Android工具导航栏
今天继续Android学习之旅之导航栏的记录。本文采用了两种方式实现:1.用ActivityGroup和DataGrid相结合实现;2.采用继承FragmentActivity和RadioButton相组合实现;
先定义了一个图片适配器类(也可以直接用SimpleAdapter 类),继承自BaseAdapter:
至此框架完成,其他要注意的细节:这边在选中时添加了个背景图片以便醒目;各个页面的图片显示问题,我这边采用了跟手机一样像素的图片才正好铺满屏幕,开始弄的图片像素太低,就只在屏幕的左上边显示;图标和最好采用无背景的图片(相对背景为白色的,透明更美观);只要涉及到多页面就要记得在AndroidManifest.xml中配置进去;
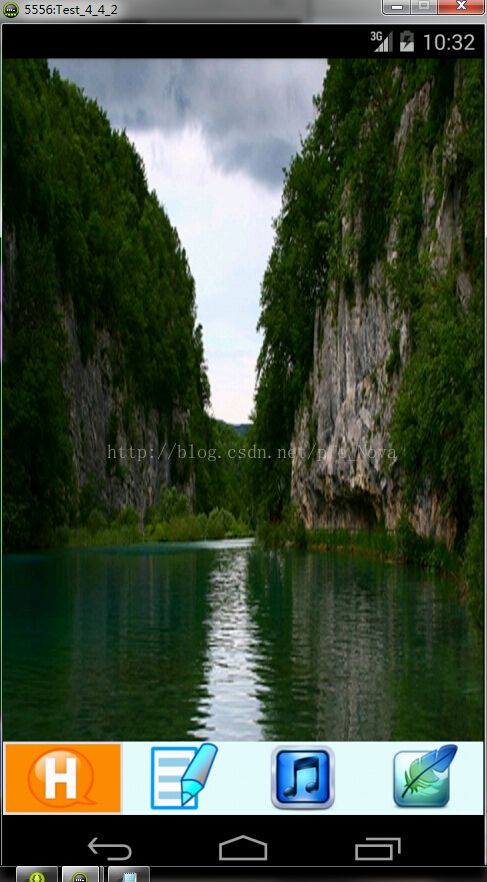
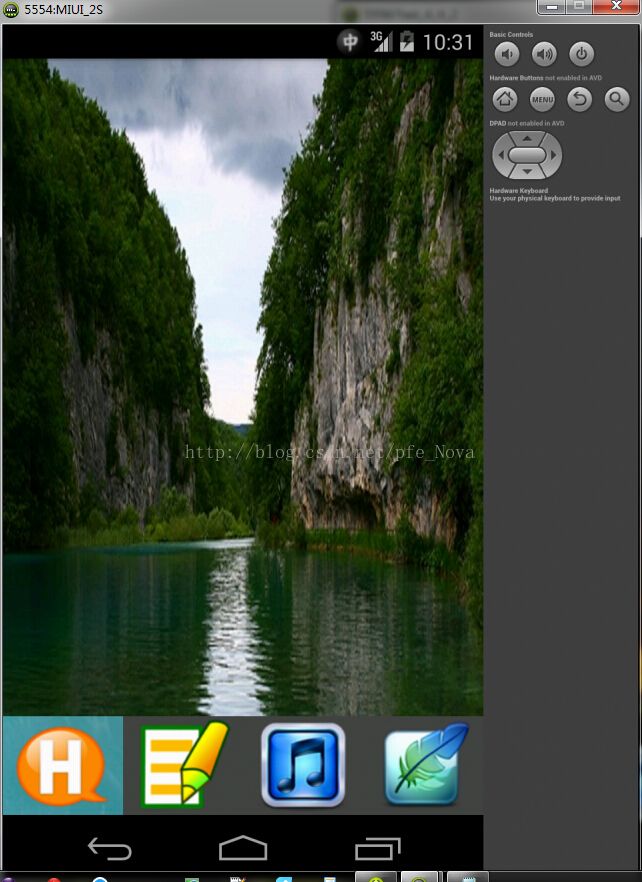
运行截图如下:
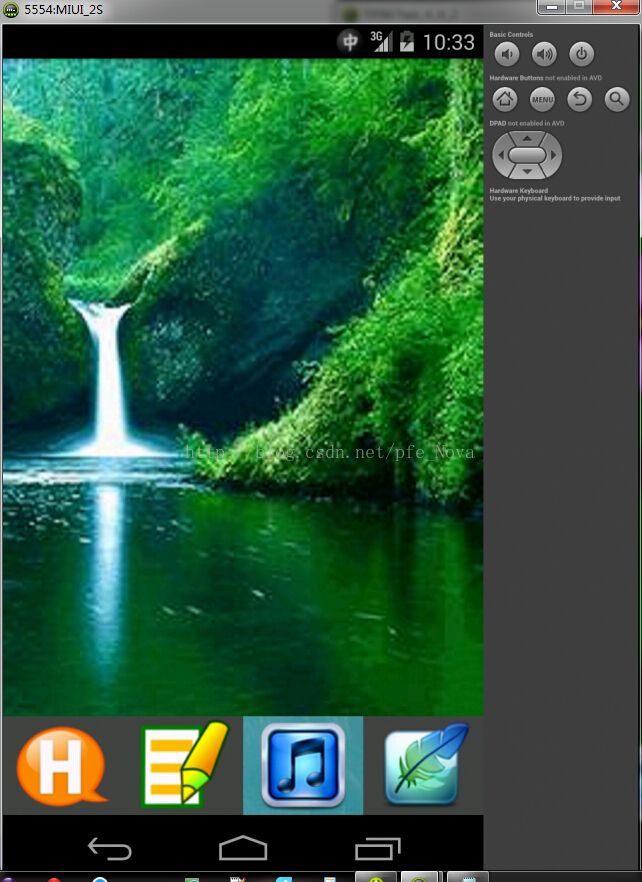
项目运行截图跟上例类似:
1.用ActivityGroup和DataGrid相结合实现
首先是用ActivityGroup和DataGrid相结合实现,思想是在一个页面上将子页面与导航栏上下布局,每次点击时跳转到指定的页面,在上面显示。主页面的布局activity_main.xml:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:layout_width="fill_parent"
android:layout_height="fill_parent"
android:orientation="vertical" >
<RelativeLayout
android:layout_width="fill_parent"
android:layout_height="fill_parent" >
<LinearLayout
android:id="@+id/content"
android:layout_width="fill_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:orientation="vertical" >
</LinearLayout>
<GridView
android:id="@+id/gridView"
android:layout_width="fill_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_alignParentBottom="true"
android:fadingEdge="vertical"
android:fadingEdgeLength="5px" >
</GridView>
</RelativeLayout>
</LinearLayout>
content中显示需要跳转的页面,gridView专门显示导航栏。
此例中四个要跳转的页面都很简单,只是显示一张图片,布局都一样,所以共用一个布局文件(实际应用时一般都是各不相同,第二个例子就是各自用各自的布局文件),布局文件view_layout.xml代码如下:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:layout_width="fill_parent"
android:layout_height="fill_parent"
android:orientation="vertical" >
<ImageView
android:id="@+id/imageView_Back"
android:layout_width="fill_parent"
android:layout_height="fill_parent"
android:scaleType="fitXY"/>
</LinearLayout> 下面要做的就剩两步了,一是加载gridView,一个是触发点击事件跳转页面。加载gridView的方法如下(不熟悉没关系,可以参考 Android之GridView):
先定义了一个图片适配器类(也可以直接用SimpleAdapter 类),继承自BaseAdapter:
package com.example.activitygroup0817;
import android.content.Context;
import android.view.View;
import android.view.ViewGroup;
import android.widget.BaseAdapter;
import android.widget.GridView;
import android.widget.ImageView;
public class ImageAdapter extends BaseAdapter {
private Context context = null;
private ImageView[] menuImg = null;
private int selectedMenuImg;
public ImageAdapter(Context context, int imgIds[], int width, int height,
int selectedMenuImg) {
this.context = context;
this.selectedMenuImg = selectedMenuImg;
this.menuImg = new ImageView[imgIds.length];
for (int i = 0; i < imgIds.length; i++) {
this.menuImg[i] = new ImageView(this.context);
//定义布局参数
this.menuImg[i].setLayoutParams(new GridView.LayoutParams(width,
height));
//不调整边界
this.menuImg[i].setAdjustViewBounds(false);
this.menuImg[i].setPadding(3, 3, 3, 3);
this.menuImg[i].setImageResource(imgIds[i]);
}
}
@Override
public int getCount() {
return this.menuImg.length;
}
