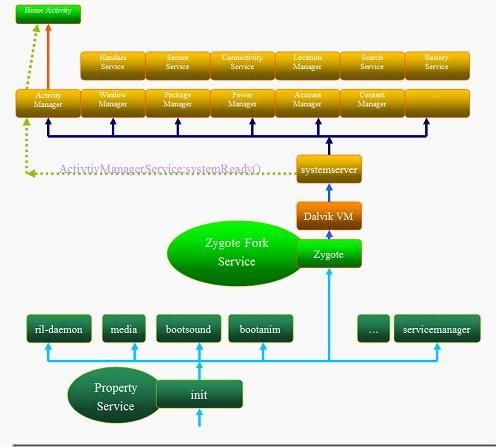
Android4.0 Zygote和启动过程
在Android系统中,所有的应用程序进程以及系统服务进程SystemServer都是由Zygote进程孕育(fork)出来的。Android系统是基于Linux内核的,而在Linux系统中,所有的进程都是init进程的子孙进程,也就是说,所有的进程都是直接或者间接地由init进程fork出来的。Zygote进程也不例外,它是在系统启动的过程,由init进程创建的。在系统启动脚本system/core/rootdir/init.rc文件中。
一、在init.rc脚本文件中:
service zygote /system/bin/app_process -Xzygote /system/bin --zygote --start-system-server
class main
socket zygote stream 666
onrestart write /sys/android_power/request_state wake
onrestart write /sys/power/state on
onrestart restart media
onrestart restart netd
service zygote init进程创建一个名为"zygote"的进程
/system/bin/app_process zygote进程要执行的程序
-Xzygote 传递给VM的选项,-Xzygote 选项用来区分要在虚拟机中运行的类是Zygote,还是在Zygote中运行的其他Android应用程序。
/system/bin 运行目录参数/system/bin 保存到 parentDir 变量中。
--zygote 用来指定加载到虚拟机中类的名称,表示加载com.android.internel.os.ZygoteInit类。
--start-system-server 作为选项传递给生成的类,用于启动运行System server。
socket zygote stream 666 套接字的名称,种类,访问权限
Zygote进程要执行的程序便是system/bin/app_process了,在frameworks/base/cmds/app_process/app_main.cpp文件中,入口函数是main。
int main(int argc, const char* const argv[])
{
// These are global variables in ProcessState.cpp
mArgC = argc;
mArgV = argv;
mArgLen = 0;
for (int i=0; i<argc; i++) {
mArgLen += strlen(argv[i]) + 1;
}
mArgLen--;
AppRuntime runtime;
const char* argv0 = argv[0];
// Process command line arguments
// ignore argv[0]
argc--;
argv++;
// Everything up to '--' or first non '-' arg goes to the vm
int i = runtime.addVmArguments(argc, argv);//
// Parse runtime arguments. Stop at first unrecognized option.
bool zygote = false;
bool startSystemServer = false;
bool application = false;
const char* parentDir = NULL;
const char* niceName = NULL;
const char* className = NULL;
while (i < argc) {
const char* arg = argv[i++];//运行目录参数/system/bin 保存到 parentDir 变量中
if (!parentDir) {
parentDir = arg;
} else if (strcmp(arg, "--zygote") == 0) {
zygote = true;
niceName = "zygote";
} else if (strcmp(arg, "--start-system-server") == 0) {
startSystemServer = true;
} else if (strcmp(arg, "--application") == 0) {
application = true;
} else if (strncmp(arg, "--nice-name=", 12) == 0) {
niceName = arg + 12;
} else {
className = arg;
break;
}
}
if (niceName && *niceName) {
setArgv0(argv0, niceName);
set_process_name(niceName);
}
runtime.mParentDir = parentDir;
if (zygote) {
runtime.start("com.android.internal.os.ZygoteInit",
startSystemServer ? "start-system-server" : "");
//调用AppRuntime的start()成员函数,生成并初始化虚拟机,然后将ZygoteInit()类加载到虚拟机中,执行其中的main()方法。
} else if (className) {
// Remainder of args get passed to startup class main()
runtime.mClassName = className;
runtime.mArgC = argc - i;
runtime.mArgV = argv + i;
runtime.start("com.android.internal.os.RuntimeInit",
application ? "application" : "tool");
} else {
fprintf(stderr, "Error: no class name or --zygote supplied.\n");
app_usage();
LOG_ALWAYS_FATAL("app_process: no class name or --zygote supplied.");
return 10;
}
}
此函数主要工作:分析传递给虚拟机的参数,并保存到AppRuntime类的对象中,然后加载对象,调用对象的main()方法。
二、进入到AndroidRuntime.cpp 中start()函数中
void AndroidRuntime::start(const char* className, const char* options)
{
LOGD("\n>>>>>> AndroidRuntime START %s <<<<<<\n",
className != NULL ? className : "(unknown)");
blockSigpipe();
/*
* 'startSystemServer == true' means runtime is obsolete and not run from
* init.rc anymore, so we print out the boot start event here.
