直线拟合,图像组件轮廓的检测和计算机描述
四、直线拟合
在一些应用,不仅要求检测出图像中的直线,还要求对图像中的直线精准的估计出位置和方向。下面我们将介绍opencv中如何通过一些点拟合出最适合的直线。
直线拟合的主要原理是,最小二乘法,即计算各点与直线的最小距离,求出最小距离之和的直线就是最合适的直线。
我们选择前面通过概率霍夫变换(cv::HoughLinesP)求出的第一个线段为实例,与Canny算子实现出的边缘按位与,得到一系列边缘点,程序和结果如下:
// Display one line
image= cv::imread("road.jpg",0);
int n=0;
cv::line(image, cv::Point(li[n][0],li[n][1]),cv::Point(li[n][2],li[n][3]),cv::Scalar(255),5);
cv::namedWindow("One line of the Image");
cv::imshow("One line of the Image",image);
cv::imwrite("One line of the Image.jpg",image);
// Extract the contour pixels of the first detected line
cv::Mat oneline(image.size(),CV_8U,cv::Scalar(0));
cv::line(oneline, cv::Point(li[n][0],li[n][1]),cv::Point(li[n][2],li[n][3]),cv::Scalar(255),5);
cv::bitwise_and(contours,oneline,oneline);
cv::Mat onelineInv;
cv::threshold(oneline,onelineInv,128,255,cv::THRESH_BINARY_INV);
cv::namedWindow("One line");
cv::imshow("One line",onelineInv);
cv::imwrite("One line.jpg",onelineInv); One line of the Image.jpg
One line.jpg
然后将这条直线存入Point中
std::vector<cv::Point> points;
// Iterate over the pixels to obtain all point positions
for( int y = 0; y < oneline.rows; y++ ) {
uchar* rowPtr = oneline.ptr<uchar>(y);
for( int x = 0; x < oneline.cols; x++ ) {
// if on a contour
if (rowPtr[x]) {
points.push_back(cv::Point(x,y));
}
}
} 最后通过opencv提供的cv::fitLine函数,进行直线拟合,
cv::Vec4f line;
cv::fitLine(cv::Mat(points),line,CV_DIST_L2,0,0.01,0.01);
std::cout << "line: (" << line[0] << "," << line[1] << ")(" << line[2] << "," << line[3] << ")\n";
int x0= line[2];
int y0= line[3];
int x1= x0-200*line[0];
int y1= y0-200*line[1];
image= cv::imread("road.jpg",0);
cv::line(image,cv::Point(x0,y0),cv::Point(x1,y1),cv::Scalar(0),3);
cv::namedWindow("Estimated line");
cv::imshow("Estimated line",image);
五、检测组件的轮廓
图像是由组件组成,图像分析的一个目标就是检测和提取这些目标物体。在目标检测、识别中,第一步就是禅城一个二值图像,使我们能够粗略的估计感兴趣区域的大概位置,无论二值图像是怎么获得的(例如直方图映射,运动分析等等中获得),第二步就是从这些0,1集合中检测出目标。
5.1 检测组件轮廓的实现
我们以下面图形为例子(打开和关闭的形态学滤波操作后加上简单的门限处理形成的图形),介绍怎么检测目标组件。
opencv提供简单的函数cv::findContours:
函数定义:
//! retrieves contours and the hierarchical information from black-n-white image.
CV_EXPORTS_W void findContours( InputOutputArray image, OutputArrayOfArrays contours,
OutputArray hierarchy, int mode,
int method, Point offset=Point());
//! retrieves contours from black-n-white image.
