Android开发学习之二 Android程序架构
2.1 Android程序架构
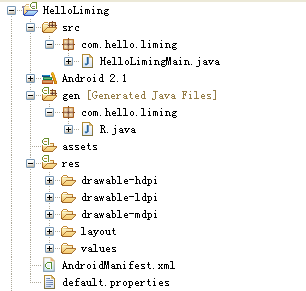
我们建立一个Android Project项目,展开项目文件,项目的文件结构为:
2.1.1 src
在src下是主程序类。如果在建立项目时,选择并填写了Create Activity时,会自动生成名为填写内容的,继承自android.app.Activity的类。在类中重写了onCreate()方法。方法中的setContentView为设置这个Activity的显示布局(R.layout.main),布局文件在res/layout下。R.layout.main实际上是指res/layout/main.xml布局文件。
- import android.app.Activity;
- import android.os.Bundle;
- public class HelloLimingMain extends Activity {
- /** Called when the activity is first created. */
- @Override
- public void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
- super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
- setContentView(R.layout.main);
- }
- }
import android.app.Activity;import android.os.Bundle;public class HelloLimingMain extends Activity { /** Called when the activity is first created. */ @Override public void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) { super.onCreate(savedInstanceState); setContentView(R.layout.main); }}
2.1.2 gen
Gen中的文件为编译器自动生成的。R文件:放在res中的元素,会在R中自动生成一个ID,在程序中可以直接引用ID来获取元素。使用aidl通讯模式时,也会在gen中生成对应的类。
2.1.3 res
在res下为资源文件,包括:
| res/anim |
逐帧动画的XML表示。 |
| res/drawable |
png、jpg格式图片 |
| res/layout |
View对象的XML表示 |
| res/values |
字符串String、颜色color、样式style、尺寸dimen、数组array的xml表示 |
| res/xml |
用户自定义的xml文件 |
| res/raw |
任意格式的、未编译的文件,可直接添加到设备中 |
2.1.4 assets
程序其他的资源文件。例如html文件、js文件、图片文件等其他文件。
WebView加载html文件时,URI地址这样写:webView.loadUrl("file:///android_asset/index.html");
2.1.5 AndroidMainifest配置文件
每个项目都有AndroidMainifest.xml配置文件,内容例如:
- <?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
- <manifest xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
- package="com.hello.liming"
- android:versionCode="1"
- android:versionName="1.0">
- <application android:icon="@drawable/icon" android:label="@string/app_name">
- <activity android:name="HelloLimingMain"
- android:label="@string/app_name">
- <intent-filter>
- <action android:name="android.intent.action.MAIN" />
- <category android:name="android.intent.category.LAUNCHER" />
- </intent-filter>
- </activity>
- </application>
- <uses-sdk android:minSdkVersion="7" />
- </manifest>
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?><manifest xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android" package="com.hello.liming" android:versionCode="1" android:versionName="1.0"> <application android:icon="@drawable/icon" android:label="@string/app_name"> <activity android:name="HelloLimingMain" android:label="@string/app_name"> <intent-filter> <action android:name="android.intent.action.MAIN" /> <category android:name="android.intent.category.LAUNCHER" /> </intent-filter> </activity> </application> <uses-sdk android:minSdkVersion="7" /></manifest>
首先是manifest元素的声明,包括包声明和Android的命名空间。然后是application,定义了图标和名称属性,可以定义
name属性,来使用扩展Application的对象来进行存储屏幕之间共享的数据。
接下来是application 的子元素Activity、Service或Receiver。
| 元素 |
位置 |
说明 |
| <manifest> |
root |
定义应用程序的包名和android命名空间 |
| <users-permission> |
root |
请求一个安全权限,开gps、发短信等功能的 |
| <permission> |
root |
生命一个安全权限 |
| <instrumentation> |
root |
声明一个检测设备组件 |
| <uses-sdk> |
root |
sdk最低兼容版本 |
| <application> |
|
|
|
|
|
|
| <activity> |
<application>子元素 |
|
| <service> |
<application>子元素 |
|
| <receiver> |
<application>子元素 |
|
| <provider> |
<application>子元素 |
|
| <uses-library> |
<application>子元素 |
引用其他包时,需要声明。 |
|
|
|
|
| <intent-filter> |
<activity,service,receiver>子元素 |
|
| <action> |
<intent-filter>子元素 |
intent动作 |
| <category> |
<intent-filter>子元素 |
intent类别 |
| <data> |
<intent-filter>子元素 |
intent 的MIME类型、URI方案、URI授权、URI路径 |