动态规划(4)详细讲解各最短路径算法及比较
1 最短路径问题(The shortest-path problem, SPP)
最短路径问题是图论研究中的一个经典算法问题,旨在寻找图中两结点之间的最短路径。 算法具体的形式包括:
1) 确定起点的最短路径问题 - 即已知起始结点,求最短路径的问题。
2) 确定终点的最短路径问题 - 与确定起点的问题相反,该问题是已知终结点,求最短路径的问题。在无向图中该问题与确定起点的问题完全等同,在有向图中该问题等同于把所有路径方向反转的确定起点的问题。
3)确定起点终点的最短路径问题 - 即已知起点和终点,求两结点之间的最短路径。
4)全局最短路径问题 - 求图中所有的最短路径。
最短路径在导航中有重要应用,如从出发地到目的地的最短路径,从救灾处到受灾处的最短路径等。
各最短路径算法比较
2 Dijkstra(迪杰斯特拉)算法
2.1 定义
Dijkstra(迪杰斯特拉)算法是典型的单源最短路径算法,用于计算一个节点到其他所有节点的最短路径。主要特点是以起始点为中心向外层层扩展,直到扩展到终点为止。Dijkstra算法是很有代表性的最短路径算法,在很多专业课程中都作为基本内容有详细的介绍,如数据结构,图论,运筹学等等。举例来说,如果图中的顶点表示城市,而边上的权重表示著城市间开车行经的距离,该算法可以用来找到两个城市之间的最短路径。
2.2 算法描述
这个算法是通过为每个顶点 v 保留目前为止所找到的从s到v的最短路径来工作的。初始时,原点 s 的路径长度值被赋为 0 (d[s] = 0),若存在能直接到达的边(s,m),则把d[m]设为w(s,m),同时把所有其他(s不能直接到达的)顶点的路径长度设为无穷大,即表示我们不知道任何通向这些顶点的路径(对于 V 中所有顶点 v 除 s 和上述 m 外 d[v] = ∞)。当算法退出时,d[v] 中存储的便是从 s 到 v 的最短路径,或者如果路径不存在的话是无穷大。 Dijkstra 算法的基础操作是边的拓展:如果存在一条从 u 到 v 的边,那么从 s 到 v 的最短路径可以通过将边(u, v)添加到尾部来拓展一条从 s 到 u 的路径。这条路径的长度是 d[u] + w(u, v)。如果这个值比目前已知的 d[v] 的值要小,我们可以用新值来替代当前 d[v] 中的值。拓展边的操作一直运行到所有的 d[v] 都代表从 s 到 v 最短路径的花费。这个算法经过组织因而当d[u] 达到它最终的值的时候每条边(u, v)都只被拓展一次。
算法维护两个顶点集 S 和 Q。集合 S 保留了我们已知的所有 d[v] 的值已经是最短路径的值顶点,而集合 Q 则保留其他所有顶点。集合S初始状态为空,而后每一步都有一个顶点从 Q 移动到 S。这个被选择的顶点是 Q 中拥有最小的 d[u] 值的顶点。当一个顶点 u 从 Q 中转移到了 S 中,算法对每条外接边 (u, v) 进行拓展。
2.2 算法过程图解
以下图为例,具体说明算法的执行过程。
我们将图中的节点分为3类:
1)当前访问的点Current vertex
2) 与当前访问节点相通,但是未访问过的点Fringe vertex
3) 已经访问过的点Visited vertex
为便于图中识别,用下述颜色区分这3种节点:
同时,为了保存当前得到的从开始节点到各个节点的最短路径,我们需要用一个小本本来记录这些值,如下图中的表格(第一行表示各个节点,其下的值代表当前从开始节点到目标节点的最短路径,值后边括号如110(via B)表示到达该节点前要通过的前一个节点是B)。
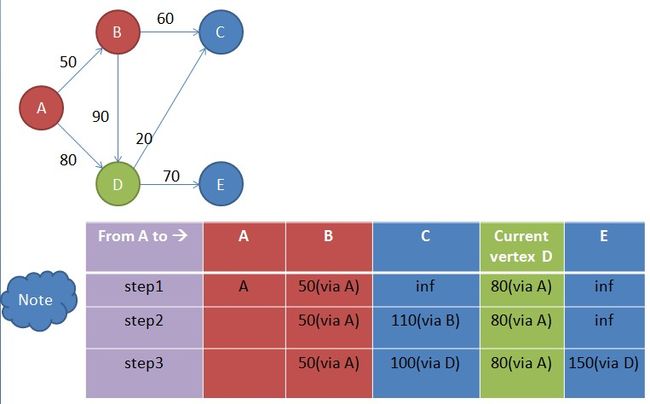
step 1初始化
