LeetCode 题解(96): The Skyline Problem
题目:
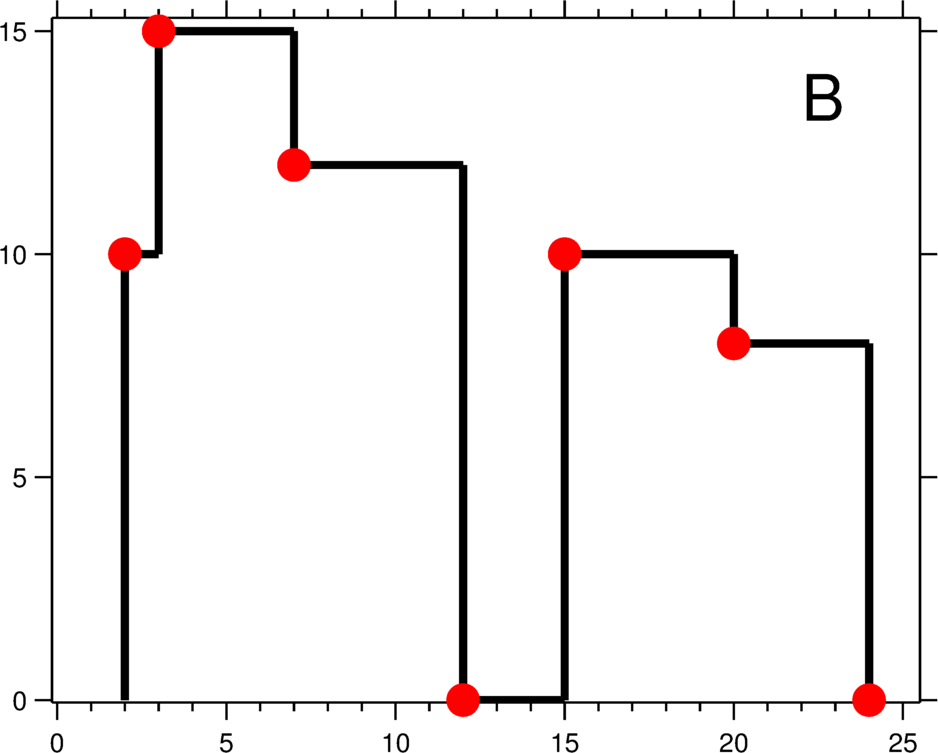
A city's skyline is the outer contour of the silhouette formed by all the buildings in that city when viewed from a distance. Now suppose you aregiven the locations and height of all the buildings as shown on a cityscape photo (Figure A), write a program tooutput the skyline formed by these buildings collectively (Figure B).
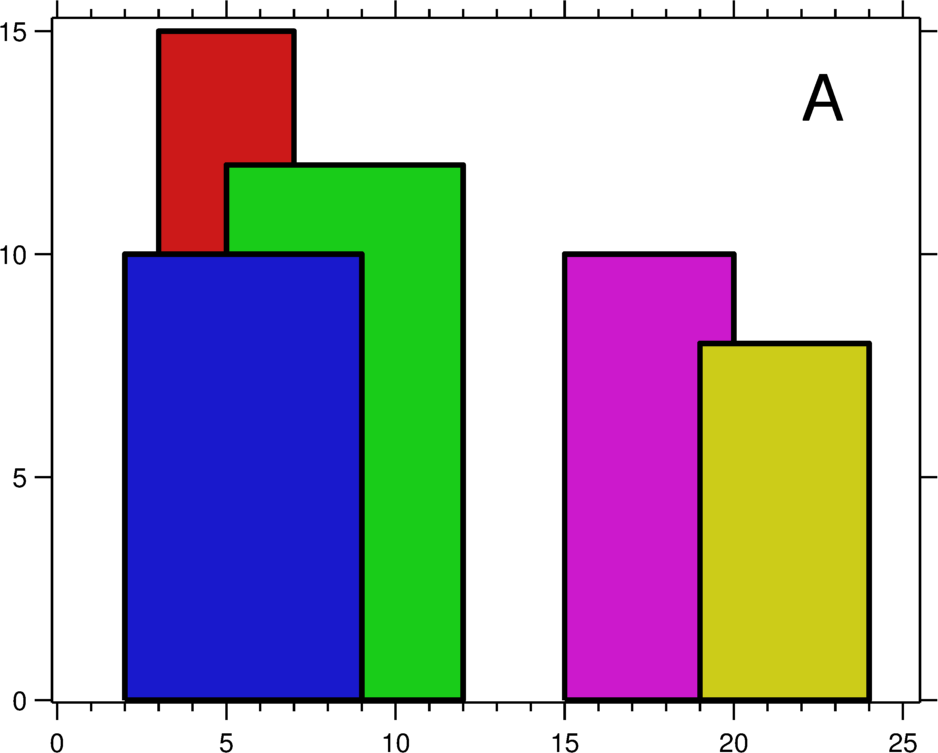
The geometric information of each building is represented by a triplet of integers[Li, Ri, Hi], whereLi and Ri are the x coordinates of the left and right edge of the ith building, respectively, andHi is its height. It is guaranteed that0 ≤ Li, Ri ≤ INT_MAX,0 < Hi ≤ INT_MAX, and Ri - Li > 0. You may assume all buildings are perfect rectangles grounded on an absolutely flat surface at height 0.
For instance, the dimensions of all buildings in Figure A are recorded as: [ [2 9 10], [3 7 15], [5 12 12], [15 20 10], [19 24 8] ] .
The output is a list of "key points" (red dots in Figure B) in the format of[ [x1,y1], [x2, y2], [x3, y3], ... ] that uniquely defines a skyline.A key point is the left endpoint of a horizontal line segment. Note that the last key point, where the rightmost building ends, is merely used to mark the termination of the skyline, and always has zero height. Also, the ground in between any two adjacent buildings should be considered part of the skyline contour.
For instance, the skyline in Figure B should be represented as:[ [2 10], [3 15], [7 12], [12 0], [15 10], [20 8], [24, 0] ].
Notes:
- The number of buildings in any input list is guaranteed to be in the range
[0, 10000]. - The input list is already sorted in ascending order by the left x position
Li. - The output list must be sorted by the x position.
- There must be no consecutive horizontal lines of equal height in the output skyline. For instance,
[...[2 3], [4 5], [7 5], [11 5], [12 7]...]is not acceptable; the three lines of height 5 should be merged into one in the final output as such:[...[2 3], [4 5], [12 7], ...]
解法一:总体思想是Divide and Conquer,但是Conquer的时候需要特殊处理左边重叠的情况。Merge的基本思路是设两个变量h1 = 0, h2 = 0,以及maxH用于记录上次的高度。取两个序列中x小的,相应的改变h1或h2的值。同时merge后的新元素为(x.min, max(h1, h2)),并且只有当max(h1,h2) != maxH的时候才更新,这样可以防止添加进高度一样的元素。然后令maxH = max(h1, h2)保存当次的高度值,用于下次更新时的比较。
C++版:
class Solution {
public:
vector<pair<int, int>> getSkyline(vector<vector<int>>& buildings) {
