flume学习(五):Flume Channel Selectors使用
package com.besttone.flume;
import java.util.Date;
import org.apache.commons.logging.Log;
import org.apache.commons.logging.LogFactory;
public class WriteLog2 {
protected static final Log logger = LogFactory.getLog(WriteLog2.class);
/**
* @param args
* @throws InterruptedException
*/
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
while (true) {
logger.info(new Date().getTime());
logger.info("{\"requestTime\":"
+ System.currentTimeMillis()
+ ",\"requestParams\":{\"timestamp\":1405499314238,\"phone\":\"02038824941\",\"cardName\":\"测试商家名称\",\"provinceCode\":\"440000\",\"cityCode\":\"440106\"},\"requestUrl\":\"/image-api/reporter/reporter12/init.do\"}");
Thread.sleep(2000);
}
}
}
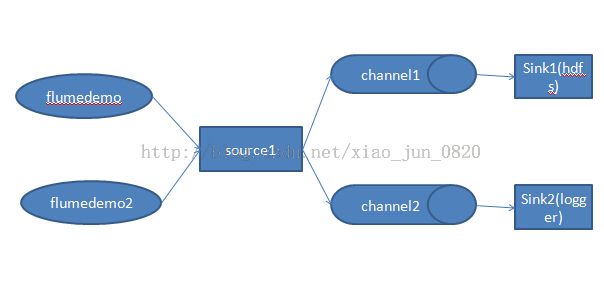
现在有这么一个需求描述:要求flumedemo的项目的log4j日志输出到hdfs,而flumedemo2项目的log4j日志输出到agent的log日志中。
我们还是采用log4jappender来配置log4j输出给flume的souce,现在的需求明显是有两个sink了,一个sink为hdfs,一个sink为logger。于是现在的拓扑结构应该是这样的:
需要实现这么一个拓扑接口,就需要使用到channel selectors,让不同的项目日志通过不同的channel到不同的sink中去。
官方文档上channel selectors 有两种类型:
Replicating Channel Selector (default)
Multiplexing Channel Selector
这两种selector的区别是:Replicating 会将source过来的events发往所有channel,而Multiplexing 可以选择该发往哪些channel。对于上面的例子来说,如果采用Replicating ,那么demo和demo2的日志会同时发往channel1和channel2,这显然是和需求不符的,需求只是让demo的日志发往channel1,而demo2的日志发往channel2。
综上所述,我们选择Multiplexing Channel Selector。这里我们有遇到一个棘手的问题,Multiplexing 需要判断header里指定key的值来决定分发到某个具体的channel,我们现在demo和demo2同时运行在同一个服务器上,如果在不同的服务器上运行,我们可以在 source1上加上一个 host 拦截器(上一篇有介绍过),这样可以通过header中的host来判断event该分发给哪个channel,而这里是在同一个服务器上,由host是区分不出来日志的来源的,我们必须想办法在header中添加一个key来区分日志的来源。
设想一下,如果header中有一个key:flume.client.log4j.logger.source,我们通过设置这个key的值,demo设为app1,demo2设为app2,这样我们就能通过设置:
tier1.sources.source1.channels=channel1 channel2
tier1.sources.source1.selector.type=multiplexing
tier1.sources.source1.selector.header=flume.client.log4j.logger.source
tier1.sources.source1.selector.mapping.app1=channel1
tier1.sources.source1.selector.mapping.app2=channel2
来将不同项目的的日志输出到不同的channel了。
我们按照这个思路继续下去,遇到了困难,log4jappender没有这样的参数来让你设置。怎么办?翻看了一下log4jappender的源码,发现可以很容易的实现扩展参数,于是我复制了一份log4jappender代码,新加了一个类叫Log4jExtAppender.java,里面扩展了一个参数叫:source,代码如下:
package com.besttone.flume;
import java.io.ByteArrayOutputStream;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.nio.charset.Charset;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Map;
import java.util.Properties;
import org.apache.avro.Schema;
import org.apache.avro.generic.GenericRecord;
import org.apache.avro.io.BinaryEncoder;
import org.apache.avro.io.DatumWriter;
import org.apache.avro.io.EncoderFactory;
import org.apache.avro.reflect.ReflectData;
import org.apache.avro.reflect.ReflectDatumWriter;
import org.apache.avro.specific.SpecificRecord;
import org.apache.flume.Event;
import org.apache.flume.EventDeliveryException;
import org.apache.flume.FlumeException;
import org.apache.flume.api.RpcClient;
import org.apache.flume.api.RpcClientConfigurationConstants;
import org.apache.flume.api.RpcClientFactory;
import org.apache.flume.clients.log4jappender.Log4jAvroHeaders;
import org.apache.flume.event.EventBuilder;
import org.apache.log4j.AppenderSkeleton;
import org.apache.log4j.helpers.LogLog;