从节点A开始,A的Fringe vertex 是B和D(图中inf代表infinite,表示从当前节点到目标节点的路径值还未知,我们设为无穷大)
step 2
get mini in note
从note中获取到达未访问节点的最短路径为当前节点,所以当前节点为B
update distance in note
更新note中从开始点到各个节点的路径,使从开始节点到各个节点的路径最短。具体步骤如下:
startToFringe=startToCurrent+ currentToFringe
其中startToCurrent为开始节点到当前节点的路径(该值从note中获得),currentToFringe为当前节点到Frignge节点的路径(该值从原始图中获得)。
当前节点为B,Fringe vertex 为C和D,以Fringe C为例
startToC=startToB+ currentToC=50+60=110
2) 获取Fringe vertex 在note中的路径( fringeInNoteDist)
以Fringe C为例,CInNoteDist=inf
3)比较startToFringe和 fringeInNoteDist,如果startToFringe< fringeInNoteDis,则更新note中的Fringe vertex的值为startToFringe,并修改其前一个经由的节点为当前点。因为startToC<CInNoteDist,所以note中到达C的值为110(B)
同样,对Fringe D,做同样的计算:
startToD=startToB+currentToD=50+90=140
DInNoteDist=80
startToD>DInNoteDist,所以D在note中的值不变
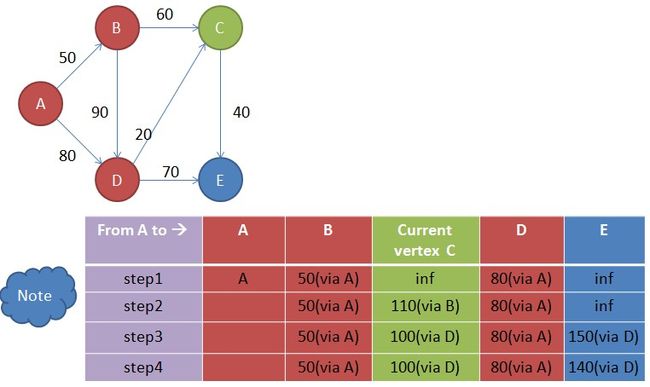
step 3
get mini in note
从note中获取到达未访问节点的最短路径为当前节点,所以当前节点为D
update distance in note
更新note中从开始点到各个点的路径,使从开始点到各个点的路径最短。具体步骤如下:
1)计算从开始点到Fringe Vertex的路径(startToFringe),计算公式如下
startToFringe=startToCurrent+ currentToFringe
其中startToCurrent为开始点到当前点的路径,currentToFringe为当前点到Frignge点的路径。
当前点为D,Fringe vertex 为C和E,以Fringe C为例
startToC=startToD+ currentToC=80+20=100
2) 获取Fringe vertex 在note中的路径( fringeInNoteDist)
以Fringe C为例,CInNoteDist=110
3)比较startToFringe和 fringeInNoteDist,如果startToFringe< fringeInNoteDis,则更新note中的Fringe vertex的值为startToFringe,并修改其前一个经由的节点为当前点。
因为startToC<CInNoteDist,所以note中到达C的值为100(D)
同样,对Fringe E,做同样的计算:
startToE=startToD+currentToE=80+70=150
DInNoteDist=inf
startToD<DInNoteDist,所以note中到达E的值为150(D)
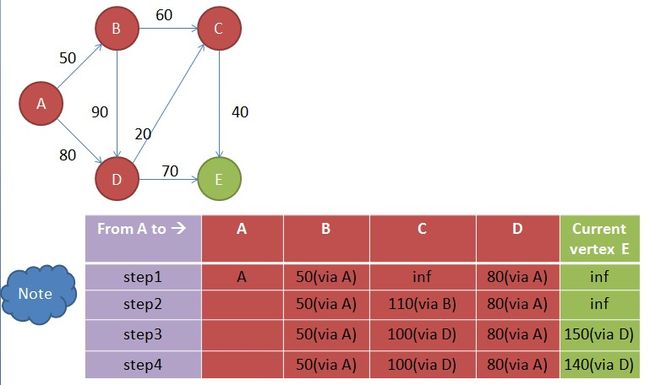
step4