CV_EXPORTS void findContours( InputOutputArray image, OutputArrayOfArrays contours,
int mode, int method, Point offset=Point()); 函数使用实例:
// Get the contours of the connected components std::vector<std::vector<cv::Point>> contours; cv::findContours(image, contours, // a vector of contours CV_RETR_EXTERNAL, // retrieve the external contours CV_CHAIN_APPROX_NONE); // retrieve all pixels of each contoursint mode:
CV_RETR_EXTERNAL: 只对轮廓外面检索,内部洞的检索忽略(上面的图)
CV_RETR_LIST, // retrieve all contours :对所有轮廓检索(下面的图)
int method:
CV_CHAIN_APPROX_NONE:检测所有的边界
OutputArray hierarchy: 当轮廓检测选择CV_RETR_LIST,时,轮廓中有小洞,这是就可以建立等级,大轮廓包含小轮廓的等级。
轮廓显示程序:
// draw black contours on white image cv::Mat result(image.size(),CV_8U,cv::Scalar(255)); cv::drawContours(result,contours, -1, // draw all contours cv::Scalar(0), // in black 2); // with a thickness of 2
两种模式检索出的结果如下:
// Eliminate too short or too long contours 删除太长和太短的轮廓
int cmin= 100; // minimum contour length
int cmax= 1000; // maximum contour length
std::vector<std::vector<cv::Point>>::const_iterator itc= contours.begin();
while (itc!=contours.end()) {
if (itc->size() < cmin || itc->size() > cmax)
itc= contours.erase(itc);
else
++itc;
}
// draw contours on the original image
cv::Mat original= cv::imread("group.jpg");
cv::drawContours(original,contours,
-1, // draw all contours
cv::Scalar(255,255,255), // in white
2); // with a thickness of 2
cv::namedWindow("Contours on Animals");
cv::imshow("Contours on Animals",original);
cv::imwrite("Contours on Animals.jpg",original);
程序结果:
六、组件轮廓的描述
一个组件经常对应一个图形中具体的一个物体,检测这个物体,或者同其他物体进行比较,或者根据组件的轮廓特征进行提取,都是组件描述的应用。这节中我们将介绍opencv中几种常见的组件描述。
bounding box:边界矩形,
enclosing circle:封闭圆
approximate polygon:近似多边形
convex hull:凸包 即形状最小的凸多边形
opencv中还提供一些组件轮廓形状的描述和其他功能函数
如:cv::minAreaRect 最小面积矩形,可以倾斜的在组件轮廓上选择矩阵面积最小的长和宽
cv::contourArea 估计组件的面积,即像素点的多少
cv::pointPolygonTest 判断一个点在轮廓里面还是外面
cv::matchShapes 测量两个组件轮廓的相似性
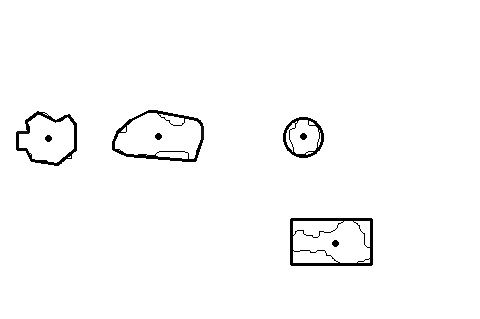
组件轮廓形状的程序实例:
image= cv::imread("binaryGroup.bmp",0);
// testing the bounding box
cv::Rect r0= cv::boundingRect(cv::Mat(contours[0]));
cv::rectangle(result,r0,cv::Scalar(0),2);
// testing the enclosing circle
float radius;
cv::Point2f center;
cv::minEnclosingCircle(cv::Mat(contours[1]),center,radius);
cv::circle(result,cv::Point(center),static_cast<int>(radius),cv::Scalar(0),2);
// cv::RotatedRect rrect= cv::fitEllipse(cv::Mat(contours[1]));
// cv::ellipse(result,rrect,cv::Scalar(0),2);
// testing the approximate polygon
std::vector<cv::Point> poly;
cv::approxPolyDP(cv::Mat(contours[2]),poly,5,true);
std::cout << "Polygon size: " << poly.size() << std::endl;
// Iterate over each segment and draw it
std::vector<cv::Point>::const_iterator itp= poly.begin();
while (itp!=(poly.end()-1)) {
cv::line(result,*itp,*(itp+1),cv::Scalar(0),2);
++itp;
}
// last point linked to first point
cv::line(result,*(poly.begin()),*(poly.end()-1),cv::Scalar(20),2);
// testing the convex hull
std::vector<cv::Point> hull;
cv::convexHull(cv::Mat(contours[3]),hull);
// Iterate over each segment and draw it
std::vector<cv::Point>::const_iterator it= hull.begin();
while (it!=(hull.end()-1)) {
cv::line(result,*it,*(it+1),cv::Scalar(0),2);
++it;
}
// last point linked to first point
cv::line(result,*(hull.begin()),*(hull.end()-1),cv::Scalar(20),2);
// testing the moments
// iterate over all contours
itc= contours.begin();
while (itc!=contours.end()) {
// compute all moments
cv::Moments mom= cv::moments(cv::Mat(*itc++));
// draw mass center
cv::circle(result,
// position of mass center converted to integer
cv::Point(mom.m10/mom.m00,mom.m01/mom.m00),
2,cv::Scalar(0),2); // draw black dot
}
cv::namedWindow("Some Shape descriptors");
cv::imshow("Some Shape descriptors",result);
cv::imwrite("Some Shape descriptors.jpg",result);
// New call to findContours but with CV_RETR_LIST flag
image= cv::imread("binaryGroup.bmp",0);
// Get the contours of the connected components
cv::findContours(image,
contours, // a vector of contours
CV_RETR_LIST, // retrieve the external and internal contours
CV_CHAIN_APPROX_NONE); // retrieve all pixels of each contours
// draw black contours on white image
result.setTo(cv::Scalar(255));
cv::drawContours(result,contours,
-1, // draw all contours
cv::Scalar(0), // in black
2); // with a thickness of 2
cv::namedWindow("All Contours");
cv::imshow("All Contours",result);
cv::imwrite("All Contours.jpg",result); 程序结果: