linux下pthread_exit在主线程中的用途
1.pthread_exit在main中有只终止main线程,而不终止整个进程的作用(注意不存在父子线程的概念),下面是posix中关于pthread_exit的一段描述:
When you program with POSIX Threads API,there is one thing about pthread_exit() that you may ignore for mistake. In subroutines that complete normally, there is nothing special you have to do unless you want to pass a return code back using pthread_exit(). The completion won't affect the other threads which were created by the main thread of this subroutine. However, in main(), when the code has been executed to the end,there could leave a choice for you. If you want to kill all the threads that main() created before, you can dispense with(无需) calling any functions. But if you want to keep the process and all the other threads (except for the main thread ) alive after the exit of main(), then you can call pthread_exit() to realize it. And any files opened inside the main thread will remain openafter its termination.
这段话的意思就是:在main线程终止时如果调用了pthread_exit(),那么此时终止的只是main线程,而进程的资源会为其他由main线程创建的线程保持打开的状态,直到其他线程都终止。而在其他的由main线程创建的线程中pthread_exit并没有这种作用。
下面给出实例,编译方式: g++ pthread_exit.cpp -o pthread_exit -lpthread
//pthread_exit.cpp
#include <iostream>
#include <sys/time.h>
#include <unistd.h>
int which1=1;
int which2=2;
void * cchild_thread(void*arg){
int i=0;
while(i++<5){
sleep(2);
std::cout<<"child child"<<std::endl;
}//while
}//cchild_thread
void* child_thread1(void*arg){
sleep(1);
std::cout<<"child thread run !"<<std::endl;
pthread_t tid;
pthread_attr_t attr;
pthread_attr_init(&attr);
pthread_attr_setdetachstate(&attr,PTHREAD_CREATE_DETACHED);
pthread_create(&tid,&attr,cchild_thread,(void*)which1);
int a=0;
while(a++<3)
std::cout<<pthread_self()<<" a="<<a<<std::endl;
}//child_thread
void* child_thread2(void*arg){
sleep(1);
std::cout<<"child thread run !"<<std::endl;
pthread_t tid;
pthread_attr_t attr;
pthread_attr_init(&attr);
pthread_attr_setdetachstate(&attr,PTHREAD_CREATE_DETACHED);
pthread_create(&tid,&attr,cchild_thread,(void*)which2);
int a=0;
while(a++<3)
std::cout<<pthread_self()<<" a="<<a<<std::endl;
pthread_exit((void*)1);
}//child_thread2
int main(int argc,char** argv){
pthread_t tid;
pthread_attr_t attr;
pthread_attr_init(&attr);
pthread_attr_setdetachstate(&attr,PTHREAD_CREATE_DETACHED);
int a=5;
pthread_create(&tid,&attr,child_thread1,(void *)a);
pthread_create(&tid,&attr,child_thread2,(void *)a);
sleep(1);
std::cout<<"main thread will exit"<<std::endl;
//pthread_exit(1);
std::cout<<"call pthread_exit"<<std::endl;
pthread_exit((void*)1);
}
2.此时主线程是fork生成的子进程中的线程,如果fork生成的子进程死亡,那么其下面的线程也会死亡:
//fork_thread.cpp : g++ fork_thread.cpp -o fork_thread -lpthread
#include <iostream>
#include <sys/time.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <fstream>
int which1=1;
std::ifstream fIn;
void * cchild_thread(void*arg){
int i=0;
while(i++<5){
sleep(2);
std::cout<<"child child"<<std::endl;
}//while
std::string mid;
if(fIn>>mid)
std::cout<<"read from txt:"<<mid<<std::endl;
else std::cout<<"file has been closed"<<std::endl;
}//cchild_thread
void* child_thread1(void*arg){
fIn.open("test.txt");
if(!fIn)
std::cout<<"open file failed"<<std::endl;
else
std::cout<<"open file successful"<<std::endl;
sleep(1);
std::cout<<"child thread run !"<<std::endl;
pthread_t tid;
pthread_attr_t attr;
pthread_attr_init(&attr);
pthread_attr_setdetachstate(&attr,PTHREAD_CREATE_DETACHED);
pthread_create(&tid,&attr,cchild_thread,(void*)which1);
int a=0;
while(a++<3)
std::cout<<pthread_self()<<" a="<<a<<std::endl;
fIn.close();
}//child_thread
int main(int argc,char** argv){
pthread_t tid;
pthread_attr_t attr;
pthread_attr_init(&attr);
pthread_attr_setdetachstate(&attr,PTHREAD_CREATE_DETACHED);
int a=5;
pid_t p1;
if((p1=fork())==0){
std::cout<<"main thread in process child"<<std::endl;
int iret=0;
if((iret=pthread_create(&tid,&attr,child_thread1,(void *)a))!=0){
perror("Create thread error");
}else{
std::cout<<"test"<<std::endl;
}
std::cout<<"main thread will exit"<<std::endl;
std::cout<<"call pthread_exit"<<std::endl;
pthread_exit((void*)1);
}else if(p1>0){
std::cout<<"type in q to exit parent process"<<std::endl;
char tmp;
do{
std::cin>>tmp;
sleep(1);
}while(tmp!='q');
}
}//main
3.