get mini in note
从note中获取到达未访问节点的最短路径为当前节点,所以当前节点为C
update distance in note
更新note中从开始点到各个点的路径,使从开始点到各个点的路径最短。具体步骤如下:
1)计算从开始点到Fringe Vertex的路径(startToFringe),计算公式如下
startToFringe=startToCurrent+ currentToFringe
其中startToCurrent为开始点到当前点的路径,currentToFringe为当前点到Frignge点的路径。
当前点为C,Fringe vertex 为E,以Fringe E为例
startToE=startToC+ currentToE=100+40=140
2) 获取Fringe vertex 在note中的路径( fringeInNoteDist)
以Fringe E为例,EInNoteDist=150
3)比较startToFringe和 fringeInNoteDist,如果startToFringe< fringeInNoteDis,则更新note中的Fringe vertex的值为startToFringe,并修改其前一个经由的节点为当前点。
因为startToE<EInNoteDist,所以note中到达E的值为140(C)
step5
从note中获取到达未访问节点的最短路径为当前节点,所以当前节点为E,但是图中没有未访问过的点,及其他点都已经访问过,如下图
因此,E为最后一个点,因此将E标识为已访问过的点,至此算法结束
最后,note中得到的值是从开始点到各个点的最短路径。
2.3 算法实现
2.3.1 算法主框架设计
我们看到上述算法过程,主要是以下3个步骤:
1)initial初始化
选择开始节点,初始化小本本note中的值。
2)get mini in note 获取下一个当前节点
从note中获取到达未访问节点的最短路径的节点为当前节点,有点拗口,这样说吧,即获取当前note中未访问节点中有最小值的那个。
3)update distance in note
更新note中未访问节点的值,使这个值最小(要记住,这个值代表从开始节点到该节点的当前最短路径。)
具体步骤如下:
1)计算从开始节点到Fringe Vertex的路径(startToFringe),计算公式如下
startToFringe=startToCurrent+ currentToFringe
其中startToCurrent为开始节点到当前节点的路径(该值从note中获得),currentToFringe为当前节点到Frignge节点的路径(该值从原始图中获得)。
2) 获取Fringe vertex 在note中的路径( fringeInNoteDist)
3)比较startToFringe和 fringeInNoteDist,如果startToFringe< fringeInNoteDis,则更新note中的Fringe vertex的值为startToFringe,并修改其前一个经由的节点为当前点。
因为startToC<CInNoteDist,所以note中到达C的值为110(B)
算法什么时候结束呢?重复上述步骤2和3直到所有的节点都访问过结束。
要实现该算法,结合上述算法过程,需要解决如下问题:
1)上图中的3类节点在代码中如何表示
Fringe vertex可以从图的邻接矩阵或邻接链表中获得, Current vertex 从小本本note中获得, un-visited vertex可以在节点中加入属性(如isInTree)来标识。
2)小本本note如何表示?
