Hibernate继承映射
1.每棵类继承树一张表
因为类继承肯定是对应多个类,要把多个类的信息存放在一张表中,必须有某种机制来区分哪些记录是属于哪个类的。因此在表中添加一个字段,用这个字段的值来进行区分。父类用普通的<class>标签定义
在父类中定义一个discriminator,即指定这个区分的字段的名称和类型如:<discriminator column=”XXX” type=”string”/>
子类使用<subclass>标签定义,Subclass标签的name属性是子类的全路径名,在Subclass标签中,用discriminator-value属性来标明本子类的discriminator字段(用来区分不同类的字段)的值Subclass标签。
Subclass标签既可以被class标签所包含(这种包含关系正是表明了类之间的继承关系),也可以与class标签平行。 当subclass标签的定义与class标签平行的时候,需要在subclass标签中,添加extends属性,里面的值是父类的全路径名称。
子类的其它属性,像普通类一样,定义在subclass标签的内部。
get和hql支持多态查询,即hibernate在加载数据的时候,能够采用instancof鉴别出其真正的类型。但是load默认支持lazy,即<class>标签中lazy=“true”不能多态查询。
如Animal a = (Animal)session.load(Animal.class, 1);得的是Animal的代理,采用instanceof无法鉴别出真正的类型。
而load在lazy设置为false的情况下支持多态查询,此时load得的不是代理。
示例:
Animal父类:
public class Animal {
private int id;
private String name;
public int getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(int id) {
this.id = id;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
} Bird子类:
public class Bird extends Animal {
private int height;
public int getHeight() {
return height;
}
public void setHeight(int height) {
this.height = height;
}
} Pig子类:
public class Pig extends Animal {
private int weight;
public int getWeight() {
return weight;
}
public void setWeight(int weight) {
this.weight = weight;
}
} Extends.hbm.xml
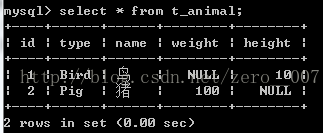
<?xml version="1.0"?> <!DOCTYPE hibernate-mapping PUBLIC "-//Hibernate/Hibernate Mapping DTD 3.0//EN" "http://hibernate.sourceforge.net/hibernate-mapping-3.0.dtd"> <hibernate-mapping package="com.zero.hibernate.vo"> <class name="Animal" table="t_animal" lazy="false"> <id name="id"> <generator class="native" /> </id> <discriminator column="type" type="string" /> <!-- 鉴别标签,会在 t_animal表加type字段 --> <property name="name" /> <property name="sex" /> <subclass name="Pig" discriminator-value="Pig"> <!-- discriminator-value 鉴别值 --> <property name="weight" /> </subclass> <subclass name="Bird" discriminator-value="Bird"> <!-- discriminator-value 鉴别值 --> <property name="height" /> </subclass> </class> </hibernate-mapping>生成的建表语句:
drop table if exists t_animal
create table t_animal (
id integer not null auto_increment,
type varchar(255) not null,
name varchar(255),
weight integer,
height integer,
primary key (id)
) 测试:
Bird bird = new Bird();
bird.setName("鸟");
bird.setHeight(10);
session.save(bird);
Pig pig = new Pig();
pig.setName("猪");
pig.setWeight(100);
session.save(pig);
Animal animal = (Animal)session.load(Animal.class, 1);
if (animal instanceof Pig) {
Pig pig = (Pig) animal;
System.out.println(pig.getWeight());
}else {
Bird bird = (Bird) animal;
System.out.println(bird.getHeight());
}
List animalList = session.createQuery("from Animal").list();
for (Iterator iter=animalList.iterator(); iter.hasNext();) {
Animal animal = (Animal)iter.next();
//采用hql查询返回的是真正的类型,所以hql支持多态查询
if (animal instanceof Pig) {
System.out.println(animal.getName());
}else if (animal instanceof Bird) {
System.out.println(animal.getName());
}
}
2.每个子类一张表
这种策略是使用union-subclass标签来定义子类的。每个子类对应一张表,而且这个表的信息是完备的。此时父类的class标签中abstract设置为true。但是,在保存对象的时候id不能重复(不能使用数据库的自增方式生成主键)。
示例:
Extends.hbm.xml
<?xml version="1.0"?> <!DOCTYPE hibernate-mapping PUBLIC "-//Hibernate/Hibernate Mapping DTD 3.0//EN" "http://hibernate.sourceforge.net/hibernate-mapping-3.0.dtd"> <hibernate-mapping package="com.zero.hibernate.vo"> <class name="Animal" table="t_animal" abstract="true"><!-- abstract="true"将不会生成表 --> <id name="id"> <generator class="assigned" /><!-- 手动分配 id --> </id> <property name="name" /> <union-subclass name="Pig" table="t_pig"> <property name="weight" /> </union-subclass> <union-subclass name="Bird" table="t_bird"> <property name="height" /> </union-subclass> </class> </hibernate-mapping>生成的建表语句:
drop table if exists t_bird
drop table if exists t_pig
create table t_bird (
id integer not null,
name varchar(255),
height integer,
primary key (id)
)
create table t_pig (
id integer not null,
name varchar(255),
weight integer,
primary key (id)
) 测试:
Pig pig = new Pig();
pig.setId(1);
pig.setName("猪");
pig.setWeight(100);
session.save(pig);
Bird bird = new Bird();
bird.setId(2);
bird.setName("鸟");
bird.setHeight(10);
session.save(bird);
//Hibernate: insert into t_pig (name, weight, id) values (?, ?, ?)