vector<pair<int, int>> results;
if (buildings.size() == 0)
return results;
if (buildings.size() == 1) {
results.push_back(pair<int, int>(buildings[0][0], buildings[0][2]));
results.push_back(pair<int, int>(buildings[0][1], 0));
return results;
}
vector<pair<int, int>> left = divide(0, (buildings.size() - 1) / 2, buildings);
vector<pair<int, int>> right = divide((buildings.size() - 1) / 2 + 1, buildings.size() - 1, buildings);
results = conquer(left, right);
return results;
}
vector<pair<int, int>> divide(int start, int end, vector<vector<int>>& buildings) {
if (start == end) {
vector<pair<int, int>> result;
result.push_back(pair<int, int>(buildings[start][0], buildings[start][2]));
result.push_back(pair<int, int>(buildings[start][1], 0));
return result;
}
int mid = (end + start) / 2;
vector<pair<int, int>> left = divide(start, mid, buildings);
vector<pair<int, int>> right = divide(mid + 1, end, buildings);
vector<pair<int, int>> result = conquer(left, right);
return result;
}
vector<pair<int, int>> conquer(vector<pair<int, int>>& left, vector<pair<int, int>>& right) {
vector<pair<int, int>> result;
int i = 0, j = 0, h1 = 0, h2 = 0;
int maxH = max(h1, h2);
while (i != left.size() && j != right.size()) {
if (left[i].first < right[j].first) {
h1 = left[i].second;
if (maxH != max(h1, h2))
result.push_back(pair<int, int>(left[i].first, max(h1, h2)));
maxH = max(h1, h2);
i++;
}
else if (left[i].first > right[j].first) {
h2 = right[j].second;
if (maxH != max(h1, h2))
result.push_back(pair<int, int>(right[j].first, max(h1, h2)));
maxH = max(h1, h2);
j++;
} else {
if(left[i].second >= right[j].second) {
h1 = left[i].second;
h2 = right[j].second;
if(maxH != max(h1, h2))
result.push_back(pair<int, int>(left[i].first, left[i].second));
maxH = max(h1, h2);
i++;
j++;
} else {
h1 = left[i].second;
h2 = right[j].second;
if(maxH != max(h1, h2))
result.push_back(pair<int, int>(right[j].first, right[j].second));
maxH = max(h1, h2);
i++;
j++;
}
}
}
while (j < right.size()) {
result.push_back(right[j]);
j++;
}
while (i != left.size()) {
result.push_back(left[i]);
i++;
}
return result;
}
};注意当
left[i].first == right[j].first时,需要同时更新h1, h2, 并计算maxH,同时i,j都进一位。
解法二:
使用multiset,可以保存有序的重复值。
class Solution {
public:
vector<pair<int, int>> getSkyline(vector<vector<int>>& buildings) {
vector<pair<int, int>> results;
if (buildings.size() == 0)
return results;
vector<pair<int, int>> corners;