import org.apache.log4j.spi.LoggingEvent;
/**
*
* Appends Log4j Events to an external Flume client which is decribed by the
* Log4j configuration file. The appender takes two required parameters:
* <p>
* <strong>Hostname</strong> : This is the hostname of the first hop at which
* Flume (through an AvroSource) is listening for events.
* </p>
* <p>
* <strong>Port</strong> : This the port on the above host where the Flume
* Source is listening for events.
* </p>
* A sample log4j properties file which appends to a source would look like:
*
* <pre>
* <p>
* log4j.appender.out2 = org.apache.flume.clients.log4jappender.Log4jAppender
* log4j.appender.out2.Port = 25430
* log4j.appender.out2.Hostname = foobarflumesource.com
* log4j.logger.org.apache.flume.clients.log4jappender = DEBUG,out2</p>
* </pre>
* <p>
* <i>Note: Change the last line to the package of the class(es), that will do
* the appending.For example if classes from the package com.bar.foo are
* appending, the last line would be:</i>
* </p>
*
* <pre>
* <p>log4j.logger.com.bar.foo = DEBUG,out2</p>
* </pre>
*
*
*/
public class Log4jExtAppender extends AppenderSkeleton {
private String hostname;
private int port;
private String source;
public String getSource() {
return source;
}
public void setSource(String source) {
this.source = source;
}
private boolean unsafeMode = false;
private long timeout = RpcClientConfigurationConstants.DEFAULT_REQUEST_TIMEOUT_MILLIS;
private boolean avroReflectionEnabled;
private String avroSchemaUrl;
RpcClient rpcClient = null;
/**
* If this constructor is used programmatically rather than from a log4j
* conf you must set the <tt>port</tt> and <tt>hostname</tt> and then call
* <tt>activateOptions()</tt> before calling <tt>append()</tt>.
*/
public Log4jExtAppender() {
}
/**
* Sets the hostname and port. Even if these are passed the
* <tt>activateOptions()</tt> function must be called before calling
* <tt>append()</tt>, else <tt>append()</tt> will throw an Exception.
*
* @param hostname
* The first hop where the client should connect to.
* @param port
* The port to connect on the host.
*
*/
public Log4jExtAppender(String hostname, int port, String source) {
this.hostname = hostname;
this.port = port;
this.source = source;
}
/**
* Append the LoggingEvent, to send to the first Flume hop.
*
* @param event
* The LoggingEvent to be appended to the flume.
* @throws FlumeException
* if the appender was closed, or the hostname and port were not
* setup, there was a timeout, or there was a connection error.
*/
@Override
public synchronized void append(LoggingEvent event) throws FlumeException {
// If rpcClient is null, it means either this appender object was never
// setup by setting hostname and port and then calling activateOptions
// or this appender object was closed by calling close(), so we throw an
// exception to show the appender is no longer accessible.
if (rpcClient == null) {
String errorMsg = "Cannot Append to Appender! Appender either closed or"
+ " not setup correctly!";
LogLog.error(errorMsg);
if (unsafeMode) {
return;
}
throw new FlumeException(errorMsg);
}
if (!rpcClient.isActive()) {
reconnect();
}
// Client created first time append is called.
