Socket编程实践 -- Select I/O复用
原文地址:http://blog.csdn.net/zjf280441589/article/details/41778347
Select函数
Man-Page
- /* According to POSIX.1-2001 */
- #include <sys/select.h>
- /* According to earlier standards */
- #include <sys/time.h>
- #include <sys/types.h>
- #include <unistd.h>
- int select(int nfds, fd_set *readfds, fd_set *writefds,
- fd_set *exceptfds, struct timeval *timeout);
Select使用说明:
• 监视readfds来查看是否read的时候会被堵塞,注意,即便到了end-of-file,fd也是可读的。
• 监视writefds看写的时候会不会被堵塞。
• 监视exceptfd是否出现了异常。主要用来读取OOB数据,异常并不是指出错。
• 注意当一个套接口出错时,它会变得既可读又可写。
• 如果有了状态改变,会将其他fd清零,只有那些发生改变了的fd保持置位,以用来指示set中的哪一个改变了状态。
• 参数n是所有set里所有fd里,具有最大值的那个fd的值加1
Select实现说明:
调用select时通过参数告诉内核用户感兴趣的IO描述符
关心的IO状态: 输入,输出或错误
调用者等待时间
返回之后内核告诉调用者多个描述符准备好了
哪些描述符发生了变化
调用返回后对准备好的描述符调用读写操作
不关心的描述符集合传NULL
参数说明:
1.nfds is the highest-numbered file descriptor in any of the three sets,plus 1.
2.fd_set[四个宏用来对fd_set进行操作]
- FD_CLR(int fd, fd_set *set);
- FD_ISSET(int fd, fd_set *set);
- FD_SET(int fd, fd_set *set);
- FD_ZERO(fd_set *set);
3.timeout[从调用开始到select返回前,会经历的最大等待时间]
Timeval结构:
- struct timeval
- {
- long tv_sec; /* seconds */
- long tv_usec; /* microseconds */
- };
说明:
一些调用使用3个空的set, n为0, 一个非空的timeout来达到较为精确的sleep.
Linux中, select函数改变了timeout值,用来指示还剩下的时间,但很多实现并不改timeout;因此为了较好的可移植性,timeout在循环中需要被重新赋初值。
Timeout取值:
timeout== NULL
无限等待,被信号打断时返回-1, errno 设置成 EINTR
timeout->tv_sec == 0 && tvptr->tv_usec == 0
不等待立即返回
timeout->tv_sec != 0 || tvptr->tv_usec != 0
等待特定时间长度, 超时返回0
返回值:
On success, select() and pselect() return the number of file descriptors contained in the three returned descriptor sets (that is, the total number of bits that are set in readfds, writefds, exceptfds) which may be zero if the timeout expires before anything interesting happens. On error, -1 is returned, and errno is set appropriately; the sets and timeout become undefined, so do not rely on their contents after an error.
如果成功,返回所有sets中描述符的个数;如果超时,返回0;如果出错,返回-1.
示例:(from man-page)
- #include <stdio.h>
- #include <stdlib.h>
- #include <sys/time.h>
- #include <sys/types.h>
- #include <unistd.h>
- int main()
- {
- fd_set rfds;
- struct timeval tv;
- int retval;
- /* Watch stdin (fd 0) to see when it has input. */
- FD_ZERO(&rfds);
- FD_SET(0, &rfds);
- /* Wait up to five seconds. */
- tv.tv_sec = 5;
- tv.tv_usec = 0;
- retval = select(1, &rfds, NULL, NULL, &tv);
- /* Don't rely on the value of tv now! */
- if (retval == -1)
- perror("select()");
- else if (retval)
- {
- if (FD_ISSET(0,&rfds))
- {
- char buf[BUFSIZ];
- cin >> buf;
- cout << "fd 0 is OK! and you input is: " << buf << endl;
- }
- }
- else
- {
- printf("No data within five seconds.\n");
- }