*/
if (strcmp(options, "start-system-server") == 0) {
/* track our progress through the boot sequence */
const int LOG_BOOT_PROGRESS_START = 3000;
LOG_EVENT_LONG(LOG_BOOT_PROGRESS_START,
ns2ms(systemTime(SYSTEM_TIME_MONOTONIC)));
}
const char* rootDir = getenv("ANDROID_ROOT");
if (rootDir == NULL) {
rootDir = "/system";
if (!hasDir("/system")) {
LOG_FATAL("No root directory specified, and /android does not exist.");
return;
}
setenv("ANDROID_ROOT", rootDir, 1);
}
//const char* kernelHack = getenv("LD_ASSUME_KERNEL");
//LOGD("Found LD_ASSUME_KERNEL='%s'\n", kernelHack);
/* start the virtual machine *///创建java虚拟机
JNIEnv* env;
if (startVm(&mJavaVM, &env) != 0) {//mJavaVM 生成的JavaVM类的接口指针,env JNIEnv类的接口指针,方便访问虚拟机
return;
}
onVmCreated(env);
/*
* Register android functions.
*/
if (startReg(env) < 0) {//注册虚拟机要使用的JNI函数,以后运行在虚拟机中的JAVA类就可以调用本地函数。
LOGE("Unable to register all android natives\n");
return;
}
/*
* We want to call main() with a String array with arguments in it.
* At present we have two arguments, the class name and an option string.
* Create an array to hold them.
*/
jclass stringClass;
jobjectArray strArray;
jstring classNameStr;
jstring optionsStr;
stringClass = env->FindClass("java/lang/String");
assert(stringClass != NULL);
strArray = env->NewObjectArray(2, stringClass, NULL);
assert(strArray != NULL);
classNameStr = env->NewStringUTF(className);
assert(classNameStr != NULL);
env->SetObjectArrayElement(strArray, 0, classNameStr);
optionsStr = env->NewStringUTF(options);
env->SetObjectArrayElement(strArray, 1, optionsStr);
/*
* Start VM. This thread becomes the main thread of the VM, and will
* not return until the VM exits.
*/
char* slashClassName = toSlashClassName(className);//将类名称中的 "."替换成"/",
jclass startClass = env->FindClass(slashClassName);//在由类名称解析出来的路径下查找指定的类,若存在,测加载。
if (startClass == NULL) {
LOGE("JavaVM unable to locate class '%s'\n", slashClassName);
/* keep going */
} else {
jmethodID startMeth = env->GetStaticMethodID(startClass, "main",
"([Ljava/lang/String;)V");//在类中查找形式参数为String数组且返回值为void的main()静态方法。
if (startMeth == NULL) {
LOGE("JavaVM unable to find main() in '%s'\n", className);
/* keep going */
} else {
env->CallStaticVoidMethod(startClass, startMeth, strArray);//找到次方法,调用此方法,此时程序的执行转到虚拟机中运行的java应用程序上。
//进入到ZygoteInit.java--ZygoteInit::main()方法中
... ...
}
}
... ...
}
三、进入到ZygoteInit.java--ZygoteInit::main()方法中
public static void main(String argv[]) {
try {
// Start profiling the zygote initialization.
