Dataquest用户数据分析
Thinking Through Analytics Data
本文将介绍如何从头到尾对数据进行分析。我们将探索Dataquest这个网站上用户的匿名化分析数据。我们将探索用户是如何进行学习的,数据源主要有两个:
- 数据库
- 网站前端的收集的数据
A Quick Look At Dataquest
首先需要明确Dataquest这个网站是怎样构造的:当前处在一个任务中,任务是由远程数据库,以及一些知识点组成。每个任务包含多个屏幕(screen),屏幕的目录在右边,可以点击它跳到相应的屏幕中。这些屏幕可以是code屏幕,也可以是文本屏幕,code屏幕通常需要你写答案,然后点击运行来检测答案的正确性。系统所使用的语言是python3.
Looking At Student Data
第一个数据集来自数据库,包含了:
- 学习进展信息(progress data):是否成功完成某个屏幕,学生所写的代码,比如你刚完成了一个屏幕的内容就产生了一个新的记录(是否成功完成以及你的代码)。每个progress数据由一个pk值唯一确定。
尝试数据(attempt data):包含学生对每个任务所作的各种代码尝试记录,每个progress data都有一个或多个与之关联的attempt data,每一个attempt数据有一个pk值唯一确定,attempt中的screen_progress属性就是progress的pk值,这是attempt的外键,通过这个外键将attempt与progress联系到一起。
为了使分析更简单,本文提取了50个学生的数据库信息:
# The attempts are stored in the attempts variable, and progress is stored in the progress variable.
# Here's how one progress record looks.
print("Progress Record:")
# Pretty print is a custom function we made to output json data in a nicer way.
pretty_print(progress[0])
print("\n")
# Here's how one attempt record looks.
print("Attempt Record:")
pretty_print(attempts[0])
'''
# 一条Progress记录有fields,model,pk三个键,而fields中有attempts,complete,user等更详细的键。
Progress Record:
{
"fields": {
"attempts": 0,
"complete": true,
"created": "2015-04-07T21:21:57.316Z",
"last_code": "# We'll be coding in python.\n# Python is a great general purpose language, and is used in a lot of data science and machine learning applications.\n# If you don't know python, that's okay -- important concepts will be introduced as we go along.\n# In python, any line that starts with a # is called a comment, and is used to put in notes and messages.\n# It isn't part of the code, and isn't executed.",
"last_context": null,
"last_correct_code": "# We'll be coding in python.\n# Python is a great general purpose language, and is used in a lot of data science and machine learning applications.\n# If you don't know python, that's okay -- important concepts will be introduced as we go along.\n# In python, any line that starts with a # is called a comment, and is used to put in notes and messages.\n# It isn't part of the code, and isn't executed.",
"last_output": "{\"check\":true,\"output\":\"\",\"hint\":\"\",\"vars\":{},\"code\":\"# We'll be coding in python.\\n# Python is a great general purpose language, and is used in a lot of data science and machine learning applications.\\n# If you don't know python, that's okay -- important concepts will be introduced as we go along.\\n# In python, any line that starts with a # is called a comment, and is used to put in notes and messages.\\n# It isn't part of the code, and isn't executed.\"}",
"screen": 1,
"updated": "2015-04-07T21:25:07.799Z",
"user": 48309
},
"model": "missions.screenprogress",
"pk": 299076
}
# 一条Attempt 记录有fields,model,pk三个键,同样fields中有更详细的键screen_progress等。
Attempt Record:
{
"fields": {
"code": "# We'll be coding in python.\n# Python is a great general purpose language, and is used in a lot of data science and machine learning applications.\n# If you don't know python, that's okay -- important concepts will be introduced as we go along.\n# In python, any line that starts with a # is called a comment, and is used to put in notes and messages.\n# It isn't part of the code, and isn't executed.",
"correct": true,
"created": "2015-03-01T16:33:56.537Z",
"screen_progress": 231467,
"updated": "2015-03-01T16:33:56.537Z"
},
"model": "missions.screenattempt",
"pk": 62474
}
'''The Structure Of The Data
可以发现progress以及attempts都是字典格式的数据。
Progress record
- pk – the id of the record in the database
- fields
- attempts – a count of how many attempts the student made on the
screen. - complete – whether the student successfully passed the screen (True
if they have / False if not). - created – what time the student first saw the screen.
- last_code – the text of the last code the student wrote.
- last_correct_code – the last code the student wrote that was
correct. Null if they don’t have anything correct. - screen – the id of the screen this progress is associated with.
- user – the id of the user this progress is associated with.
- attempts – a count of how many attempts the student made on the
Attempt record
- pk – the id of the record in the database
- fields
- code – the code that was submitted for this attempt.
- correct – whether or not the student got the answer right.
- screen_progress – the id of the progress record this attempt is associated with.
# This gets the fields attribute from the first attempt, and prints it
# As you can see, fields is another dictionary
# The keys for fields are listed above
pretty_print(attempts[0]["fields"]) ''' { "code": "# We'll be coding in python.\n# Python is a great general purpose language, and is used in a lot of data science and machine learning applications.\n# If you don't know python, that's okay -- important concepts will be introduced as we go along.\n# In python, any line that starts with a # is called a comment, and is used to put in notes and messages.\n# It isn't part of the code, and isn't executed.", "correct": true, "created": "2015-03-01T16:33:56.537Z", "screen_progress": 231467,
"updated": "2015-03-01T16:33:56.537Z"
}
'''
# This gets the "correct" attribute from "fields" in the first attempt record
print(attempts[0]["fields"]["correct"])
'''
True
'''Exploring The Data
得到详细的数据后,可以计算一些东西,来进一步了解数据:
- The number of attempts.
- The number of progress records.
- The number of attempts each student makes per screen (# of attempts / # of progress records).
# Number of screens students have seen
progress_count = len(progress) print(progress_count)
# Number of attempts
attempt_count = len(attempts) print(attempt_count)
'''
2134
3995
'''Get User ID
- 我们需要获取用户是如何与网站进行交互的,比如用户通过了多少个任务等等,所以首先需要获取有多少个用户id,然后根据id分组计算频数:
# A list to put the user ids
all_user_ids = []
for record in progress:
user_id = record["fields"]["user"]
all_user_ids.append(user_id)
# This pulls out only the unique user ids
all_user_ids = list(set(all_user_ids))
'''
all_user_ids : list (<class 'list'>)
[51331,
52100,
58628,
54532,
55945,
46601,
50192,
...
'''Matrices
- 矩阵是二维数组,矩阵的索引形式如下matrix[1,2]。
import numpy as np
# if we pass a list to asarray, it converts them to a vector
# If we pass a list of lists to asarray, it converts them to a matrix.
matrix = np.asarray([
[1,2,3],
[4,5,6],
[7,8,9],
[10,11,12]
])
matrix_1_1 = matrix[1,1]
matrix_0_2 = matrix[0,2]Pandas DataFrame
- Dataframe和矩阵相似,但是Dataframes存储的数据的每个列可以是不同的数据类型。并且有许多內建的函数可以用来做数据分析和数据可视化。创建一个Dataframe对象的最简单的方法就是通过字典列表来初始化。但是这个字典里面不能有嵌套,也就是所有的键都在同一个水平上。所以对于我们的数据需要做些调整。由于之前一条progress记录包含pk,field主键,而field里面又有很多子键,因此将field去掉,将其子键提取出来和pk在同一个水平。
# "Flatten" the progress records out.
flat_progress = []
for record in progress:
# Get the fields dictionary, and use it as the start of our flat record.
flat_record = record["fields"]
# Store the pk in the dictionary
flat_record["pk"] = record["pk"]
# Add the flat record to flat_progress
flat_progress.append(flat_record)
flat_attempts = []
for record in attempts:
flat_record = record["fields"]
flat_record["pk"] = record["pk"]
flat_attempts.append(flat_record)Creating Dataframes
- 将JOSN数据转化为DataFrame数据
import pandas as pd
progress_frame = pd.DataFrame(flat_progress)
# Print the names of the columns
print(progress_frame.columns)
''' Index(['attempts', 'complete', 'created', 'last_code', 'last_context', 'last_correct_code', 'last_output', 'pk', 'screen', 'updated', 'user'], dtype='object') '''
attempt_frame = pd.DataFrame(flat_attempts)Users’ Progresss Count
- 现在通过Dataframe的一些内建函数可以很快速简单的获取一些统计信息,比如有多少个用户user_ids,以及每个用户的progress个数user_id_counts,以及每个屏幕被记录了多少次screen_counts.并且value_counts()是按照值从小到大排序的。