- exit(EXIT_SUCCESS);
- }

Select实现原理
fd_set是一个位向量, 每位表示一个描述符

- int FD_ISSET(int fd, fd_set *fdset); //测试某个描述符是否在集合内
- void FD_CLR(int fd, fd_set *fdset); //从集合内把一个描述符移除
- void FD_SET(int fd, fd_set *fdset); //把一个描述符加入集合
- void FD_ZERO(fd_set *fdset); //清空描述符集合
执行下列代码后:
- fd_set readset;
- fd_set writeset;
- FD_ZERO(&readset);
- FD_ZERO(&writeset);
- FD_SET(0,&readset);
- FD_SET(3,&readset);
- FD_SET(1,&writeset);
- FD_SET(2,&writeset);
- select(4,&readset,&writeset,NULL,NULL);
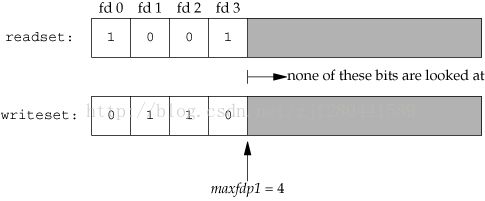
Fd_set说明:
• 可以把同一个描述符同时放取读和写集合
• 当读和写者准备好时, 返回值的计数分别加1次
• 普通文件的三种状态总是返回准备好的状态
• 是否阻塞式IO不会影响select的结果
• 如果一个描述符到了文件结尾,select返回的状态是准备好
• 对一个准备好的描述符, 读出长度是0表示到达结尾
实践:用select优化客户端代码
- #include "commen.h"
- int main()
- {
- int sockfd = mkATCPClient(9001,"127.0.0.1");
- char sendBuf[BUFSIZ];
- char recvBuf[BUFSIZ];
- while (true)
- {
- int fdCount = sockfd > STDIN_FILENO ? sockfd+1 : STDIN_FILENO+1;
- fd_set rdset;
- FD_ZERO(&rdset);
- FD_SET(sockfd,&rdset);
- FD_SET(STDIN_FILENO,&rdset);
- int nReady = select(fdCount,&rdset,NULL,NULL,NULL);
- if (nReady == -1)
- {
- err_exit("select error");
- }
- //server端有数据可读
- if (FD_ISSET(sockfd,&rdset))
- {
- //从socket中读取数据
- int readCount = read(sockfd,recvBuf,sizeof(recvBuf));
- if ( readCount == -1)
- {
- err_exit("read socket error");
- }
- else if (readCount == 0) //如果对端结束链接
- {
- peerClosePrint();
- }
- fputs(recvBuf,stdout);
- memset(recvBuf,0,sizeof(recvBuf));
- }
- //标准输入上有数据可读:从键盘读取数据 -> 发送至socket
- if (FD_ISSET(STDIN_FILENO,&rdset));
- {
- if(fgets(sendBuf,sizeof(sendBuf),stdin) != NULL)
- {
- if (write(sockfd,sendBuf,strlen(sendBuf)) == -1) //发送到socket上
- {
- err_exit("write error");
- }
- memset(sendBuf,0,sizeof(sendBuf));
- }
- }
- }
- close(sockfd);
- return 0;
- }
- /**说明:
- Server端代码同前(echo server)
- */
附-commen.h源代码
- #ifndef COMMEN_H_INCLUDED
- #define COMMEN_H_INCLUDED
- #include <unistd.h>
- #include <signal.h>
- #include <errno.h>
- #include <fcntl.h>
- #include <sys/types.h>
- #include <sys/wait.h>
- #include <sys/stat.h>
- #include <sys/ipc.h>
- #include <sys/shm.h>
- #include <sys/msg.h>
- #include <sys/sem.h>
- #include <sys/socket.h>
- #include <sys/select.h>
- #include <arpa/inet.h>
- #include <sys/socket.h>
- #include <netinet/in.h>
- #include <arpa/inet.h>
- #include <string.h>
- #include <stdio.h>
- #include <stdlib.h>
- #include <iostream>
- using namespace std;
- void err_exit(std::string str)
- {
- perror(str.c_str());
- exit(EXIT_FAILURE);
- }
- void peerClosePrint(std::string str = "peer connect closed")
- {
- cout << str << endl;
- _exit(0);
- }
- //return a socket that have start listened.