SamplingProfilerIntegration.start();
registerZygoteSocket();//1、绑定套接字, 接受新android应用程序运行请求
EventLog.writeEvent(LOG_BOOT_PROGRESS_PRELOAD_START,
SystemClock.uptimeMillis());
preload();//2、加载 android application framework 使用的类和资源 ,
EventLog.writeEvent(LOG_BOOT_PROGRESS_PRELOAD_END,
SystemClock.uptimeMillis());
// Finish profiling the zygote initialization.
SamplingProfilerIntegration.writeZygoteSnapshot();
// Do an initial gc to clean up after startup
gc();
// If requested, start system server directly from Zygote
if (argv.length != 2) {
throw new RuntimeException(argv[0] + USAGE_STRING);
}
if (argv[1].equals("start-system-server")) {
startSystemServer();//3、运行systemserver
} else if (!argv[1].equals("")) {
throw new RuntimeException(argv[0] + USAGE_STRING);
}
Log.i(TAG, "Accepting command socket connections");
if (ZYGOTE_FORK_MODE) {
runForkMode();
} else {
runSelectLoopMode();//4、处理新android应用程序运行请求
}
closeServerSocket();
} catch (MethodAndArgsCaller caller) {
caller.run();
} catch (RuntimeException ex) {
Log.e(TAG, "Zygote died with exception", ex);
closeServerSocket();
throw ex;
}
}
首先分析第一点:registerZygoteSocket();//1、绑定套接字, 接受新android应用程序运行请求
private static void registerZygoteSocket() {
if (sServerSocket == null) {
int fileDesc;
try {
String env = System.getenv(ANDROID_SOCKET_ENV);//获取套接字的文件描述符。它记录在ANDROID_SOCKET_zygote环境变量中。
fileDesc = Integer.parseInt(env);
} catch (RuntimeException ex) {
throw new RuntimeException(
ANDROID_SOCKET_ENV + " unset or invalid", ex);
}
try {
sServerSocket = new LocalServerSocket(
createFileDescriptor(fileDesc));//使用套接字文件描述符创建LocalServerSocket的实例,将其与/dev/socket/zygote绑定在一起
} catch (IOException ex) {
throw new RuntimeException(
"Error binding to local socket '" + fileDesc + "'", ex);
}
}
}
第二点:加载 android application framework 使用的类和资源
static void preload() {
preloadClasses();
preloadResources();
}
private static void preloadClasses() {
final VMRuntime runtime = VMRuntime.getRuntime();
InputStream is = ZygoteInit.class.getClassLoader().getResourceAsStream(
PRELOADED_CLASSES);//获取一个输入流,以便读取proloaded-classes文件中的类 ,framework/base/preloafed-classes文件。
... ...
try {
BufferedReader br
= new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(is), 256);//创建BufferedReader对象,并读取文件中的内容。
... ...
line = line.trim();//忽略文件中的注释和空行,读取下一行
if (line.startsWith("#") || line.equals("")) {
continue;
}
... ...
Class.forName(line);//将读取到得类动态的加载到内存中
... ...
}
第三点:运行systemserver,在ZygoteInit.java中startSystemServer()方法中
private static boolean startSystemServer()
throws MethodAndArgsCaller, RuntimeException {
/* Hardcoded command line to start the system server */
String args[] = {
"--setuid=1000",
"--setgid=1000",
"--setgroups=1001,1002,1003,1004,1005,1006,1007,1008,1009,1010,1018,3001,3002,3003,3006,3007",
"--capabilities=130104352,130104352",
"--runtime-init",
"--nice-name=system_server",
"com.android.server.SystemServer",//用于指定systemserver类
};
... ...
pid = Zygote.forkSystemServer(
parsedArgs.uid, parsedArgs.gid,
parsedArgs.gids,
parsedArgs.debugFlags,
null,
parsedArgs.permittedCapabilities,
parsedArgs.effectiveCapabilities);//创建新进程,并运行systemserver
... ...
/* For child process */
if (pid == 0) {
handleSystemServerProcess(parsedArgs);//在生成的systemserver进程中运行com.android.server.SystemServer类的main()方法
}
... ...
}
进入handleSystemServerProcess()中
private static void handleSystemServerProcess(
ZygoteConnection.Arguments parsedArgs)
throws ZygoteInit.MethodAndArgsCaller {
... ...
RuntimeInit.zygoteInit(parsedArgs.targetSdkVersion, parsedArgs.remainingArgs);
... ...
}
进入RuntimeInit.java 中zygoteinit方法中
public static final void zygoteInit(int targetSdkVersion, String[] argv)
throws ZygoteInit.MethodAndArgsCaller {
if (DEBUG) Slog.d(TAG, "RuntimeInit: Starting application from zygote");
redirectLogStreams();
commonInit();
zygoteInitNative();//1、native层初始化
applicationInit(targetSdkVersion, argv);
}
在进入applicationInit()中
private static void applicationInit(int targetSdkVersion, String[] argv)
throws ZygoteInit.MethodAndArgsCaller {
... ...
invokeStaticMain(args.startClass, args.startArgs);
//2、调用startclass,也就是com.android.server.SystemServer类的main()函数
}
分析上面两点:
1、native层初始化 zygoteInitNative()
public static final native void zygoteInitNative();他是一个本地函数,经过JNI调用AndroidRuntime.cpp中的
static void com_android_internal_os_RuntimeInit_zygoteInit(JNIEnv* env, jobject clazz)
{
gCurRuntime->onZygoteInit();
}
gCurRuntime是指什么?
gCurRuntime
在app_main.cpp main()函数中
int main(int argc, const char* const argv[])
{
...
AppRuntime runtime;
... ...
}
看其定义
class AppRuntime : public AndroidRuntime
继承AndroidRuntime类
static AndroidRuntime* gCurRuntime = NULL; //为全局变量
AndroidRuntime.cpp中
AndroidRuntime::AndroidRuntime()
{
SkGraphics::Init();
... ...
gCurRuntime = this; // gCurRuntime 被设置为AndroidRuntime对象自己
}
故:此时启动App_main.cpp中onZygoteInit()函数
virtual void onZygoteInit()
{
sp<ProcessState> proc = ProcessState::self();
LOGV("App process: starting thread pool.\n");
proc->startThreadPool();//启动一个线程,用于binder通信
}
2、invokeStaticMain(args.startClass, args.startArgs)
调用startclass,也就是com.android.server.SystemServer类的main()函数
private static void invokeStaticMain(String className, String[] argv)
throws ZygoteInit.MethodAndArgsCaller {
... ...
m = cl.getMethod("main", new Class[] { String[].class });
//找到com.android.server.SystemServer类的main()函数
... ...
throw new ZygoteInit.MethodAndArgsCaller(m, argv);//抛出一个异常
}
将在ZygoteInit的main函数中截获到,
ZygoteInit.java的main()中
public static void main(String argv[]) {
... ...
try {
... ...
if (argv[1].equals("start-system-server")) {
startSystemServer();//运行systemserver 在此中抛出一个异常
} else if (!argv[1].equals("")) {
throw new RuntimeException(argv[0] + USAGE_STRING);
}
} catch (MethodAndArgsCaller caller) {
caller.run();
... ...
}
将进入MethodAndArgsCaller 的run函数
public void run() {
try {
//mMethod为com.android.server.SystemServer的main()函数
mMethod.invoke(null, new Object[] { mArgs });
} catch (IllegalAccessException ex) {
throw new RuntimeException(ex);
} catch (InvocationTargetException ex) {
... ...
}
现在进入到SystemServer.java的main中
public static void main(String[] args) {
... ...
VMRuntime.getRuntime().setTargetHeapUtilization(0.8f);
System.loadLibrary("android_servers");//加载android_servers本地库文件
init1(args);
}
进入init1()为本地方法,将进入
native public static void init1(String[] args);
com_android_server_SystemServer.cpp中的
static void android_server_SystemServer_init1(JNIEnv* env, jobject clazz)
{
system_init();
}
extern "C" int system_init();将调用system_init.cpp中的system_init(0函数
extern "C" status_t system_init(){
... ...
property_get("system_init.startsurfaceflinger", propBuf, "1");
if (strcmp(propBuf, "1") == 0) {
// Start the SurfaceFlinger
SurfaceFlinger::instantiate();//注册本地服务
}
......
jmethodID methodId = env->GetStaticMethodID(clazz, "init2", "()V");//调用init2()方法
... ...
}
init2()方法
public static final void init2() {
Slog.i(TAG, "Entered the Android system server!");
Thread thr = new ServerThread();
thr.setName("android.server.ServerThread");
thr.start();/创建一个线程android.server.ServerThread,并启动它
}
第四点:处理新android应用程序运行请求 runSelectLoopMode()
private static void runSelectLoopMode() throws MethodAndArgsCaller {
... ...
fds.add(sServerSocket.getFileDescriptor());//将套接字的描述符添加到描述符数组中
......
boolean done;
done = peers.get(index).runOnce();//处理新连接的输入输出套接字,并生成新的android应用程序。
... ...
}
进入zygoteconnection.java中的runonce()中
boolean runOnce() throws ZygoteInit.MethodAndArgsCaller {
.... ...
args = readArgumentList();//读取请求信息,请求信息包含创建新进程的参数选项
... ...
parsedArgs = new Arguments(args);//分析请求信息中的字符数组,为运行进程设置好各个选项
... ...
pid = Zygote.forkAndSpecialize(parsedArgs.uid, parsedArgs.gid,
parsedArgs.gids, parsedArgs.debugFlags, rlimits);//创建新进程
if (pid == 0) {
// in child
IoUtils.closeQuietly(serverPipeFd);//
serverPipeFd = null;
handleChildProc(parsedArgs, descriptors, childPipeFd, newStderr);//加载新进程所需的类,并调用类的main()方法。启动新的应用程序。子进程处理
// should never get here, the child is expected to either
// throw ZygoteInit.MethodAndArgsCaller or exec().
return true;
} else {
// in parent...pid of < 0 means failure
IoUtils.closeQuietly(childPipeFd);
childPipeFd = null;
return handleParentProc(pid, descriptors, serverPipeFd, parsedArgs);//zygote进程
}
}
进入到新进程创建的子进程中的处理 handleChildProc()
ZygoteConnection.java
private void handleChildProc(Arguments parsedArgs,
FileDescriptor[] descriptors, FileDescriptor pipeFd, PrintStream newStderr)
throws ZygoteInit.MethodAndArgsCaller {
... ...
RuntimeInit.zygoteInit(parsedArgs.targetSdkVersion,
parsedArgs.remainingArgs);
... ...
}
在进入到RuntimeInit.java中的zygoteinit()方法中最终调用了
invokeStaticMain(args.startClass, args.startArgs);函数,前面已经分析。
android 启动过程
Android从Linux系统启动有4个步骤;
(1) init进程启动
(2) Native服务启动
(3) System Server,Android服务启动
(4) Home启动
SystemServer组件接下来就要通过ActivityManagerService来启动Home应用程序Launcher了,Launcher在启动的时候便会通过PackageManagerServic把系统中已经安装好的应用程序以快捷图标的形式展示在桌面上。
第一步:在上面,讲到了启动systemserver的过程
SystemServer.java的main函数
public static void main(String[] args) {
... ...
System.loadLibrary("android_servers");
init1(args);
}
启动init1()函数,
native public static void init1(String[] args);
Init1()是一个本地函数,将会进入到
static void android_server_SystemServer_init1(JNIEnv* env, jobject clazz)
{
system_init();
}
调用extern "C" int system_init();
会进入到System_init.cpp中的system_init中
extern "C" status_t system_init()
{
... ...
jclass clazz = env->FindClass("com/android/server/SystemServer");
if (clazz == NULL) {
return UNKNOWN_ERROR;
}
jmethodID methodId = env->GetStaticMethodID(clazz, "init2", "()V");
... ...