小本本可以用数组或优先队列来实现,小本本中的值可以用以下对象进行抽象:
class DistPar // distance and parent
{ // items stored in sPath array
public int distance; // distance from start to this vertex
public int parentVert; // current parent of this vertex
// -------------------------------------------------------------
public DistPar(int pv, int d) // constructor
{
distance = d;
parentVert = pv;
}
// -------------------------------------------------------------
} // end class DistPar
根据上述过程,算法主框架实现如下:
// -------------------------------------------------------------
public void path() // find all shortest paths
{
//1 initial
int currentVerIndex = 0; // start at vertex 0
vertexList[currentVerIndex].isInTree = true; //isInTree records whether the vertex's visited
nTree = 1; // record how many vertices has been visited
// transfer row of distances from adjMat to sPath
for(int j=0; j<nVerts; j++)
{
int tempDist = adjMat[currentVerIndex][j];
sPath[j] = new DistPar(currentVerIndex, tempDist); //sPath is the note, here represent as an array
}
while(nTree < nVerts) //base case: until all vertices are in the tree
{
//2 get minimum from sPath
currentVerIndex = getMin();
//3 update path
updatePath(currentVerIndex);
} // end while(nTree<nVerts)
displayPaths(); // display sPath[] contents
nTree = 0; // clear tree
for(int j=0; j<nVerts; j++)
vertexList[j].isInTree = false;
} // end path()
2.3.2 具体实现
上述方法 //2 get minimum from sPath
currentVerIndex = getMin();
//3 update path
updatePath(currentVerIndex);
具体实现如下:
// -------------------------------------------------------------
public int getMin() // get entry from sPath
{ // with minimum distance
int minDist = INFINITY; // assume minimum
int indexMin = 0;
for(int j=1; j<nVerts; j++) // for each vertex,
{ // if it's in tree and
if( !vertexList[j].isInTree && // smaller than old one
sPath[j].distance < minDist )
{
minDist = sPath[j].distance;
indexMin = j; // update minimum
}
} // end for
return indexMin; // return index of minimum
} // end getMin()
// -------------------------------------------------------------
public void updatePath()
{
// adjust values in shortest-path array sPath
int column = 1; // skip starting vertex
while(column < nVerts) // go across columns
{
// if this column's vertex already in tree, skip it
if( vertexList[column].isInTree )
{
column++;
continue;
}
// calculate distance for one sPath entry
// get edge from currentVert to column
int currentToFringe = adjMat[currentVert][column];
// add distance from start
int startToFringe = startToCurrent + currentToFringe;
// get distance of current sPath entry
int sPathDist = sPath[column].distance;
// compare distance from start with sPath entry
if(startToFringe < sPathDist) // if shorter,
{ // update sPath
sPath[column].parentVert = currentVert;
sPath[column].distance = startToFringe;
}
column++;
} // end while(column < nVerts)
} // end adjust_sPath()
2.3.3 全部算法代码
// path.java
// demonstrates shortest path with weighted, directed graphs
// to run this program: C>java PathApp
////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
class DistPar // distance and parent
{ // items stored in sPath array
public int distance; // distance from start to this vertex
public int parentVert; // current parent of this vertex
// -------------------------------------------------------------
public DistPar(int pv, int d) // constructor
{
distance = d;
parentVert = pv;
}
// -------------------------------------------------------------
} // end class DistPar
///////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
class Vertex
{
public char label; // label (e.g. 'A')
public boolean isInTree;