Map<String, String> hdrs = new HashMap<String, String>();
hdrs.put(Log4jAvroHeaders.LOGGER_NAME.toString(), event.getLoggerName());
hdrs.put(Log4jAvroHeaders.TIMESTAMP.toString(),
String.valueOf(event.timeStamp));
// 添加日志来源
if (this.source == null || this.source.equals("")) {
this.source = "unknown";
}
hdrs.put("flume.client.log4j.logger.source", this.source);
// To get the level back simply use
// LoggerEvent.toLevel(hdrs.get(Integer.parseInt(
// Log4jAvroHeaders.LOG_LEVEL.toString()))
hdrs.put(Log4jAvroHeaders.LOG_LEVEL.toString(),
String.valueOf(event.getLevel().toInt()));
Event flumeEvent;
Object message = event.getMessage();
if (message instanceof GenericRecord) {
GenericRecord record = (GenericRecord) message;
populateAvroHeaders(hdrs, record.getSchema(), message);
flumeEvent = EventBuilder.withBody(
serialize(record, record.getSchema()), hdrs);
} else if (message instanceof SpecificRecord || avroReflectionEnabled) {
Schema schema = ReflectData.get().getSchema(message.getClass());
populateAvroHeaders(hdrs, schema, message);
flumeEvent = EventBuilder
.withBody(serialize(message, schema), hdrs);
} else {
hdrs.put(Log4jAvroHeaders.MESSAGE_ENCODING.toString(), "UTF8");
String msg = layout != null ? layout.format(event) : message
.toString();
flumeEvent = EventBuilder.withBody(msg, Charset.forName("UTF8"),
hdrs);
}
try {
rpcClient.append(flumeEvent);
} catch (EventDeliveryException e) {
String msg = "Flume append() failed.";
LogLog.error(msg);
if (unsafeMode) {
return;
}
throw new FlumeException(msg + " Exception follows.", e);
}
}
private Schema schema;
private ByteArrayOutputStream out;
private DatumWriter<Object> writer;
private BinaryEncoder encoder;
protected void populateAvroHeaders(Map<String, String> hdrs, Schema schema,
Object message) {
if (avroSchemaUrl != null) {
hdrs.put(Log4jAvroHeaders.AVRO_SCHEMA_URL.toString(), avroSchemaUrl);
return;
}
LogLog.warn("Cannot find ID for schema. Adding header for schema, "
+ "which may be inefficient. Consider setting up an Avro Schema Cache.");
hdrs.put(Log4jAvroHeaders.AVRO_SCHEMA_LITERAL.toString(),
schema.toString());
}
private byte[] serialize(Object datum, Schema datumSchema)
throws FlumeException {
if (schema == null || !datumSchema.equals(schema)) {
schema = datumSchema;
out = new ByteArrayOutputStream();
writer = new ReflectDatumWriter<Object>(schema);
encoder = EncoderFactory.get().binaryEncoder(out, null);
}
out.reset();
try {
writer.write(datum, encoder);
encoder.flush();
return out.toByteArray();
} catch (IOException e) {
throw new FlumeException(e);
}
}
// This function should be synchronized to make sure one thread
// does not close an appender another thread is using, and hence risking
// a null pointer exception.
/**
* Closes underlying client. If <tt>append()</tt> is called after this
* function is called, it will throw an exception.
*
* @throws FlumeException
* if errors occur during close
*/
@Override
public synchronized void close() throws FlumeException {
// Any append calls after this will result in an Exception.
if (rpcClient != null) {
try {
rpcClient.close();
} catch (FlumeException ex) {
LogLog.error("Error while trying to close RpcClient.", ex);
if (unsafeMode) {
return;
}
throw ex;
} finally {
rpcClient = null;
}
} else {
String errorMsg = "Flume log4jappender already closed!";
LogLog.error(errorMsg);
if (unsafeMode) {
return;
}
throw new FlumeException(errorMsg);
}
}
@Override
public boolean requiresLayout() {
// This method is named quite incorrectly in the interface. It should
// probably be called canUseLayout or something. According to the docs,
// even if the appender can work without a layout, if it can work with
// one,
// this method must return true.
return true;
}
/**
* Set the first flume hop hostname.