- int mkATCPServer(int serverPort, int backlog = SOMAXCONN)
- {
- int sockfd = socket(AF_INET,SOCK_STREAM,0);
- if (sockfd == -1)
- {
- err_exit("socket error");
- }
- //add address reused
- int on = 1;
- if (setsockopt(sockfd,SOL_SOCKET,SO_REUSEADDR,&on,sizeof(on)) == -1)
- {
- err_exit("setsockopt SO_REUSEADDR error");
- }
- //band a local address and port
- struct sockaddr_in serverAddr;
- serverAddr.sin_family = AF_INET;
- serverAddr.sin_port = htons(serverPort);
- serverAddr.sin_addr.s_addr = INADDR_ANY; //band an any IP address
- if (bind(sockfd,(struct sockaddr *)&serverAddr,sizeof(serverAddr)) == -1)
- {
- err_exit("bind error");
- }
- //start to listen.
- if (listen(sockfd,backlog) == -1)
- {
- err_exit("listen error");
- }
- return sockfd;
- }
- //return a socket that have connected to server.
- int mkATCPClient(int serverPort, string serverIPAddr)
- {
- //first. create a socket
- int sockfd = socket(AF_INET,SOCK_STREAM,0);
- if (sockfd == -1)
- {
- err_exit("socket error");
- }
- //second. connect to a server
- struct sockaddr_in serverAddr;
- serverAddr.sin_family = AF_INET;
- serverAddr.sin_port = htons(serverPort);
- serverAddr.sin_addr.s_addr = inet_addr(serverIPAddr.c_str());
- if (connect(sockfd,(struct sockaddr *)&serverAddr,sizeof(serverAddr)) == -1)
- {
- err_exit("connect error");
- }
- return sockfd;
- }
- void onCatchSIGCHLD(int signalNumber)
- {
- int ret = 0;
- while ((ret = waitpid(-1,NULL,WNOHANG) != -1))
- ;
- }
- ssize_t readn(int fd,void *buf,size_t count)
- {
- size_t nLeft = count;
- ssize_t nRead = 0;
- char *ptr = static_cast<char *>(buf);
- while (nLeft > 0)
- {
- if ((nRead = read(fd,ptr,nLeft)) < 0)
- {
- //一点东西都没读
- if (nLeft == count)
- {
- return -1; //error
- }
- else
- {
- break; //error, return amount read so far
- }
- }
- else if (nRead == 0)
- {
- break; //EOF
- }
- nLeft -= nRead;
- ptr += nRead;
- }
- return count - nLeft;
- }
- ssize_t writen(int fd, const void *buf, size_t count)
- {
- size_t nLeft = count;
- ssize_t nWritten;
- const char *ptr = static_cast<const char *>(buf);
- while (nLeft > 0)
- {
- if ((nWritten = write(fd,ptr,nLeft)) < 0)
- {
- //一点东西都没写
- if (nLeft == count)
- {
- return -1; //error
- }
- else
- {
- break; //error, return amount write so far
- }
- }
- else if (nWritten == 0)
- {
- break; //EOF
- }
- nLeft -= nWritten;
- ptr += nWritten;
- }
- return count - nWritten;
- }
- //只是查看一下网络中的数据,并不是将之真正取走:MSG_PEEK
- ssize_t recv_peek(int fd, void *buf, size_t count)
- {
- int nRead = 0;
- //如果读取网络数据出错,则继续读取
- while ((nRead = recv(fd,buf,count,MSG_PEEK)) == -1);
- return nRead;
- }
- ssize_t readline(int fd, void *buf, size_t maxline)
- {
- char *pBuf = (char *)buf;
- int nLeft = maxline;
- while (true)
- {
- //查看缓冲区中的数据,并不真正取走
- int nTestRead = recv_peek(fd,pBuf,nLeft);
- //检测这次读来的数据中是否包含'\n';
- //如果有,则将之全部读取出来
- for (int i = 0; i < nTestRead; ++i)
- {
- if (pBuf[i] == '\n')
- {
- //真正的从缓冲区中将数据取走
- if (readn(fd,pBuf,i+1) != i+1)
- {
- err_exit("readn error");
- }
- else
- {
- return i + 1;
- }
- }
- }
- //如果这次读的缓冲区中没有'\n'
- //如果读超了:读道德数目大于一行最大数,则做异常处理
- if (nTestRead > nLeft)
- {
- exit(EXIT_FAILURE);
- }
- nLeft -= nTestRead; //若缓冲区没有'\n',则将剩余的数据读走
- if (readn(fd,pBuf,nTestRead) != nTestRead)
- {
- exit(EXIT_FAILURE);
- }
- pBuf += nTestRead;
- }
- return -1;
- }
- #endif // COMMEN_H_INCLUDED