// -------------------------------------------------------------
public Vertex(char lab) // constructor
{
label = lab;
isInTree = false;
}
// -------------------------------------------------------------
} // end class Vertex
////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
class Graph
{
private final int MAX_VERTS = 20;
private final int INFINITY = 1000000;
private Vertex vertexList[]; // list of vertices
private int adjMat[][]; // adjacency matrix
private int nVerts; // current number of vertices
private int nTree; // number of verts in tree
private DistPar sPath[]; // array for shortest-path data
private int currentVert; // current vertex
private int startToCurrent; // distance to currentVert
// -------------------------------------------------------------
public Graph() // constructor
{
vertexList = new Vertex[MAX_VERTS];
// adjacency matrix
adjMat = new int[MAX_VERTS][MAX_VERTS];
nVerts = 0;
nTree = 0;
for(int j=0; j<MAX_VERTS; j++) // set adjacency
for(int k=0; k<MAX_VERTS; k++) // matrix
adjMat[j][k] = INFINITY; // to infinity
sPath = new DistPar[MAX_VERTS]; // shortest paths
} // end constructor
// -------------------------------------------------------------
public void addVertex(char lab)
{
vertexList[nVerts++] = new Vertex(lab);
}
// -------------------------------------------------------------
public void addEdge(int start, int end, int weight)
{
adjMat[start][end] = weight; // (directed)
}
// -------------------------------------------------------------
// find all shortest paths
public void path(){
//step1 initial
int startTree = 0; // start at vertex 0
vertexList[startTree].isInTree = true; //isInTree records whether the vertex's visited
nTree = 1; //record how many vertices has been visited
// transfer row of distances from adjMat to sPath
for(int j=0; j<nVerts; j++){
int tempDist = adjMat[startTree][j];
sPath[j] = new DistPar(startTree, tempDist); //sPath is the note, here represent as an array
}
while(nTree < nVerts) { //base case: until all vertices are in the tree
//step2 get minimum from sPath
int indexMin = getMin();
int minDist = sPath[indexMin].distance;
//special case: if all infinite or in tree,sPath is complete
if(minDist == INFINITY) {
System.out.println("There are unreachable vertices");
break;
}
else{ // reset currentVert
currentVert = indexMin; // to closest vert
// minimum distance from startTree is to currentVert, and is startToCurrent
startToCurrent = sPath[indexMin].distance;
}
// put current vertex in tree
vertexList[currentVert].isInTree = true;
nTree++;
//step3 update path
updatePath(); // update sPath[] array
} // end while(nTree<nVerts)
//step4 printout all shortest path
displayPaths(); // display sPath[] contents
nTree = 0; // clear tree
for(int j=0; j<nVerts; j++)
vertexList[j].isInTree = false;
} // end path()
// -------------------------------------------------------------
public int getMin() // get entry from sPath
{ // with minimum distance
int minDist = INFINITY; // assume minimum
int indexMin = 0;
for(int j=1; j<nVerts; j++) // for each vertex,
{ // if it's in tree and
if( !vertexList[j].isInTree && // smaller than old one
sPath[j].distance < minDist )
{
minDist = sPath[j].distance;
indexMin = j; // update minimum
}
} // end for
return indexMin; // return index of minimum
} // end getMin()
// -------------------------------------------------------------
public void updatePath()
{
// adjust values in shortest-path array sPath
int column = 1; // skip starting vertex
while(column < nVerts) // go across columns
{
// if this column's vertex already in tree, skip it
if( vertexList[column].isInTree )