*
* @param hostname
* The first hop where the client should connect to.
*/
public void setHostname(String hostname) {
this.hostname = hostname;
}
/**
* Set the port on the hostname to connect to.
*
* @param port
* The port to connect on the host.
*/
public void setPort(int port) {
this.port = port;
}
public void setUnsafeMode(boolean unsafeMode) {
this.unsafeMode = unsafeMode;
}
public boolean getUnsafeMode() {
return unsafeMode;
}
public void setTimeout(long timeout) {
this.timeout = timeout;
}
public long getTimeout() {
return this.timeout;
}
public void setAvroReflectionEnabled(boolean avroReflectionEnabled) {
this.avroReflectionEnabled = avroReflectionEnabled;
}
public void setAvroSchemaUrl(String avroSchemaUrl) {
this.avroSchemaUrl = avroSchemaUrl;
}
/**
* Activate the options set using <tt>setPort()</tt> and
* <tt>setHostname()</tt>
*
* @throws FlumeException
* if the <tt>hostname</tt> and <tt>port</tt> combination is
* invalid.
*/
@Override
public void activateOptions() throws FlumeException {
Properties props = new Properties();
props.setProperty(RpcClientConfigurationConstants.CONFIG_HOSTS, "h1");
props.setProperty(RpcClientConfigurationConstants.CONFIG_HOSTS_PREFIX
+ "h1", hostname + ":" + port);
props.setProperty(
RpcClientConfigurationConstants.CONFIG_CONNECT_TIMEOUT,
String.valueOf(timeout));
props.setProperty(
RpcClientConfigurationConstants.CONFIG_REQUEST_TIMEOUT,
String.valueOf(timeout));
try {
rpcClient = RpcClientFactory.getInstance(props);
if (layout != null) {
layout.activateOptions();
}
} catch (FlumeException e) {
String errormsg = "RPC client creation failed! " + e.getMessage();
LogLog.error(errormsg);
if (unsafeMode) {
return;
}
throw e;
}
}
/**
* Make it easy to reconnect on failure
*
* @throws FlumeException
*/
private void reconnect() throws FlumeException {
close();
activateOptions();
}
}
然后然后将这个类打了一个jar包:Log4jExtAppender.jar,扔在了flumedemo和flumedemo2的lib目录下。
这时候flumedemo的log4j.properties如下:
log4j.rootLogger=INFO
log4j.category.com.besttone=INFO,flume,console,LogFile
#log4j.appender.flume = org.apache.flume.clients.log4jappender.Log4jExtAppender
log4j.appender.flume = com.besttone.flume.Log4jExtAppender
log4j.appender.flume.Hostname = localhost
log4j.appender.flume.Port = 44444
log4j.appender.flume.UnsafeMode = false
log4j.appender.flume.Source = app1
log4j.appender.console= org.apache.log4j.ConsoleAppender
log4j.appender.console.Target= System.out
log4j.appender.console.layout= org.apache.log4j.PatternLayout
log4j.appender.console.layout.ConversionPattern= %d{yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss} %5p %c{1}: %L - %m%n
log4j.appender.LogFile= org.apache.log4j.DailyRollingFileAppender
log4j.appender.LogFile.File= logs/app.log
log4j.appender.LogFile.MaxFileSize=10KB
log4j.appender.LogFile.Append= true
log4j.appender.LogFile.Threshold= DEBUG
log4j.appender.LogFile.layout= org.apache.log4j.PatternLayout
log4j.appender.LogFile.layout.ConversionPattern= %-d{yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss} [%t:%r] - [%5p] %m%n