# Get all the unique values from a column.
user_ids = progress_frame["user"].unique()
# Make a table of how many screens each user attempted
user_id_counts = progress_frame["user"].value_counts()
print(user_id_counts)
screen_counts = progress_frame["screen"].value_counts()
''' 46578 177 48108 136 49340 135 54823 131 47451 123 42983 118 52584 108 ... '''Making Charts
- 用可视化技术来分析数据最直观,使用matplotlib来观察一下用户完成progress的情况:
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
# Plot how many screens each user id has seen.
# The value_counts method sorts everything in descending order. user_counts = progress_frame["user"].value_counts() # The range function creates an integer range from 1 to the specified number. x_axis = range(len(user_counts)) # Make a bar plot of the range labels against the user counts. plt.bar(x_axis, user_counts) # We have to use this to show the plot. plt.show()- 下图显示的是每用户的progess(完成的屏幕数量)数量,由于user_counts是排好序的,因此图中的从打大小排下来的。可以发现数据呈现长尾分布,大部分人只学习了少量的任务。
Pandas Filtering
- 选择第一个屏幕的progress数据:
screen_1_frame = progress_frame[progress_frame["screen"] == 1]Matching Attempts To Progress
将每个attempt和对应的progess(每个用户对每个screen都会产生一个pregress记录)联系在一起,这样才可以统计每个screen总共有多少个attempt,他们中有多少个是正确的。attempt可以通过screen_progress (the id of the progress record this attempt is associated with)这个属性将其与progess(pk)联系在一起。
- 下面这个代码是找到1137条progress记录的的尝试情况:
# 这是个布尔型Series,找到第1137条progress(某个人对某个screen的详细信息)的记录的尝试信息。
has_progress_row_id = attempt_frame["screen_progress"] == progress_frame["pk"][1137]
progress_attempts = attempt_frame[has_progress_row_id]
# 一共有49条尝试,正确的有5条,错误的有44条
correct_attempts_count = progress_attempts[progress_attempts["correct"] == True].shape[0]
incorrect_attempts_count = progress_attempts[progress_attempts["correct"] == False].shape[0]Figuring Out Attempt Ratios
- 现在已经可以将progress和attempt联系起来,我们想要知道用户在每个progress上是否第一次尝试就correct了,这可以体现这个任务的难易程度,也可以暗示用户放弃了学习(如果一次都没有成功)。
- DataFrame对象通过groupby函数根据某列”screen_progress”的取值将其分组得到一个GroupBy对象。然后利用groups.aggregate将DataFrameGroupBy对象中某个取值进行聚合。
- 下面的代码:我们将每个screen_progress对应的成功的attempt除以attempt的总数,就可以知道该用户在这个任务上的成功率,然后可视化所有的用户的成功率分布。
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
# Split the data into groups
groups = attempt_frame.groupby("screen_progress")
ratios = []
# Compute ratios for each group
# Loop over each group, and compute the ratio.
for name, group in groups:
# The ratio we want is the number of correct attempts divided by the total number of attempts.
# Taking the mean of the correct column will do this.
# If you take the sum or mean of a boolean column, True values will become 1, and False values 0.
ratio = np.mean(group["correct"])
# Add the ratio to the ratios list.
ratios.append(ratio)
''' ratios list (<class 'list'>) [1.0, 1.0, 1.0, 1.0, '''
# This code does the same thing as the segment above, but it's simpler.
# We aggregate across each group using the np.mean function.
# This takes the mean of every column in each group, then makes a dataframe with all the means.
# We only care about correctness, so we only select the correct column at the end.
easier_ratios = groups.aggregate(np.mean)["correct"]
''' easier_ratios Series (<class 'pandas.core.series.Series'>) screen_progress 231467 1 231470 1 231474 1 231476 1 '''