//Hibernate: insert into t_bird (name, height, id) values (?, ?, ?)
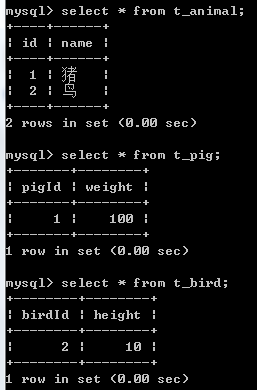
3.每个类一张表
这种策略是使用joined-subclass标签来定义子类的。父类、子类,每个类都对应一张数据库表。在父类对应的数据库表中,实际上会存储所有的记录,包括父类和子类的记录;在子类对应的数据库表中,这个表只定义了子类中所特有的属性映射的字段。子类与父类,通过相同的主键值来关联。父类用普通的<class>标签,不再需要定义discriminator字段
子类用<joined-subclass>标签定义,在定义joined-subclass的时候,Joined-subclass标签的name属性是子类的全路径名,Joined-subclass标签需要包含一个key标签,这个标签指定了子类和父类之间是通过哪个字段来关联的。
示例:
Extends.hbm.xml
<?xml version="1.0"?> <!DOCTYPE hibernate-mapping PUBLIC "-//Hibernate/Hibernate Mapping DTD 3.0//EN" "http://hibernate.sourceforge.net/hibernate-mapping-3.0.dtd"> <hibernate-mapping package="com.zero.hibernate.vo"> <class name="Animal" table="t_animal"> <id name="id"> <generator class="native" /> </id> <property name="name" /> <joined-subclass name="Pig" table="t_pig"> <key column="pigId" /> <property name="weight" /> </joined-subclass> <joined-subclass name="Bird" table="t_bird"> <key column="birdId" /> <property name="height" /> </joined-subclass> </class> </hibernate-mapping>生成的建表语句:
alter table t_bird
drop
foreign key FK_ihcyneoc7iub1oyax1p781ly1
alter table t_pig
drop
foreign key FK_2cjrm0mijyj0mul5hqeck0v36
drop table if exists t_animal
drop table if exists t_bird
drop table if exists t_pig
create table t_animal (
id integer not null auto_increment,
name varchar(255),
primary key (id)
)
create table t_bird (
birdId integer not null,
height integer,
primary key (birdId)
)
create table t_pig (
pigId integer not null,
weight integer,
primary key (pigId)
)
alter table t_bird
add constraint FK_ihcyneoc7iub1oyax1p781ly1
foreign key (birdId)
references t_animal (id)
alter table t_pig
add constraint FK_2cjrm0mijyj0mul5hqeck0v36
foreign key (pigId)
references t_animal (id) 测试:
Pig pig = new Pig();
pig.setName("猪");
pig.setWeight(100);
session.save(pig);
Bird bird = new Bird();
bird.setName("鸟");
bird.setHeight(10);
session.save(bird);
//Hibernate: insert into t_animal (name) values (?)
//Hibernate: insert into t_pig (weight, pigId) values (?, ?)
//Hibernate: insert into t_animal (name) values (?)
//Hibernate: insert into t_bird (height, birdId) values (?, ?)