【2013.1.29】擎天柱:我们要拯救人类——Composite(使用Vector)
// // // // // // // // //
///2013.1.29
// // // // // // // // //
Composite模式也称为树模式。
这个比喻是非常贴切的。
因为Composite模式的结构就是一个树状结构。
组成此模式的物体既是对象又是容器,
通过将复杂的对象依次分解为多个相似的小对象,
从而使用简单的接口来操作复杂的对象。
【核心】对象组成容器,容器装载对象。
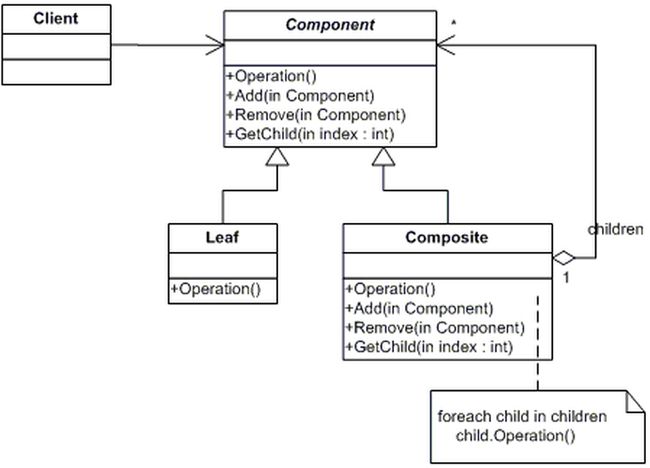
UML:
代码实例:
【大致思路】
Component作为共有的基类,被Composite与Leaf所继承。Composite本身具有与Component相同的方法(Add,Remove等),可以作为容器来装载Leaf。
Leaf却只有Operation方法,不能作为容器。
Component.h
#ifndef _COMPONENT_H_
#define _COMPONENT_H_
#include<vector>
class Component
{
public:
Component(){}
~Component(){}
virtual void Add(Component* com) {}
virtual void Remove(Component* com){}
virtual Component* GetChild(int index){return nullptr;}
virtual void Operation() {}
};
class Composite: public Component
{
public:
Composite(){}
~Composite(){}
void Add(Component* com);
void Remove(Component* com);
Component* GetChild(int index);
void Operation();
private:
std::vector<Component*> comList;
};
//Leaf Can't add or remove other component
//because it's the base structure.
class Leaf: public Component
{
public:
Leaf(){}
~Leaf(){}
void Operation();
};
#endif
#include"Component.h"
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
void Composite::Add(Component* com)
{
//Add to the List.
comList.push_back(com);
}
void Composite::Remove(Component* com)
{
//Remove from the List.
vector<Component*>::iterator itr;
for(itr = comList.begin();itr != comList.end();itr++)
{
if(*itr == com)
{
comList.erase(itr);
break;
}
}
}
void Composite::Operation()
{
//Use the vector's iterator.
vector<Component*>::iterator itr;
if(comList.size() != 0)
{
for(itr = comList.begin();itr != comList.end();itr++)
{
//Don't forget the bracket,otherwise it's wrong!!!
(*itr) ->Operation();
}
}
else
cout<<"No elements"<<endl;
}
Component* Composite::GetChild(int index)
{
return comList[index];
}
void Leaf::Operation()
{
cout<<"Leaf's operation"<<endl;
}
main.cpp
#include "Component.h"
int main()
{
Leaf* firstLeaf = new Leaf();
firstLeaf->Operation();
Composite* tree = new Composite();
tree->Add(firstLeaf);
tree->Operation();
tree->Remove(firstLeaf);
//It's forbiddened because there is no more elements in the list.
tree->Operation();
return 0;
}
运行结果:
【注意事项】
Composite与Leaf的主要区别就是在于是否可以作为容器使用。
注意在Composite内部有一个装载Component*类型的vector,
Add与Remove的操作对象就是此vector,
因此要注意在Remove中删除元素要先使用iterator遍历,
寻找相等的元素再进行删除。
因时间匆忙,
没有做一些Bug预防措施,
其实在Remove中应该对是否有元素以及是否包含这一元素进行提前判断,
来防止发生错误内存访问Bug。
希望读者在使用此模式时注意这点(相同的还有GetChild方法)。
P.S.可以参考Composite类中的Operation()。
除此之外,
容器不一定是vector,
推广开来,
链表,哈希表之类的数据结构都可以作为容器。
甚至在元素个数有限的情况下,也可以使用指针数组。
但无论如何,
所选取的数据结构一定要能实现以下四个个基础方法:
Add,Remove,GetChild,Operation.
望诸君切记。