{
column++;
continue;
}
// calculate distance for one sPath entry
// get edge from currentVert to column
int currentToFringe = adjMat[currentVert][column];
// add distance from start
int startToFringe = startToCurrent + currentToFringe;
// get distance of current sPath entry
int sPathDist = sPath[column].distance;
// compare distance from start with sPath entry
if(startToFringe < sPathDist) // if shorter,
{ // update sPath
sPath[column].parentVert = currentVert;
sPath[column].distance = startToFringe;
}
column++;
} // end while(column < nVerts)
} // end adjust_sPath()
// -------------------------------------------------------------
public void displayPaths()
{
for(int j=0; j<nVerts; j++) // display contents of sPath[]
{
System.out.print(vertexList[j].label + "="); // B=
if(sPath[j].distance == INFINITY)
System.out.print("inf"); // inf
else
System.out.print(sPath[j].distance); // 50
char parent = vertexList[ sPath[j].parentVert ].label;
System.out.print("(" + parent + ") "); // (A)
}
System.out.println("");
}
// -------------------------------------------------------------
} // end class Graph
////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
class PathApp
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
Graph theGraph = new Graph();
theGraph.addVertex('A'); // 0 (start)
theGraph.addVertex('B'); // 1
theGraph.addVertex('C'); // 2
theGraph.addVertex('D'); // 3
theGraph.addVertex('E'); // 4
theGraph.addEdge(0, 1, 50); // AB 50
theGraph.addEdge(0, 3, 80); // AD 80
theGraph.addEdge(1, 2, 60); // BC 60
theGraph.addEdge(1, 3, 90); // BD 90
theGraph.addEdge(2, 4, 40); // CE 40
theGraph.addEdge(3, 2, 20); // DC 20
theGraph.addEdge(3, 4, 70); // DE 70
theGraph.addEdge(4, 1, 50); // EB 50
System.out.println("Shortest paths");
theGraph.path(); // shortest paths
System.out.println();
} // end main()
} // end class PathApp
////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
注:代码来自于书《Data Structure & Algorithm in JAVA》
Floyd-Warshall算法(动态规划)
是解决任意两点间的最短路径的一种算法,时间复杂度为O(N^3),空间复杂度为O(N^2)。可以正确处理有向图或负权的最短路径问题。
设 dist(i,j) 为从节点i到节点j的最短距离
若最短路径经过点k,则dist(i,j)=dist(i,k) + dist(k,j),将该路径与先前的dist(i,j)比较获取最小值,即
dist(i,j)=min( dist(i,k) + dist(k,j) ,dist(i,j) )
Floyd-Warshall算法的描述如下:
//根据图的邻接矩阵,或邻接链表,初始化dist(i,j)
//其中dist(i,j)表示由点i到点j的代价,当dist(i,j)为 inf 表示两点之间没有任何连接。
For i←1 to n do
For j←1 to n do
dist(i,j) = weight(i,j)
//计算最短路径
for k ← 1 to n do
for i ← 1 to n do
for j ← 1 to n do
if (dist(i,k) + dist(k,j) < dist(i,j)) then // 是否是更短的路径?
dist(i,j) = dist(i,k) + dist(k,j)
Bellman-Ford(动态规划)
求单源最短路,可以判断有无负权回路(若有,则不存在最短路),时效性较好,时间复杂度O(VE)。
step1:初始化dist(i),除了初始点的值为0,其余都为infinit(表示无穷大,不可到达),pred表示经过的前一个顶点
step2:执行n-1(n等于图中点的个数)次松弛计算:dist(j)=min( dist(i)+weight(i,j),dist(j) )
step3:再重复操作一次,如国dist(j) > distdist(i)+weight(i,j)表示途中存在从源点可达的权为负的回路。
因为,如果存在从源点可达的权为负的回路,则应为无法收敛而导致不能求出最短路径。
因为负权环可以无限制的降低总花费,所以如果发现第n次操作仍可降低花销,就一定存在负权环。
int[] dist=new int[n];
int[] pre=new int[n];
public void Bellman_Ford(){
//初始化
for(int i=1;i<n-1;i++){
dist[i]=infinit; //TODO
}//end for
dist[s]=0 //起始点的值
for (int i=1;i<=n-1;i++){
for(int j=1;j<=edgenum; j++){
if(dist(i)+weight(i,j) <dist(j) ){
dist(j)=dist(i)+weight(i,j);
pred(j)=i;
}//end if
}//end for
}//end for
//
for(int j=1;j<=edgenum;j++){
if(dist(i)+weight(i,j)<dist()j )
return "有负权回路,不存在最短路径";
}//end for
}//end Bellman_Ford()
A*算法
A*搜寻算法,俗称A星算法,作为启发式搜索算法中的一种,这是一种在图形平面上,有多个节点的路径,求出最低通过成本的算法。常用于游戏中的NPC的移动计算,或线上游戏的BOT的移动计算上。该算法像Dijkstra算法一样,可以找到一条最短路径;也像BFS一样,进行启发式的搜索。
详细见http://blog.csdn.net/v_JULY_v/article/details/6093380
次最短路径
将最短路径中边在图中去掉,然后再求一次最小生成树其他
【google笔试题】,一个环形公路,给出相邻两点的距离(一个数组),让你求任意两点的最短距离,要求空间复杂度不超过O(N)