如下面的情况,在进程中调用(即在主线程中调用)pthread_exit,那么主线程将等待线程1、2、3、4。总之线程没有父子关系,都是共享创建其的进程的数据。
代码如下:
//g++ pthread_exit.cpp -o pthread_exit -lpthread
#include <iostream>
#include <sys/time.h>
#include <unistd.h>
int which1=1;
int which2=2;
void * cchild_thread(void*arg){
int i=0;
while(i++<5){
sleep(2);
std::cout<<"child child"<<std::endl;
}//while
}//cchild_thread
void* child_thread1(void*arg){
sleep(1);
std::cout<<"child thread1 run !"<<std::endl;
pthread_t tid;
pthread_attr_t attr;
pthread_attr_init(&attr);
pthread_attr_setdetachstate(&attr,PTHREAD_CREATE_DETACHED);
pthread_create(&tid,&attr,cchild_thread,(void*)which1);
std::cout<<"child thread1 exit!"<<std::endl;
}//child_thread
void* child_thread2(void*arg){
sleep(1);
std::cout<<"child thread2 run !"<<std::endl;
pthread_t tid;
pthread_attr_t attr;
pthread_attr_init(&attr);
pthread_attr_setdetachstate(&attr,PTHREAD_CREATE_DETACHED);
pthread_create(&tid,&attr,cchild_thread,(void*)which2);
int a=0;
std::cout<<"child thread2 exit!"<<std::endl;
pthread_exit((void*)1);
}//child_thread2
int main(int argc,char** argv){
pthread_t tid;
pthread_attr_t attr;
pthread_attr_init(&attr);
pthread_attr_setdetachstate(&attr,PTHREAD_CREATE_DETACHED);
int a=5;
pthread_create(&tid,&attr,child_thread1,(void *)a);
pthread_create(&tid,&attr,child_thread2,(void *)a);
sleep(1);
std::cout<<"main thread will exit"<<std::endl;
std::cout<<"call pthread_exit"<<std::endl;
pthread_exit((void*)1);
}
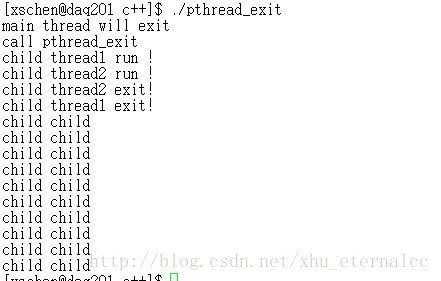
运行结果:
4.pthread_exit()会清除局部变量(即栈上的变量),所以当采用这种方法等待所创建的线程,如果被等待的线程中用到了进程栈上的数据,会出现断错误。下面给出pthread_exit释放栈变量的代码:
#include<iostream>
#include<cstdlib>
#include<pthread.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <signal.h>
class test{
int id;
public:
test(int i):id(i){
std::cout<<"constructor in test id="<<id<<", in process :"<<getpid()<<std::endl;
}
~test(){
std::cout<<"deconstructor in test id="<<id<<", in process :"<<getpid()<<std::endl;
}
};
void * thread(void * argv){
for(int i=0;i<5;i++){
sleep(2);
std::cout<<"thread :threadID="<<pthread_self()<<",pid="<<getpid()<<",parent pid ="<<getppid()<<std::endl;
}//
}//
test t1(1);
int main(int argc,char** argv){
pthread_t thid;
pthread_attr_t attr;
pthread_attr_init(&attr);
pthread_attr_setdetachstate(&attr,PTHREAD_CREATE_DETACHED);
pid_t pid;
test t2(2);
if((pid=fork())==0){
sleep(5);
}else if(pid>0){
if((pthread_create(&thid,&attr,thread,NULL))!=0)
std::cout<<"create thread failed"<<std::endl;
else
std::cout<<"create thread successed"<<std::endl;
//sleep(10);
pthread_exit(0);//in main for wait
}else{
std::cout<<"fork sub process failed"<<std::endl;
}
return EXIT_SUCCESS;
}
输出结果为: