一起来学Objective-C(3)——如何声明和定义类
通过前边的hello world程序,我们知道了如何包含头文件,以及NSLog的基本用法,从本节开始,通过一个简单的类来讲解如何声明和定义类,以及类中的成员函数长什么摸样。
在第一节中描述的HOME中添加以下三个文件Rec.h、Rec.c、main.m:
/** * @file Rec.h * @brief * @author Don Hao * @date 2011-8-21 12:14:13 * @version * <pre><b>copyright: </b></pre> * <pre><b>email: </b>[email protected]</pre> * <pre><b>company: </b>http://blog.csdn.net/donhao</pre> * <pre><b>All rights reserved.</b></pre> * <pre><b>modification:</b></pre> * <pre>Write modifications here.</pre> */ #import <Foundation/Foundation.h> @interface Rec : NSObject { int length; int width; } -(void) setLength: (int) len setWidth: (int) wid; -(int) getLength; -(int) getWidth; +(void) testStaticMethod:(NSString*) nsstr printCStr:(const char*) cstr; @end
/** * @file Rec.m * @brief * @author Don Hao * @date 2011-8-21 12:14:13 * @version * <pre><b>copyright: </b></pre> * <pre><b>email: </b>[email protected]</pre> * <pre><b>company: </b>http://blog.csdn.net/donhao</pre> * <pre><b>All rights reserved.</b></pre> * <pre><b>modification:</b></pre> * <pre>Write modifications here.</pre> */ #import "Rec.h" @implementation Rec -(void) setLength: (int) len setWidth: (int) wid { NSLog(@"SET: Length=%d, Width=%d\n", len, wid); length = len; width = wid; } -(int) getLength { return length; } -(int) getWidth { return width; } +(void) testStaticMethod:(NSString*) nsstr printCStr:(const char*) cstr { NSLog(@"This is NSString: %@ This is C String: %s\n", nsstr, cstr); } @end
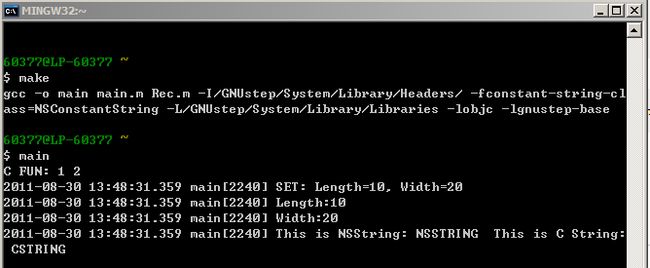
/** * @file main.m * @brief * @author Don Hao * @date 2011-8-21 12:14:13 * @version * <pre><b>copyright: </b></pre> * <pre><b>email: </b>[email protected]</pre> * <pre><b>company: </b>http://blog.csdn.net/donhao</pre> * <pre><b>All rights reserved.</b></pre> * <pre><b>modification:</b></pre> * <pre>Write modifications here.</pre> */ #import "Rec.h" int testCFun(int length, int width) { printf("C FUN: %d %d\n", length, width); } int main(int arvc, char* argv[]) { testCFun(1, 2); Rec* r = [Rec new]; [r setLength:10 setWidth:20]; NSLog(@"Length:%d\n", [r getLength]); NSLog(@"Width:%d\n", [r getWidth]); NSString* nsstr = @"NSSTRING"; const char* cstr = "CSTRING"; [Rec testStaticMethod:nsstr printCStr:cstr]; return 0; }
Makefile的内容(如果不清楚,请看第一节):
gen: gcc -o main main.m Rec.m -I/GNUstep/System/Library/Headers/ -fconstant-string-class=NSConstantString -L/GNUstep/System/Library/Libraries -lobjc -lgnustep-base
运行结果如下:
下面及后续章节对相关内容逐一进行说明。
大家习惯于C/C++/C#/Java代码风格的话,看到Objective-C的代码难免觉得难以接受。无需有排斥的感觉,等看习惯了就好了。
本节先来将一下Objective-C是如何声明和定义类的。
上边是一个Rec类(矩形),我们将类的声明放到了.h头文件(C++中类的定义可以放到.h中),类的定义放到了.m文件中。
1. 类的声明
类的声明格式为:
@interface 类名 : 父类
{
//属性
}
//方法声明
@end
其中,该类必须直接或间接继承自NSObject,@interface用于指示这是对类的定义,类名后边的冒号是继承(同C++),属性放到大括弧中,在大括弧之后是类的方法,最后是@end(这个可以不写,但为了让其他人知道这个类定义到这里就结束了,写上更好)。
2. 类的定义
类的定义格式为:
@implementation 类名 //方法定义 @end
3 示例说明
在上边的示例中对类Rec的定义:
a. 类Rec继承自NSObject
b. 有两个属性:length和width
c. 有四个方法:具体的方法下节进行解释。
d. 通过+/-来修饰方法,如果为-,则表明该方法属于对象,如果为+,则表明该方法属于类(即静态方法)
Objective-C与C++的类的不同之处在于:
a. C++通过Class来标识类,而Objective-C通过@interface/@implementation来标识类;
b. C++通过static来区分是否是静态方法,而Objective-C通过+/-来区分;
c. C++类的方法定义在类的大括弧中,而Objective-C在大括弧外;
e. C++对属性和方法有public、private、protected等访问限制属性,而Objective-C中属性为Protected,方法为Public;
f. C++支持多继承,而Objective-C不支持多继承;
一起来学Objective-C(1)——Window下开发环境安装和Hello World
一起来学Objective-C(2)——Hello World深入
一起来学Objective-C(3)——如何声明和定义类