for (auto i : buildings) {
corners.push_back(pair<int, int>(i[0], -i[2]));
corners.push_back(pair<int, int>(i[1], i[2]));
}
sort(corners.begin(), corners.end());
multiset<int> height;
int lastHeight = 0;
height.insert(0);
for (int i = 0; i < corners.size(); i++) {
int h = corners[i].second;
if (h < 0) {
height.insert(-h);
}
else {
height.erase(height.find(h));
}
int curHeight = *height.rbegin();
if (curHeight != lastHeight)
results.push_back(pair<int, int>(corners[i].first, curHeight));
lastHeight = curHeight;
}
return results;
}
};
Java版:
解法一:
public class Solution {
public List<int[]> getSkyline(int[][] buildings) {
List<int[]> results = new ArrayList<>();
if(buildings.length == 0)
return results;
if(buildings.length == 1) {
results.add(new int[]{buildings[0][0], buildings[0][2]});
results.add(new int[]{buildings[0][1], 0});
return results;
}
int mid = (buildings.length - 1) / 2;
List<int[]> left = divide(0, mid, buildings);
List<int[]> right = divide(mid + 1, buildings.length - 1, buildings);
results = conquer(left, right);
return results;
}
List<int[]> divide(int start, int end, int[][] buildings) {
List<int[]> result = new ArrayList<>();
if(start == end) {
result.add(new int[]{buildings[start][0], buildings[start][2]});
result.add(new int[]{buildings[start][1], 0});
return result;
}
int mid = (start + end) / 2;
List<int[]> left = divide(start, mid, buildings);
List<int[]> right = divide(mid + 1, end, buildings);
result = conquer(left, right);
return result;
}
List<int[]> conquer(List<int[]> left, List<int[]> right) {
List<int[]> result = new ArrayList<>();
int i = 0, j = 0;
int h1 = 0, h2 = 0;
int maxH = 0;
while(i < left.size() && j < right.size()) {
if(left.get(i)[0] < right.get(j)[0]) {
h1 = left.get(i)[1];
if(maxH != Math.max(h1, h2)) {
result.add(new int[]{left.get(i)[0], Math.max(h1, h2)});
}
maxH = Math.max(h1, h2);
i++;
} else if(left.get(i)[0] > right.get(j)[0]) {
h2 = right.get(j)[1];
if(maxH != Math.max(h1, h2)) {
result.add(new int[]{right.get(j)[0], Math.max(h1, h2)});
}
maxH = Math.max(h1, h2);
j++;
} else {
h1 = left.get(i)[1];
h2 = right.get(j)[1];
if(maxH != Math.max(h1, h2))
result.add(new int[]{left.get(i)[0], Math.max(h1, h2)});
maxH = Math.max(h1, h2);
i++;
j++;
}
}
while(i < left.size()) {
result.add(new int[]{left.get(i)[0], left.get(i)[1]});
i++;
}
while(j < right.size()) {
result.add(new int[]{right.get(j)[0], right.get(j)[1]});
j++;
}
return result;
}
}
