复杂链表的复制
原题来自书籍《剑指offer》,这是作者的该题的博客地址。
关于该题的题意就不再敖述,其大意有点类似C++中的深复制,需要另外的空间来保存复制的内容,而不是简单的将指针指向同一份内容。题目的分析在原博客中已有,尤其是作者推荐的第三种解法,很巧妙。不过最后生成的新链表其实是在原链表上断开并重新连接的,然后抓住新链表的头指针返回,因此在脑海里可以想象,其实“新链表”不是很干净的,因为还有一些原来的节点附在新链表节点上,只不过这些指针我们找不大访问不到了。
这里主要实现一下作者提到的第二种解法和第三种解法,在测试代码中生成十个节点的链表,为了便于测试,节点的sibing指针指向相隔一个节点的节点,即next的next。另外,为了区分复制出来的内容,我将复制的节点的val值都加上了10,便于区分。
节点node的结构如下:
struct node{
int val;
node* next;
node* sibling;
};
测试代码如下,其中包括链表的初始化,复制,打印的工作
int main()
{
// initial a linked list
node* head = new node();
head->val = 1;
head->next = NULL;
head->sibling = NULL;
node* lists = head;
for (int i = 2; i <= NUM; ++i) {
node* n = new node();
n->val = i;
n->next = NULL;
n->sibling = NULL;
lists->next = n;
lists = lists->next;
}
lists = head;
while (lists->next) {
lists->sibling = lists->next->next;
lists = lists->next;
}// end initial
// print the orignal linked list
lists = head;
while (lists) {
cout << lists->val << "->sibling = ";
if (lists->sibling)
cout << lists->sibling->val << endl;
else cout << "NULL" << endl;
lists = lists->next;
}
cout << endl; // end print
// clone the list
//node* newHead = clone1(head);
node* newHead = clone2(head);
// print the cloned linked list
while (newHead) {
cout << newHead->val << "->sibling = ";
if (newHead->sibling)
cout << newHead->sibling->val << endl;
else cout << "NULL" << endl;
newHead = newHead->next;
}// end print
} 第二种解法采用哈希表的方式,clone1代码如下:
node* clone1(node* head) {
if (!head)
return NULL;
unordered_map<node*, node*> container;
node* newHead = NULL;
node* lists = NULL;
node* iter = head;
while (iter) {
node* tmp = new node();
tmp->val = iter->val + 10;
tmp->next = NULL;
tmp->sibling = NULL;
if (!newHead) {
newHead = tmp;
lists = tmp;
}
else {
lists->next = tmp;
lists = lists->next;
}
container[iter] = lists;
iter = iter->next;
}
iter = head;
while (iter) {
container[iter]->sibling = container[iter->sibling];
iter = iter->next;
}
return newHead;
} 第三种解法,原作者的思路,自己理解之后码一遍:
void buildNextPtr(node* head) {
node* lists = head;
while (lists) {
node* tmp = new node();
tmp->val = lists->val + 10;
tmp->next = lists->next;
tmp->sibling = NULL;
lists->next = tmp;
lists = lists->next->next;
}
}
void buildSiblingPtr(node* head) {
node* lists = head;
while (lists) {
if (lists->sibling)
lists->next->sibling = lists->sibling->next;
lists = lists->next->next;
}
}
node* splitLinkedList(node* head) {
if (!head)
return NULL;
node* newHead = head->next;
node* lists = newHead;
while (lists && lists->next) {
lists->next = lists->next->next;
lists = lists->next;
}
return newHead;
}
node* clone2(node* head) {
buildNextPtr(head);
buildSiblingPtr(head);
return splitLinkedList(head);
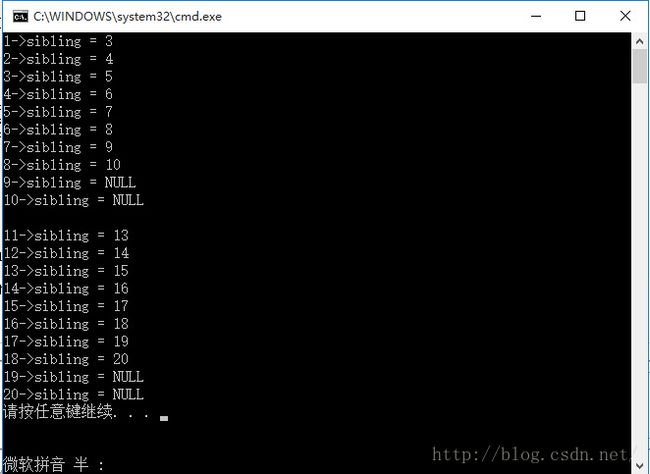
} 完整代码在最后,以下是测试运行的结果:
完整代码:
#include <iostream>
#include <unordered_map>
using namespace std;
#define NUM 10
struct node{
int val;
node* next;
node* sibling;
};
node* clone1(node*);
node* clone2(node*);
int main()
{
// initial a linked list
node* head = new node();
head->val = 1;
head->next = NULL;
head->sibling = NULL;
node* lists = head;
for (int i = 2; i <= NUM; ++i) {
node* n = new node();
n->val = i;
n->next = NULL;
n->sibling = NULL;
lists->next = n;
lists = lists->next;
}
lists = head;
while (lists->next) {
lists->sibling = lists->next->next;
lists = lists->next;
}// end initial
// print the orignal linked list
lists = head;
while (lists) {
cout << lists->val << "->sibling = ";
if (lists->sibling)
cout << lists->sibling->val << endl;
else cout << "NULL" << endl;
lists = lists->next;
}
cout << endl; // end print
// clone the list
//node* newHead = clone1(head);
node* newHead = clone2(head);
// print the cloned linked list
while (newHead) {
cout << newHead->val << "->sibling = ";
if (newHead->sibling)
cout << newHead->sibling->val << endl;
else cout << "NULL" << endl;
newHead = newHead->next;
}// end print
}
node* clone1(node* head) {
if (!head)
return NULL;
unordered_map<node*, node*> container;
node* newHead = NULL;
node* lists = NULL;
node* iter = head;
while (iter) {
node* tmp = new node();
tmp->val = iter->val + 10;
tmp->next = NULL;
tmp->sibling = NULL;
if (!newHead) {
newHead = tmp;
lists = tmp;
}
else {
lists->next = tmp;
lists = lists->next;
}
container[iter] = lists;
iter = iter->next;
}
iter = head;
while (iter) {
container[iter]->sibling = container[iter->sibling];
iter = iter->next;
}
return newHead;
}
void buildNextPtr(node* head) {
node* lists = head;
while (lists) {
node* tmp = new node();
tmp->val = lists->val + 10;
tmp->next = lists->next;
tmp->sibling = NULL;
lists->next = tmp;
lists = lists->next->next;
}
}
void buildSiblingPtr(node* head) {
node* lists = head;
while (lists) {
if (lists->sibling)
lists->next->sibling = lists->sibling->next;
lists = lists->next->next;
}
}
node* splitLinkedList(node* head) {
if (!head)
return NULL;
node* newHead = head->next;
node* lists = newHead;
while (lists && lists->next) {
lists->next = lists->next->next;
lists = lists->next;
}
return newHead;
}
node* clone2(node* head) {
buildNextPtr(head);
buildSiblingPtr(head);
return splitLinkedList(head);
}