@Override
public Object getItem(int position) {
return this.menuImg[position];
}
@Override
public long getItemId(int position) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
return 0;
}
@Override
public View getView(int position, View convertView, ViewGroup parent) {
ImageView imgView = null;
if (convertView == null) {
imgView = this.menuImg[position];
} else {
imgView = (ImageView) convertView;
}
return imgView;
}
public void setFocus(int selId) {
for (int i = 0; i < this.menuImg.length; i++) {
if (i != selId) {
//取消背景图片
this.menuImg[i].setBackgroundResource(0);
}
}
this.menuImg[selId].setBackgroundResource(this.selectedMenuImg);
}
} 然后填充GridView:
private GridView gridView = null;
private ImageAdapter menu = null;
private LinearLayout content = null;
private int menu_img[] = new int[] { R.drawable.home_select,
R.drawable.note_select, R.drawable.music, R.drawable.msg };
private int width = 0;
private int height = 0;
private Intent intent = null;
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
super.requestWindowFeature(Window.FEATURE_NO_TITLE);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_main);
this.gridView = (GridView) super.findViewById(R.id.gridView);
this.content = (LinearLayout) super.findViewById(R.id.content);
this.gridView.setNumColumns(this.menu_img.length);
this.gridView.setSelector(new ColorDrawable(Color.TRANSPARENT));
this.gridView.setGravity(Gravity.CENTER);
this.gridView.setVerticalSpacing(0);
this.gridView.setBackgroundColor(Color.DKGRAY);
this.width = super.getWindowManager().getDefaultDisplay().getWidth()
/ this.menu_img.length;
this.height = super.getWindowManager().getDefaultDisplay().getHeight() / 8;
this.menu = new ImageAdapter(this, this.menu_img, this.width,
this.height, R.drawable.menu_back);
this.gridView.setAdapter(this.menu);
//this.switchActivity(0);
//this.gridView.setOnItemClickListener(new OnItemClickListenerImpl());
} 至此显示是好了,下面就是触发点击事件了,关键代码如下:
private class OnItemClickListenerImpl implements OnItemClickListener {
@Override
public void onItemClick(AdapterView<?> parent, View view, int position,
long id) {
MainActivity.this.switchActivity(position);
}
}
private void switchActivity(int id) {
this.menu.setFocus(id);
this.content.removeAllViews();
switch (id) {
case 0:
this.intent = new Intent(MainActivity.this, HomeActivity.class);
break;
case 1:
this.intent = new Intent(MainActivity.this, NoteActivity.class);
break;
case 2:
this.intent = new Intent(MainActivity.this, MusicActivity.class);
break;
case 3:
this.intent = new Intent(MainActivity.this, MsgActivity.class);
break;
case 4:
this.exitDialog();
break;
default:
Toast.makeText(MainActivity.this, "switchActivity的id不在范围内",
Toast.LENGTH_LONG).show();
break;
}
this.intent.addFlags(Intent.FLAG_ACTIVITY_CLEAR_TOP);
Window subActivity = this.getLocalActivityManager().startActivity(
