最好的求平方根的方法(精确度VS速度)
作者:Mahmoud Hesham El-Magdoub
文章来源链接:http://www.codeproject.com/KB/cpp/Sqrt_Prec_VS_Speed.aspx
简介:
我喜欢用DirectX进行游戏编程。我注意到在我的游戏中大多数被调用函数都是在Math.h中的标准sprt方法。所以,我被迫寻找比标准sqrt函数更加快速的函数。经过一段时间的搜索,我发现很多函数都比sqrt函数快的多,但是,这些函数总是在精确度和速度之间取折中的解决方法。 这篇文章的目的是为了帮助程序员选择适合他们程序的最好的求平方根方法。
背景知识:
在这篇文章里,我以标准sqrt函数为参考,将12中不同的求平方根方法和它进行比较。对于每一种方法,我将它的精确度和速度和
sqrt 函数进行比较。
文章不包括:
1、解释每种方法的工作原理
2、计算平方根的新方法。
应用代码:
代码很简单,基本上包括:
1、main.cpp
调用所有的方法,每一个计算出和sqrt函数比较的精确度和速度。
2、SquareRootmethods.h
这个头文件包括函数的实现,和我查找这些方法的参考。
----------------------------------------------------
首先,我计算了作为参考的标准sqrt函数的精确度和速度。
为了计算速度,我记录了调用sqrt函数(M-1)次花费的时间。再将这个值赋值给 RefSpeed 作为我的参考值。
为了计算精确度,我每次调用函数时,把每次的计算结果累加,记录在变量 RefTotalPrecision 中。RefTotalPrecision 变量就是我的参考值。
为了记录函数的运行时持续速度,我应用了CDuration 类(在这个链接里找到的),CDuration 类的对象是 dur 。
for(int j=0;j<AVG;j++) { dur.Start(); for(int i=1;i<M;i++) RefTotalPrecision+=sqrt((float) i); dur.Stop(); Temp+=dur.GetDuration(); } RefTotalPrecision/=AVG; Temp/=AVG; RefSpeed=(float)(Temp)/CLOCKS_PER_SEC;
对于其它算法,我做了相同的计算,但是在最后将它们和sqrt做了比较。
for(int j=0;j<AVG;j++) { dur.Start(); for(int i=1;i<M;i++) TotalPrecision+=sqrt1((float) i); dur.Stop(); Temp+=dur.GetDuration(); } TotalPrecision/=AVG; Temp/=AVG; Speed=(float)(Temp)/CLOCKS_PER_SEC; cout<<"Precision = " <<(double)(1-abs((TotalPrecision-RefTotalPrecision)/(RefTotalPrecision)))*100<<endl;
注意:
1 我认为计算精度时 区分谁大谁小没有意义,因此用abs取其绝对值。
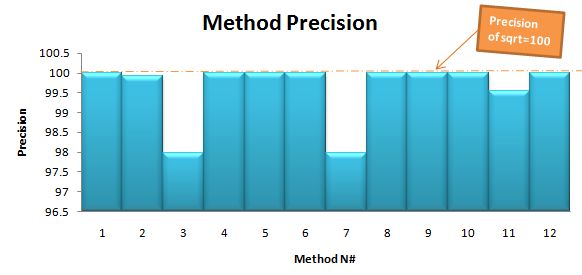
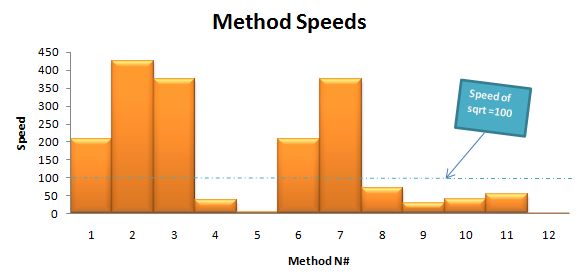
2 (针对下面两个图表)“精度表”中的数字表示计算精度(相对于math.sqrt之精度)下降的百分比,“速度表”中的数值是(相对于math.sqrt之速度)的百分比。
(这段不太理解,一下是原文:
1、I Assume that the error in Precision whether larger or smaller than the reference is equal that's why i use "abs".