}
初始化一些服务后,会调用com/android/server/SystemServer类中的init2()方法
Systemserver.java函数init2()
public static final void init2() {
Slog.i(TAG, "Entered the Android system server!");
Thread thr = new ServerThread();//创建了一个ServerThread线程
thr.setName("android.server.ServerThread");
thr.start();
}
许多android framework服务都是在这个线程中注册的,可以查看其run方法。
如:ServiceManager,ActivityManagerService,PackageManagerService等。
第二步:
在run中将启动ActivityManagerService服务,
public void run() {
EventLog.writeEvent(EventLogTags.BOOT_PROGRESS_SYSTEM_RUN,
SystemClock.uptimeMillis());
Looper.prepare();
... ...
Slog.i(TAG, "Activity Manager");
context = ActivityManagerService.main(factoryTest);//1、
... ...
ActivityManagerService.setSystemProcess();//2、
mContentResolver = context.getContentResolver();
... ...
ActivityManagerService.self().systemReady(new Runnable() {//3、
... ...
}
}
在上面的run方法中
1、在main()方法中通过AThread线程对象来内部创建了一个ActivityManagerService实例,最后将其保存到成员变量mSelf 中,然后初始化其它成员变量。
2、
public static void setSystemProcess() {
try {
ActivityManagerService m = mSelf;
//将ActivityManagerService注册到server manager中区,可以通过ServiceManager.getService接口来访问这个全局唯一的ActivityManagerService实例。
ServiceManager.addService("activity", m);
ServiceManager.addService("meminfo", new MemBinder(m));
ServiceManager.addService("gfxinfo", new GraphicsBinder(m));
if (MONITOR_CPU_USAGE) {
ServiceManager.addService("cpuinfo", new CpuBinder(m));
}
ServiceManager.addService("permission", new PermissionController(m));
ApplicationInfo info =
mSelf.mContext.getPackageManager().getApplicationInfo(
"android", STOCK_PM_FLAGS);
mSystemThread.installSystemApplicationInfo(info);
//把在应用程序框架层下面的android包加载进来
... ...
}
3、最后调用systemReady方法
在ActivityManagerServcie.java
public void systemReady(final Runnable goingCallback) {
synchronized(this) {
... ...
mMainStack.resumeTopActivityLocked(null);//启动Home应用程序
... ...
}
}
第三步:
1、将会进入到ActivityStack.java resumeTopActivityLocked()中
final boolean resumeTopActivityLocked(ActivityRecord prev) {
ActivityRecord next = topRunningActivityLocked(null);//返回的是当前系统Activity堆栈最顶端的Activity,此时还没有activity启动,故为null。
... ...
if (next == null) {
// There are no more activities! Let's just start up the
// Launcher...
if (mMainStack) {
return mService.startHomeActivityLocked();
}
}
... ...
}
2、进入到ActivityManagerService.java中的startHomeActivityLocked()
boolean startHomeActivityLocked() {
if (mFactoryTest == SystemServer.FACTORY_TEST_LOW_LEVEL
&& mTopAction == null) {
return false;
}
Intent intent = new Intent(
mTopAction,
mTopData != null ? Uri.parse(mTopData) : null);
intent.setComponent(mTopComponent);
if (mFactoryTest != SystemServer.FACTORY_TEST_LOW_LEVEL) {
intent.addCategory(Intent.CATEGORY_HOME);
}
ActivityInfo aInfo =
intent.resolveActivityInfo(mContext.getPackageManager(),
STOCK_PM_FLAGS);//向PackageManagerService查询Category类型为HOME的Activity。(AndroidManifest.xml中)
if (aInfo != null) {
intent.setComponent(new ComponentName(
aInfo.applicationInfo.packageName, aInfo.name));
// Don't do this if the home app is currently being
// instrumented.
ProcessRecord app = getProcessRecordLocked(aInfo.processName,
aInfo.applicationInfo.uid);//第一次启动这个Activity,故app为null。
if (app == null || app.instrumentationClass == null) {
intent.setFlags(intent.getFlags() | Intent.FLAG_ACTIVITY_NEW_TASK);
mMainStack.startActivityLocked(null, intent, null, null, 0, aInfo,
null, null, 0, 0, 0, false, false, null);//调用此函数启动这个Activity。
}
}
return true;
}
第四步、
调用此startActivityLocked函数后,就会启动com.android.launcher2.Launcher,然后调用它的Oncreate()方法。