"subActivity", this.intent);
this.content.addView(subActivity.getDecorView(),
LayoutParams.FILL_PARENT);
} 先根据点击的项获得对应的编号,然后分支判断,跳转到指定的页面,关键语句是最后两句:
Window subActivity = this.getLocalActivityManager().startActivity( "subActivity", this.intent); this.content.addView(subActivity.getDecorView(), LayoutParams.FILL_PARENT);这个控制显示在MainActivity这个页面上。
至此框架完成,其他要注意的细节:这边在选中时添加了个背景图片以便醒目;各个页面的图片显示问题,我这边采用了跟手机一样像素的图片才正好铺满屏幕,开始弄的图片像素太低,就只在屏幕的左上边显示;图标和最好采用无背景的图片(相对背景为白色的,透明更美观);只要涉及到多页面就要记得在AndroidManifest.xml中配置进去;
运行截图如下:
2.采用继承FragmentActivity和RadioButton相组合实现
该方法的关键之处是FragmentActivity的getSupportFragmentManager方法,通过它来控制Fragment布局页面的显示和隐藏。主界面采用相对布局,本例有四个Fragment页面和一组RadioButton,代码如下:<RelativeLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
tools:context="com.example.drawer0817.MainActivity" >
<fragment
android:id="@+id/farment_home"
android:layout_width="fill_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
class="com.example.drawer0817.HomeFrament" />
<fragment
android:id="@+id/farment_note"
android:layout_width="fill_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
class="com.example.drawer0817.NoteFrament" />
<fragment
android:id="@+id/farment_music"
android:layout_width="fill_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
class="com.example.drawer0817.MusicFrament" />
<fragment
android:id="@+id/farment_msg"
android:layout_width="fill_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
class="com.example.drawer0817.MsgFrament" />
<RadioGroup
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="55dp"
android:layout_alignParentBottom="true"
android:orientation="horizontal" >
<RadioButton
android:layout_width="0dp"
android:layout_height="55dp"
android:layout_weight="1"
android:background="@drawable/selector_common"
android:button="@null"
android:drawableTop="@drawable/selector_home"
android:onClick="homeClick" />
<RadioButton
android:layout_width="0dp"
android:layout_height="55dp"
android:layout_weight="1"
android:background="@drawable/selector_common"
android:button="@null"
android:drawableTop="@drawable/selector_note"
android:onClick="noteClick" />
<RadioButton
android:layout_width="0dp"
android:layout_height="55dp"
android:layout_weight="1"
android:background="@drawable/selector_common"
android:button="@null"
android:drawableTop="@drawable/music"
android:onClick="musicClick" />
<RadioButton
android:layout_width="0dp"
android:layout_height="55dp"
android:layout_weight="1"
android:background="@drawable/selector_common"
android:button="@null"
android:drawableTop="@drawable/msg"
android:onClick="msgClick" />
</RadioGroup>
</RelativeLayout> 可以看到四个fragment是写在一起的,实际运行时跟据需要显示其中一个。主界面后台代码主要干两件事,收集fragment和根据点击事件控制fragment的显示和隐藏,这个只要看看代码就能明白啥意思了:
package com.example.drawer0817;
import android.os.Bundle;
