POJ3468 A Simple Problem with Integers 线段树|树状数组BIT(区间增减,求和)
A Simple Problem with Integers
| Time Limit: 5000MS | Memory Limit: 131072K | |
| Total Submissions: 75499 | Accepted: 23268 | |
| Case Time Limit: 2000MS | ||
Description
You have N integers, A1, A2, ... , AN. You need to deal with two kinds of operations. One type of operation is to add some given number to each number in a given interval. The other is to ask for the sum of numbers in a given interval.
Input
The first line contains two numbers N and Q. 1 ≤ N,Q ≤ 100000.
The second line contains N numbers, the initial values of A1, A2, ... , AN. -1000000000 ≤ Ai ≤ 1000000000.
Each of the next Q lines represents an operation.
"C a b c" means adding c to each of Aa, Aa+1, ... , Ab. -10000 ≤ c ≤ 10000.
"Q a b" means querying the sum of Aa, Aa+1, ... , Ab.
Output
You need to answer all Q commands in order. One answer in a line.
Sample Input
10 5 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 Q 4 4 Q 1 10 Q 2 4 C 3 6 3 Q 2 4
Sample Output
4 55 9 15
Hint
The sums may exceed the range of 32-bit integers.
方法不唯一:
线段树:区间修改,区间求和。
用add做标记,Lazy思想。
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std;
typedef long long ll;
const int maxn=100000+10;
ll sum[maxn*4],add[maxn*4];
void pushUp(int k){
sum[k]=sum[k*2]+sum[k*2+1];
}
void pushDown(int k,int l,int r){
if(add[k]){
int lc=k*2,rc=k*2+1,m=(l+r)/2;
add[lc]+=add[k];add[rc]+=add[k];
sum[lc]+=add[k]*(m-l+1);
sum[rc]+=add[k]*(r-m);
add[k]=0;
}
}
void build(int k,int l,int r){
if(l==r){
scanf("%lld",&sum[k]);
add[k]=0;
return ;
}
int m=(l+r)/2;
build(k*2,l,m);
build(k*2+1,m+1,r);
pushUp(k);
}
void update(int a,int b,ll v,int k,int l,int r){
if(a<=l && r<=b){
add[k]+=v;sum[k]+=v*(r-l+1);return ;
}
pushDown(k,l,r);
int m=(l+r)/2;
if(a<=m)
update(a,b,v,k*2,l,m);
if(b>m)
update(a,b,v,k*2+1,m+1,r);
pushUp(k);
}
ll ask(int a,int b,int k,int l,int r){
if(a<=l && r<=b)
return sum[k];
pushDown(k,l,r);
int m=(l+r)/2;
ll res=0;
if(a<=m)
res+=ask(a,b,k*2,l,m);
if(b>m)
res+=ask(a,b,k*2+1,m+1,r);
pushUp(k);
return res;
}
int main()
{
int i,j,n,q,a,b;
char op[3];
scanf("%d%d",&n,&q);
build(1,1,n);
while(q--){
scanf("%s%d%d",op,&a,&b);
if(op[0]=='C'){
ll v;
scanf("%lld",&v);
update(a,b,v,1,1,n);
}else{
printf("%lld\n",ask(a,b,1,1,n));
}
}
return 0;
}
线段树:发现数据的共性,还可以这么做:
对于每个节点,我们可以维护一下两个数据:
a.给这个节点对应的区间内的所有元素共同加上的值 (data)
b.在这个节点对应的区间中除去a中之外其他值的和 (datb)
/*
线段树(多数组维护)
*/
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <math.h>
typedef __int64 ll;
const int maxn=100000+10;
const int maxdata=(1<<18)-1;
int n,q;
int max(int x,int y){
if(x>y) return x;
return y;
}
int min(int x,int y){
if(x<y) return x;
return y;
}
ll data[maxdata],datb[maxdata];
void add(int a,int b,int v,int k,int l,int r){
if(a<=l && r<=b){
data[k]+=v;
return ;
}
if(l<=b && a<=r){
datb[k]+=(min(b,r)-max(a,l)+1)*v;
int m=(l+r)/2;
add(a,b,v,k*2,l,m);
add(a,b,v,k*2+1,m+1,r);
}
}
ll sum(int a,int b,int k,int l,int r){
if(b<l || a>r)
return 0;
if(a<=l && r<=b){
return data[k]*(r-l+1)+datb[k];
}
ll res=(min(b,r)-max(a,l)+1)*data[k];
res+=sum(a,b,k*2,l,(l+r)/2);
res+=sum(a,b,k*2+1,(l+r)/2+1,r);
return res;
}
int main()
{
int i,a,b,c;
char op[3];
while(scanf("%d%d",&n,&q)!=EOF){
for(i=1;i<=n;i++){
scanf("%d",&a);
add(i,i,a,1,1,n);
}
while(q--){
scanf("%s%d%d",op,&a,&b);
if(op[0]=='C'){
scanf("%d",&c);
add(a,b,c,1,1,n);
}
else
printf("%I64d\n",sum(a,b,1,1,n));
}
}
return 0;
}
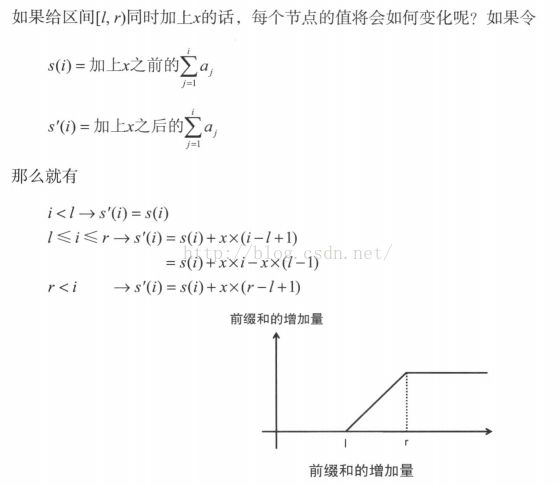
不要以为有区间修改,就想当然地想到只能用线段树的lazy思想,树状数组BIT的威力一样不小:
树状数组:
请仔细好好体会。
这还可以拓展:
如果操作得到的结果可以用i的n次多项式表示,那么就可以使用n+1个树状数组来进行维护了。
即bit0维护常数,bit1维护i的系数,bit2维护i^2的系数,.....,bitn维护i^n的系数
查询的时候只需要分别在对这些bit求和并同时乘上自己对应的i^x即可
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <math.h>
typedef __int64 ll;
const int maxn=100000+10;
ll bit0[maxn],bit1[maxn];
int n,q;
void add(ll *b,ll i,ll v){
while(i<=n){
b[i]+=v;
i+=i&(-i);
}
}
ll sum(ll *b,ll i){
ll res=0;
while(i>0){
res+=b[i];
i-=i&(-i);
}
return res;
}
int main()
{
int i,a,b,x;
char op[3];
while(scanf("%d%d",&n,&q)!=EOF){
for(i=1;i<=n;i++){
scanf("%d",&a);
add(bit0,i,a);
}
while(q--){
scanf("%s%d%d",op,&a,&b);
if(op[0]=='C'){
scanf("%d",&x);
add(bit0,a,-(x*(a-1)));
add(bit1,a,x);
add(bit1,b+1,-x);
add(bit0,b+1,x*b);
}
else {
ll res=0;
res+=sum(bit0,b)+sum(bit1,b)*b;
res-=sum(bit0,a-1)+sum(bit1,a-1)*(a-1);
printf("%I64d\n",res);
}
}
}
return 0;
}