matlab 解析 mnist 数据集
mnist database(手写字符识别) 的数据集下载地:http://yann.lecun.com/exdb/mnist/。
共有四个文件需要下载:
- train-images-idx3-ubyte.gz,训练集,共 60,000 幅(28*28)的图像数据;
- train-labels-idx1-ubyte.gz,训练集的标签信息(取值为 0-9),60,000*1
- t10k-images-idx3-ubyte.gz,测试集(t: test, 10k: 10,000),共 10,000 副(28*28)的图像数据
- t10k-labels-idx1-ubyte.gz,测试集的标签呢信息(取值为 0-9),10,000*1
文件名中的 ubyte 表示数据类型,无符号的单字节类型,对应于 matlab 中的 uchar 数据类型。
注:在 Windows 平台下解压这些文件时,操作系统会自动修改这些文件的文件名,比如会将倒数第二个短线-修改为.,也即 train-images-idx3-ubyte.gz 解压为train-images.idx3-ubyte(文件类型就自作主张地变成了idx3-ubyte),注意文件的对应。
f = fopen('./dataset/t10k-images-idx3-ubyte', 'r')
assert(f >= 3, '文件打开失败'); % 一般文件的文件标识符必须大于等于3
g = fopen('./dataset/t10k-labels-idx1-ubyte', 'r');
assert(g >= 3, '文件打开失败');我们再来看 mnist 数据集官网给出的关于这四个文件格式的说明:
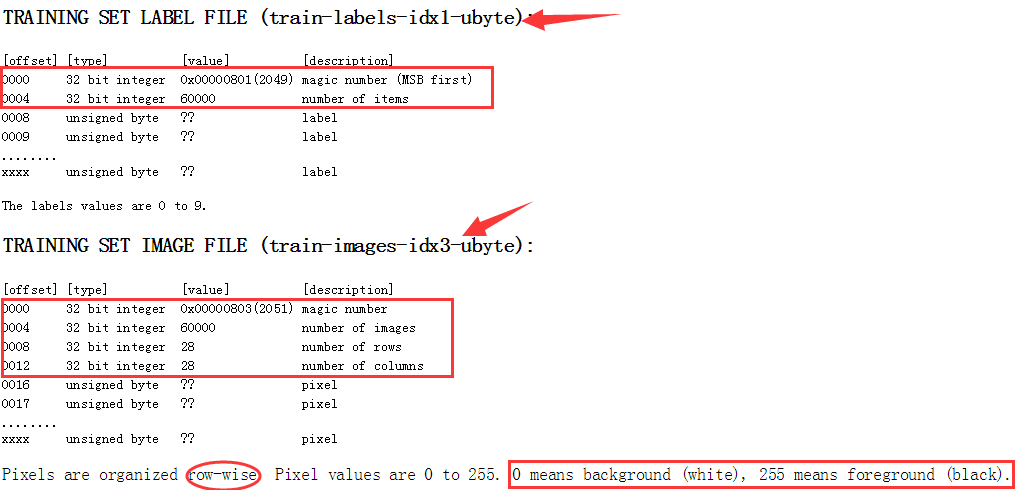
也即在真正的 label 数据或图像像素信息开始之前会有一些表头信息,对于 label 文件是 2 个 32位整型,对于 image 文件是 4 个 32位整型,所以我们需要对这两个文件分别移动文件指针,以指向正确的位置。
fread(f, 4, 'int32');
fread(g, 2, 'int32');按 label 分不同的文件,就原始数据组织成 .ascii 文件
% 首先创建这些 .ascii 文件
fids = zeros(1, 10);
for i = 0:9,
fids(i+1) = fopen(['test' num2str(i) '.ascii'], 'w');
end因为文件内容比较大,出于内存的考虑,最好不要一次全部读入内存,而是逐块逐块地读取,比如一次读 1000 个图像信息,
n = 1000;
times = 60; % 60*1000 = 60,000
for i = 1:times,
rawimages = fread(f, [28*28, n], 'uchar');
rawlabels = fread(g, n, 'uchar');
for j = 1:n,
fprintf(fids(rawlabels(j)+1), '%3d ', rawimages(:, j));
fprintf(fids(rawlabels(j)+1), '\n');
end
end最后再将 .ascii 格式文件保存为 .mat 文件,
for c = 0:9,
D = load(['test' num2str(c) '.ascii'], '-ascii');
fprintf('%5d digits of class %1d', size(D, 1), c);
save(['train' num2str(c) '.mat'], 'D', '-mat');
fclose(fids(c+1));
end别忘了删除无用的 .ascii 格式文件:
dos('del *.ascii'); % Windows 平台下dos 命令
% Linux 平台下:dos('rm *.ascii');