ordered from D[0] to D[15], separated from one another by one or more blanks. Each integer will be in the range -3...3, inclusive.
3. The remaining twenty lines of input will describe the initial population density in the culture dish. Each line describes one row of squares in the culture dish, and will contain 20 integers in the range 0...3, separated from one another by 1 or more blanks.
Output Format:
The program will produce exactly 20 lines of output, describing the population densities in the culture dish at the end of the simulation. Each line represents a row of squares in the culture dish, and will consist of 20 characters, plus the usual end-of-line terminator.
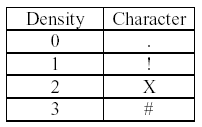
Each character will represent the population density at a single dish square, as follows:
No other characters may appear in the output.
This problem contains multiple test cases!
The first line of a multiple input is an integer N, then a blank line followed by N input blocks. Each input block is in the format indicated in the problem description. There is a blank line between input blocks.
The output format consists of N output blocks. There is a blank line between output blocks.
Sample Input:
1 2 0 1 1 1 2 1 0 -1 -1 -1 -2 -2 -3 -3 -3 -3 3 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 3 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
Sample Output:
##!................. #!.................. !................... .................... .................... .................... .................... .........!.......... ........!#!......... .......!#X#!........ ........!#!......... .........!.......... .................... .................... .................... .................... .................... .................... .................... ....................
注意:
1】注意数组初始化为0;有的编译器初始化默认是无穷
2】尽量少用类似的变量名(自己p和q傻傻分不清T_T),用有意义的
3】每个样例之间有回车,最后一个没有
4】输出的符号之间没有空格
5】学好英语,理解题意太重要了,花费太长时间…其实题目并不难,看了好多网上的讲解才明白…
感谢http://blog.csdn.net/wankaiming/article/details/8104857这篇帮助很大
#include <stdio.h>
int main(){
int m,day,i,j;
int D[16];
int p[22][22],q[22][22]; //p是培养皿。q是密度
char ch[4]={'.','!','X','#'};
freopen("zoj1051.txt","r",stdin);
scanf("%d",&m);
while(m--){
scanf("%d",&day);
for(i=0;i<16;i++) scanf("%d",&D[i]);
for(i=0;i<22;i++){
p[0][i]=0;
p[i][0]=0;
q[0][i]=0;
q[i][0]=0;
}
for(i=0;i<22;i++){
p[21][i]=0;
p[i][21]=0;
<span style="white-space:pre"> </span> q[21][i]=0;
q[i][21]=0;
}
for(i=1;i<21;i++) //初始化培养皿
for(j=1;j<21;j++){
scanf("%d",&p[i][j]);
}
while(day--){
for(i=1;i<21;i++) { //计算密度
for(j=1;j<21;j++){
q[i][j]=p[i][j]+p[i-1][j]+p[i+1][j]+p[i][j-1]+p[i][j+1];
}
}
for(i=1;i<21;i++) //计算密度
for(j=1;j<21;j++){
p[i][j]+=D[q[i][j]];
if(p[i][j]>3) p[i][j]=3;
else if(p[i][j]<0) p[i][j]=0;
}
}
for(i=1;i<21;i++){
for(j=1;j<21;j++){
printf("%c",ch[p[i][j]]);
}
printf("\n");
}
if(m) printf("\n");
}
return 0;
}