利用Python写的展示汉诺塔(hanoi)解法的小程序_Prj003
一、基本思路
解决汉诺塔问题的最核心思路是降维攻击,噢,不对,是递归法。
把5层汉诺塔降维成4层,4层降成3层...到1层时,直接把盘子移动到目标杆即可。
我们汉诺塔的三个杆子分别命名为源杆,缓冲杆,目标杆。在降维的过程中三种类型的杆会相互转变,即源杆变成目标杆或缓冲杆,要特别注意这种变化。
递归法可以很好的解决需要降维解决的问题。(具体过程直接在下述程序中给与解释)
二、程序实现
#-*- coding=utf-8 -*- # 20150903 by PosPro # http://blog.csdn.net/pospro def moveTower(height, fromPole, bufferPole, targetPole): if height>=1: #一直执行,直到没有盘子了 moveTower(height-1, fromPole, targetPole, bufferPole) #降低一维,将除底层外的所有盘子移到缓冲杆(而不是目标杆) moveSingleDisk(fromPole, targetPole) #由于上面的盘子都已经拿走,此步直接将最大盘子移到目标杆 moveTower(height-1, bufferPole, fromPole, targetPole) #把缓冲杆上的所有盘子移到目标杆,这样就完成全部过程了 def moveSingleDisk(fromPole, targetPole): #根据杆的情况,对对应list进行增减操作,以便动态显示汉诺塔的解法过程 if fromPole=='A' and targetPole=='C': C.append(A.pop()) elif fromPole=='A' and targetPole=='B': B.append(A.pop()) elif fromPole=='B' and targetPole=='C': C.append(B.pop()) elif fromPole=='B' and targetPole=='A': A.append(B.pop()) elif fromPole=='C' and targetPole=='A': A.append(C.pop()) elif fromPole=='C' and targetPole=='B': B.append(C.pop()) print "A: ", A print "B: ", B print "C: ", C print "=============\n"
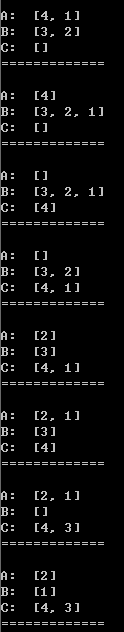
三、输出展示
测试程序如下:
A=[4,3,2,1] #四层汉诺塔示例,也可以自己调整成[7,6,5,4,3,2,1]测试一下七层的解法 B=[] C=[] print "A: ", A print "B: ", B print "C: ", C print "=============\n" moveTower(len(A),"A","B","C")
输出结果如下:(输出过长,没有完全显示,可自行执行程序察看结果)