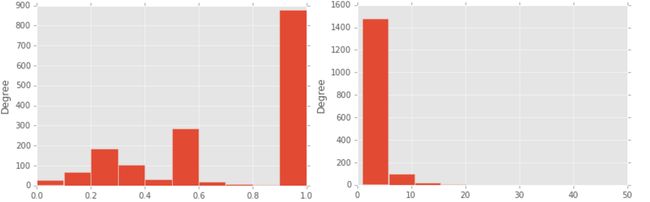
# We can plot a histogram of the easier_ratios series.
# The kind argument specifies that we want a histogram.
# Histograms show how values are distributed -- in this case, 900 of the screens have only 1 (correct) attempt.
# Many more appear to have had two attempts (a .5 ratio).
easier_ratios.plot(kind="hist")
plt.show()
counts = groups.aggregate(len)["correct"]
counts.plot(kind="hist")
plt.show()- 观察下图,成功率为1的表示用户第一次尝试就成功了,并且这个比例占据最多,表示大部分任务还是较容易的,用户第一次通过了。第二个图显示了用户完成一个屏幕内容尝试的次数在10次以内。少数要超过10,表明用户超过10次完成不了后可能会选择放弃这个任务。
Who Gives Up?
- 我们可以根据上面的信息探索谁放弃了继续学习,比如成功率为0表示一次都没有成功。我们可以适当降低这个任务的难度或者给他一点提示帮助他度过这个难关继续学习。
- 因此我们需要获知这个用户要放弃之前所做的事,就是这个用户在最后一次尝试后放弃之前他做了那些事情?我们可以建立一个模型,识别出这种规律,在捕捉到用户快要放弃的时,我们可以及时的给出帮助。
- 我们可以通过attempts分组后计算成功率为0的用户来找到放弃的用户,但是这样比较复杂。然而progress中有个属性complete记录了一个用户是否完成一个屏幕信息,我们可以直接获取这个信息来判断该用户是否放弃。的没有如果complete的那些记录,然后将与之相连的attempts提取出来。gave_up_ids 存储的是那些放弃了的process的pk值。可以通过pk值与attempt中的screen_progress 相连。来获取在用户放弃时他做了多少尝试。
gave_up = progress_frame[progress_frame["complete"] == False]
gave_up_ids = gave_up["pk"]Graphing Attempt Counts
- 现在获取那些放弃学习的用户的attempt数据,pandas中有一个isin函数返回布尔型Series,其中screen_progress在(gave_up_ids)中对应True。其中groups.aggregate(len)计算的是每组(screen_progress)的个数,其实后面groups.aggregate(len)[“correct”]还是groups.aggregate(len)[“code”]都是一样的,因为这只是计算这组数据的长度:
gave_up_boolean = attempt_frame["screen_progress"].isin(gave_up_ids)
'''
gave_up_boolean
Series (<class 'pandas.core.series.Series'>)
0 False
1 False
2 False
'''
# 所有的用户放弃前所作的尝试
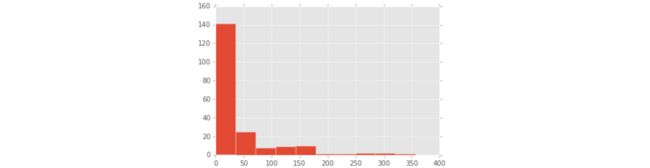
gave_up_attempts = attempt_frame[gave_up_boolean] # 按照screen_progress(用户screen对)分组得到每个用户尝试情况
groups = gave_up_attempts.groupby("screen_progress") # 计算每个用户尝试的次数 counts = groups.aggregate(len)["correct"] counts.plot(kind="hist") plt.show()Attempt Count Differential
- 可以发现大部分人进行了一次尝试失败后就放弃了,当然有些长尾数据,有个人尝试了15次才放弃了。现在看看没有放弃的那些人普遍提交了多少次:
gave_up = attempt_frame[attempt_frame["screen_progress"].isin(gave_up_ids)]
groups = gave_up.groupby("screen_progress")
counts = groups.aggregate(len)["correct"]
# We can use the .mean() method on series to compute the mean of all the values.
# This is how many attempts, on average, people who gave up made.
print(counts.mean())