flumedemo2的如下:
log4j.rootLogger=INFO
log4j.category.com.besttone=INFO,flume,console,LogFile
#log4j.appender.flume = org.apache.flume.clients.log4jappender.Log4jExtAppender
log4j.appender.flume = com.besttone.flume.Log4jExtAppender
log4j.appender.flume.Hostname = localhost
log4j.appender.flume.Port = 44444
log4j.appender.flume.UnsafeMode = false
log4j.appender.flume.Source = app2
log4j.appender.console= org.apache.log4j.ConsoleAppender
log4j.appender.console.Target= System.out
log4j.appender.console.layout= org.apache.log4j.PatternLayout
log4j.appender.console.layout.ConversionPattern= %d{yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss} %5p %c{1}: %L - %m%n
log4j.appender.LogFile= org.apache.log4j.DailyRollingFileAppender
log4j.appender.LogFile.File= logs/app.log
log4j.appender.LogFile.MaxFileSize=10KB
log4j.appender.LogFile.Append= true
log4j.appender.LogFile.Threshold= DEBUG
log4j.appender.LogFile.layout= org.apache.log4j.PatternLayout
log4j.appender.LogFile.layout.ConversionPattern= %-d{yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss} [%t:%r] - [%5p] %m%n
将原来的log4j.appender.flume 由org.apache.flume.clients.log4jappender.Log4jExtAppender改为了我重新实现添加了source参数的com.besttone.flume.Log4jExtAppender
然后flumedemo的log4j.appender.flume.Source = app1,flumedemo2的log4j.appender.flume.Source = app2。
运行flumedemo的WriteLog类,和和flumedemo2的WriteLog2类,分别去hdfs上和agent的log文件中看看内容,发现hdfs上都是app1的日志,log文件中都是app2的日志,功能实现。
完整的flume.conf如下:
tier1.sources=source1
tier1.channels=channel1 channel2
tier1.sinks=sink1 sink2
tier1.sources.source1.type=avro
tier1.sources.source1.bind=0.0.0.0
tier1.sources.source1.port=44444
tier1.sources.source1.channels=channel1 channel2
tier1.sources.source1.selector.type=multiplexing
tier1.sources.source1.selector.header=flume.client.log4j.logger.source
tier1.sources.source1.selector.mapping.app1=channel1
tier1.sources.source1.selector.mapping.app2=channel2
tier1.sources.source1.interceptors=i1 i2
tier1.sources.source1.interceptors.i1.type=regex_filter
tier1.sources.source1.interceptors.i1.regex=\\{.*\\}
tier1.sources.source1.interceptors.i2.type=timestamp
tier1.channels.channel1.type=memory
tier1.channels.channel1.capacity=10000
tier1.channels.channel1.transactionCapacity=1000
tier1.channels.channel1.keep-alive=30
tier1.channels.channel2.type=memory
tier1.channels.channel2.capacity=10000
tier1.channels.channel2.transactionCapacity=1000
tier1.channels.channel2.keep-alive=30
tier1.sinks.sink1.type=hdfs
tier1.sinks.sink1.channel=channel1
tier1.sinks.sink1.hdfs.path=hdfs://master68:8020/flume/events/%y-%m-%d
tier1.sinks.sink1.hdfs.round=true
tier1.sinks.sink1.hdfs.roundValue=10
tier1.sinks.sink1.hdfs.roundUnit=minute
tier1.sinks.sink1.hdfs.fileType=DataStream
tier1.sinks.sink1.hdfs.writeFormat=Text
tier1.sinks.sink1.hdfs.rollInterval=0
tier1.sinks.sink1.hdfs.rollSize=10240
tier1.sinks.sink1.hdfs.rollCount=0
tier1.sinks.sink1.hdfs.idleTimeout=60
tier1.sinks.sink2.type=logger
tier1.sinks.sink2.channel=channel2