解法二:
public class Solution {
public List<int[]> getSkyline(int[][] buildings) {
List<int[]> results = new ArrayList<>();
if(buildings.length == 0)
return results;
PriorityQueue<Integer> height = new PriorityQueue<>(1, new Comparator<Integer>(){
public int compare(Integer a, Integer b) {
return b - a;
}
});
height.add(0);
List<int[]> corners = new ArrayList<>();
for(int[] a: buildings) {
corners.add(new int[]{a[0], -a[2]});
corners.add(new int[]{a[1], a[2]});
}
int lastHeight = 0;
Collections.sort(corners, new Comparator<int[]>(){
public int compare(int[] a, int[] b) {
if(a[0] != b [0]) {
return a[0] - b[0];
} else {
return a[1] - b[1];
}
}
});
for(int i = 0; i < corners.size(); i++) {
int h = corners.get(i)[1];
if(h < 0) {
height.add(-h);
} else {
height.remove(h);
}
if(height.peek() != lastHeight) {
results.add(new int[]{corners.get(i)[0], height.peek()});
}
lastHeight = height.peek();
}
return results;
}
}
Python版:
解法一:
class Solution:
# @param {integer[][]} buildings
# @return {integer[][]}
def getSkyline(self, buildings):
result = []
if len(buildings) == 0:
return result
if len(buildings) == 1:
result.append([buildings[0][0], buildings[0][2]])
result.append([buildings[0][1], 0])
return result
mid = (len(buildings) - 1) / 2
left = self.divide(0, mid, buildings)
right = self.divide(mid + 1, len(buildings)-1, buildings)
result = self.conquer(left, right)
return result
def divide(self, start, end, buildings):
result = []
if start == end:
result.append([buildings[start][0], buildings[start][2]])
result.append([buildings[start][1], 0])
return result
mid = (start + end) / 2
left = self.divide(start, mid, buildings)
right = self.divide(mid+1, end, buildings)
result = self.conquer(left, right)
return result
def conquer(self, left, right):
result = []
i, j, h1, h2, maxH = 0, 0, 0, 0, 0
while i < len(left) and j < len(right):
if left[i][0] < right[j][0]:
h1 = left[i][1]
if maxH != max(h1, h2):
result.append([left[i][0], max(h1, h2)])
maxH = max(h1, h2)
i += 1
elif left[i][0] > right[j][0]:
h2 = right[j][1]
if maxH != max(h1, h2):
result.append([right[j][0], max(h1, h2)])
maxH = max(h1, h2)
j += 1
else:
h1 = left[i][1]
h2 = right[j][1]
if maxH != max(h1, h2):
result.append([right[j][0], max(h1, h2)])
maxH = max(h1, h2)
i += 1
j += 1
while i < len(left):
result.append(left[i])
i += 1
while j < len(right):
result.append(right[j])
j += 1
return result
解法二:
python没有max-heap的实现,这里就不用此方法做了。