# We can filter our attempts data to find who didn't give up (people that got the right answer).
# To do this, we use the ~ operator.
# It negates a boolean, and swaps True and False.
# This filters for all rows that aren't in gave_up_ids.
eventually_correct = attempt_frame[~attempt_frame["screen_progress"].isin(gave_up_ids)]
groups = eventually_correct.groupby("screen_progress")
counts = groups.aggregate(len)["correct"]
print(counts.mean())
''' 2.89473684211 2.4858044164 '''- 从结果中发现放弃的人提交的平均次数要大于没有放弃的人提交的平均次数。
Another Data Store
为了更好的帮助那些放弃的用户,我们需要获取更细粒度的数据。有些数据比如用户播放一个video或者点击一个按钮这种信息不会被存储在数据库中,这些数据会被存储在一个特殊的分析数据库,这些是通过网站的前端收集到的。我们挑选了其中一些信息进行分析:
- started-mission – a mission is started by a student
- started-screen – a screen in a mission is started
- show-hint – a click on the “hint” button
- run-code – a click on the “run” button
- reset-code – a click on the “reset code” button
- next-screen – a click on the “next” button
- get-answer – a click on the “show answer” button
以上这些信息被存储为一个session,一个session代表一个用户在一段时间内(开始进入dataquest学习,做任务,离开)所采取的一些点击行为(一个点击行为就是一个事件event)。每个session包含多个event字典,而sessions以list的形式存储每个session。我们随机抽样了200个用户session数据进行分析。
''' sessions list (<class 'list'>) [[{'event_type': 'started-mission', 'keen': {'created_at': '2015-06-12T23:09:03.966Z', 'id': '557b668fd2eaaa2e7c5e916b', 'timestamp': '2015-06-12T23:09:07.971Z'}, 'sequence': 1}, {'event_type': 'started-screen', 'keen': {'created_at': '2015-06-12T23:09:03.979Z', 'id': '557b668f90e4bd26c10b6ed6', 'timestamp': '2015-06-
...
'''# We have 200 sessions
print(len(sessions))
'''
200
'''
# The first session has 38 student events
print(len(sessions[0]))
'''
38
'''
# Here's the third event from the first user session -- it's a started-screen event
print(sessions[0][3])
'''
{'event_type': 'started-screen', 'mission': 1, 'type': 'code', 'sequence': 2, 'keen': {'timestamp': '2015-06-12T23:09:28.589Z', 'id': '557b66a4672e6c40cd9249f7', 'created_at': '2015-06-12T23:09:24.688Z'}}
'''
# We'll make a histogram of event counts per session
plt.hist([len(s) for s in sessions])
plt.show()
Event Structure
下面是event的数据结构:
- event_type – the type of event – there’s a list of event types in the last screen.
- created_at – when the event occured – in the keen dictionary.
- id – the unique id of the event – in the keen dictionary.
- sequence – this field varies by event type – for started-mission events, it’s the mission that was started. For all
other events, it’s the screen that the event occured on. Each mission
consists of multiple screens.- mission – If the event occurs on a screen, then this is the mission the event occurs in.
- type – if the event occurs on a screen, the type of screen (code, video, or text).
- 为了将数据整理为DataFrame,首先需要将其转换为字典列表,所以需要将键都调整为统一水平,并且添加了一个新的键session_id,因为每个session有多个event,因此通过session_id将这些event联系起来。
# Where we'll put the events after we "flatten" them
flat_events = []
# If we're going to combine everything in one dataframe, we need to keep
# track of a session id for each session, so we can link events across sessions.
session_id = 1
# Loop through each session.
for session in sessions:
# Loop through each event in each session.
for event in session:
new_event = {
"session_id": session_id,
# We use .get() to get the fields that could be missing.
# .get() will return a default null value if the key isn't found in the dictionary.
# If we used regular indexing like event["mission"], we would get an
# error if the key wasn't found.
"mission": event.get("mission"),
"type": event.get("type"),
"sequence": event.get("sequence")
}
new_event["id"] = event["keen"]["id"]
new_event["created_at"] = event["keen"]["created_at"]
new_event["event_type"] = event["event_type"]
flat_events.append(new_event)
# Increment the session id so each session has a unique id.
session_id += 1Convert To Dataframe
event_frame = pd.DataFrame(flat_events)Exploring The Session Data
- 现在可以进行event数据的分析,比如我们可以分析用户在一个session中最常做的event是什么?一个session结束表示用户在这个平台的学习结束了,这里面肯定有很好的模式值得我们去学习。这与之前的用户的放弃行为有关系,那些放弃学习的用户的学习过程也肯定有一个特殊的模式。所以首先需要将event按照created_at属性进行升序排列,因为事件是先后发生的,我们需要在时间序列上观察行为的变迁,然后按照session_id进行分组,单独观察每个用户的行为序列。对于每个session中的最后的event就是结束的event。
# Sort event_frame in ascending order of created_at.
event_frame = event_frame.sort(["created_at"], ascending=[1])
# Group events by session
groups = event_frame.groupby("session_id")
# ending_events 存储每个session的最后结束的event类型,是个series对象,一行数据,只有event_type这个数据
ending_events = []
for name, group in groups:
# The .tail() method will get the last few events from a dataframe.
# The number you pass in controls how many events it will take from the end.
# Passing in 1 ensures that it only takes the last one.
last_event = group["event_type"].tail(1)
''' last_event Series (<class 'pandas.core.series.Series'>) 7446 started-screen Name: event_type, dtype: object '''
ending_events.append(last_event)
# The concat method will combine a list of series into a dataframe.
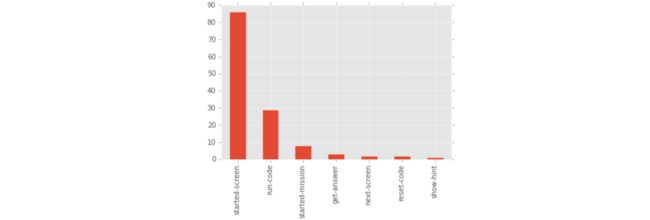
ending_events = pd.concat(ending_events)
ending_event_counts = ending_events.value_counts()
ending_event_counts.plot(kind="bar")
plt.show()- 可以发现用户离开dataquest这个平台最后做的一件事通常是started-screen。
Most Common Events
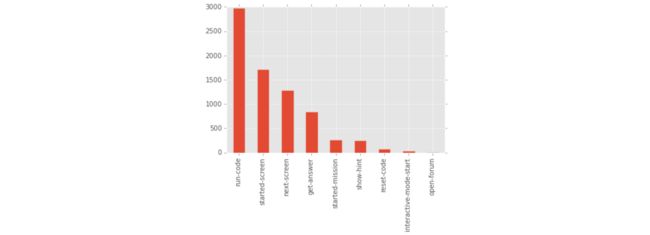
- 我们还可以每个事件发生的次数:
event_counts = event_frame["event_type"].value_counts()
event_counts.plot(kind="bar")
plt.show()Discussion
最常见的event和用户离开平台前的event有一个最主要的区别:绝大多数人在离开平台前都会触发started-screen event事件,要远远高于平均水平。主要原因分析如下:
- 当人们打开一个screen,看了一眼觉得太难了然后离开这个学习平台。
- 或者他们打开了一个screen,但是这个任务打开的时间太长(网速不行还是网站太卡等等),使得他们离开了这个网页。我们需要与用户交谈,来确定到底是什么原因导致他们离开,然后采取一些措施,提高用户学习的时间。
- 我们也可以看看哪个任务或者哪个屏幕用户在上面那个放弃了,这可以使我们意识到这个屏幕的内容或许太难或者太简单,然后做出相应的调整。
Mission Numbers
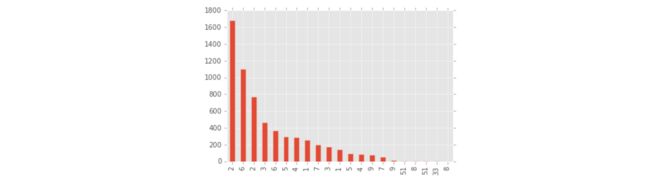
- 我们想看看哪个mission上面的event最多,很显然,最开始mission有更多的观众。
event_counts = event_frame["mission"].value_counts()
event_counts.plot(kind="bar")
plt.show()Explore!
- mission中有字符型数据和数值型数据,所以上面那个条形图是对的。
count = event_frame["mission"].unique()
''' ndarray (<class 'numpy.ndarray'>) array([None, 5, '5', '3', 3, 2, 7, '2', 6, '6', 1, '1', '9', 9, 4, '4', '7', '8', 8, '33', 51, '51'], dtype=object) '''我们可以从数据中探索下面这些有趣的问题:
- 基于一个用户当前的sequence是否能预测他下一步要采取的动作
- 是否某些events经常出现在某些missions
- 能否评估mission的困难度
- 其他的数据怎么收集