2、The Speed is refrenced as the actual percentage, while the Precision is referenced a decrease percentage. )
你可以根据自己的喜欢修改M值,我将M值初始化为10000。
你也可以修改AVG值,这个值越高,精确度就越高。
#define M 10000 #define AVG 10
有趣的要点:
标准sqrt方法的精确度是最好的,但是,其它函数能快5倍以上。我个人会选择方法N#2。因为,它精确度高,速度也快。但是,我还有把选择权教给你吧。
我抽取了5个样本进行平均。下面是输出的结果图:
注意:这些函数的运行很多程度依赖于你计算机的中央处理器,所以,一台计算机的结果和另一台的会有所不同。
方法:
Sqrt1:
参考链接:http://ilab.usc.edu/wiki/index.php/Fast_Square_Root
运算法则:Babylonian Method + 一些 IEEE 32bit浮点数表示的控制 。
float sqrt1(const float x) { union { int i; float x; } u; u.x = x; u.i = (1<<29) + (u.i >> 1) - (1<<22); // Two Babylonian Steps (simplified from:) // u.x = 0.5f * (u.x + x/u.x); // u.x = 0.5f * (u.x + x/u.x); u.x = u.x + x/u.x; u.x = 0.25f*u.x + x/u.x; return u.x; } Sqrt2
Sqrt2:
参考链接:http://ilab.usc.edu/wiki/index.php/Fast_Square_Root
运算法则:The Magic Number (Quake 3)
#define SQRT_MAGIC_F 0x5f3759df float sqrt2(const float x) { const float xhalf = 0.5f*x; union // get bits for floating value { float x; int i; } u; u.x = x; u.i = SQRT_MAGIC_F - (u.i >> 1); // gives initial guess y0 return x*u.x*(1.5f - xhalf*u.x*u.x);// Newton step, repeating increases accuracy }
Sqrt3:
参考链接:http://www.dreamincode.net/code/snippet244.htm
运算法则:Log base 2 approximation and Newton's Method
float sqrt3(const float x) { union { int i; float x; } u; u.x = x; u.i = (1<<29) + (u.i >> 1) - (1<<22); return u.x; }
Sqrt4:
参考链接:很久以前在论坛上看到的,现在忘记了,如果你有参考链接请联系我。
运算法则:Bakhsali Approximation
float sqrt4(const float m) { int i=0; while( (i*i) <= m ) i++; i--; float d = m - i*i; float p=d/(2*i); float a=i+p; return a-(p*p)/(2*a); }
Sqrt5:
参考链接:http://www.dreamincode.net/code/snippet244.htm
运算法则:Babylonian Method
float sqrt5(const float m) { float i=0; float x1,x2; while( (i*i) <= m ) i+=0.1f; x1=i; for(int j=0;j<10;j++) { x2=m; x2/=x1; x2+=x1; x2/=2; x1=x2; } return x2; }
Sqrt6:
参考链接:http://www.azillionmonkeys.com/qed/sqroot.html#calcmeth
运算法则:依赖IEEE,只在32bit上工作。
(原文如下:Dependant on IEEE representation and only works for 32 bits )
double sqrt6 (double y) { double x, z, tempf; unsigned long *tfptr = ((unsigned long *)&tempf) + 1; tempf = y; *tfptr = (0xbfcdd90a - *tfptr)>>1; x = tempf; z = y*0.5; x = (1.5*x) - (x*x)*(x*z); //The more you make replicates of this statment the higher the //accuracy, here only 2 replicates are used x = (1.5*x) - (x*x)*(x*z); return x*y; }
Sqrt7:
参考链接: http://bits.stephan-brumme.com/squareRoot.html
运算法则:依赖IEEE,只在32bit上工作。
float sqrt7(float x) { unsigned int i = *(unsigned int*) &x; // adjust bias i += 127 << 23; // approximation of square root i >>= 1; return *(float*) &i; }
Sqrt8:
参考链接: http://forums.techarena.in/software-development/1290144.htm
运算法则: Babylonian Method
double sqrt9( const double fg) { double n = fg / 2.0; double lstX = 0.0; while(n != lstX) { lstX = n; n = (n + fg/n) / 2.0; } return n; }
Sqrt9:
参考链接: http://www.functionx.com/cpp/examples/squareroot.htm
运算法则: Babylonian Method
double Abs(double Nbr) { if( Nbr >= 0 ) return Nbr; else return -Nbr; } double sqrt10(double Nbr) { double Number = Nbr / 2; const double Tolerance = 1.0e-7; do { Number = (Number + Nbr / Number) / 2; }while( Abs(Number * Number - Nbr) > Tolerance); return Number; }
Sqrt10:
参考链接: http://www.cs.uni.edu/~jacobson/C++/newton.html
运算法则: Newton's Approximation Method
double sqrt11(const double number)e { const double ACCURACY=0.001; double lower, upper, guess; if (number < 1) { lower = number; upper = 1; } else { lower = 1; upper = number; } while ((upper-lower) > ACCURACY) { guess = (lower + upper)/2; if(guess*guess > number) upper =guess; else lower = guess; } return (lower + upper)/2; }
Sqrt11:
参考链接: http://www.drdobbs.com/184409869;jsessionid=AIDFL0EBECDYLQE1GHOSKH4ATMY32JVN
运算法则: Newton's Approximation Method
double sqrt12( unsigned long N ) { double n, p, low, high; if( 2 > N ) return( N ); low = 0; high = N; while( high > low + 1 ) { n = (high + low) / 2; p = n * n; if( N < p ) high = n; else if( N > p ) low = n; else break; } return( N == p ? n : low ); }
Sqrt12:
参考链接:http://cjjscript.q8ieng.com/?p=32
运算法则: Babylonian Method
double sqrt13( int n ) { // double a = (eventually the main method will plug values into a) double a = (double) n; double x = 1; // For loop to get the square root value of the entered number. for( int i = 0; i < n; i++) { x = 0.5 * ( x+a / x ); } return x; }
最后,我希望这篇贫乏的文章可以对感兴趣的人有一点帮助。
ping:为了促进自己学习翻译一些东西,水平有限,欢迎指出错误。