import android.support.v4.app.Fragment;
import android.support.v4.app.FragmentActivity;
import android.view.View;
import android.view.Window;
public class MainActivity extends FragmentActivity {
private Fragment[] fragments;
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
requestWindowFeature(Window.FEATURE_NO_TITLE);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_main);
fragments = new Fragment[4];
fragments[0] = getSupportFragmentManager().findFragmentById(
R.id.farment_home);
fragments[1] = getSupportFragmentManager().findFragmentById(
R.id.farment_note);
fragments[2] = getSupportFragmentManager().findFragmentById(
R.id.farment_music);
fragments[3] = getSupportFragmentManager().findFragmentById(
R.id.farment_msg);
getSupportFragmentManager().beginTransaction().hide(fragments[1])
.hide(fragments[2]).hide(fragments[3]).show(fragments[0])
.commit();
}
public void homeClick(View view) {
getSupportFragmentManager().beginTransaction().hide(fragments[1])
.hide(fragments[2]).hide(fragments[3]).show(fragments[0])
.commit();
}
public void noteClick(View view) {
getSupportFragmentManager().beginTransaction().hide(fragments[0])
.hide(fragments[2]).hide(fragments[3]).show(fragments[1])
.commit();
}
public void musicClick(View view) {
getSupportFragmentManager().beginTransaction().hide(fragments[0])
.hide(fragments[1]).hide(fragments[3]).show(fragments[2])
.commit();
}
public void msgClick(View view) {
getSupportFragmentManager().beginTransaction().hide(fragments[0])
.hide(fragments[1]).hide(fragments[2]).show(fragments[3])
.commit();
}
} 然后fragment布局页面代码如下,为了跟第一个例子有所区分,这边四个页面没有合在一起(可以合在一起),这边以第一个为例,其他几个跟这个一模一样,就不写了:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:orientation="vertical" >
<ImageView
android:id="@+id/imageView_Back"
android:layout_width="fill_parent"
android:layout_height="fill_parent"
android:scaleType="fitXY"/>
</LinearLayout> 相对应的后台代码如下:
package com.example.drawer0817;
import android.os.Bundle;
import android.support.v4.app.Fragment;
import android.view.LayoutInflater;
import android.view.View;
import android.view.ViewGroup;
import android.widget.ImageView;
public class HomeFrament extends Fragment {
ImageView imageView=null;
public HomeFrament() {
}
@Override
public View onCreateView(LayoutInflater inflater, ViewGroup container,
Bundle savedInstanceState) {
View rootView = inflater.inflate(R.layout.farment_home, container,
false);
imageView=(ImageView)rootView.findViewById(R.id.imageView_Back);
imageView.setImageResource(R.drawable.home_back);
return rootView;
}
} 至此框架完成,这个例子也是有可圈可点的地方,关键看drawable这个文件夹。通过selector控制按钮的背景色随着按钮的状态而变化,可分别设置未点击时和被点击时的样式;另外可以根据shape控制边框、圆角、阴影等,具体可自行搜索学习;
项目运行截图跟上例类似:
后记,看这截图,感觉有点样子了,至少比前面写的例子好多了,不过花的时间也不少,整整一天就弄了这两个例子,些许欣慰。
至此全部完成,只是个人的一些实践,对自己是一个记录,同时希望也能对别人有些帮助,如果有什么错误,还望不吝指出,共同进步,转载请保留原文地址。
项目源码下载