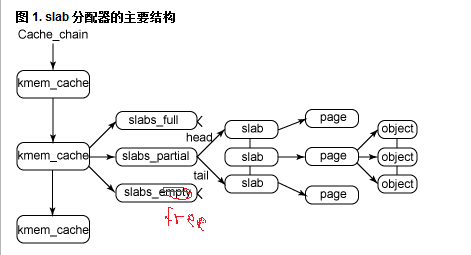
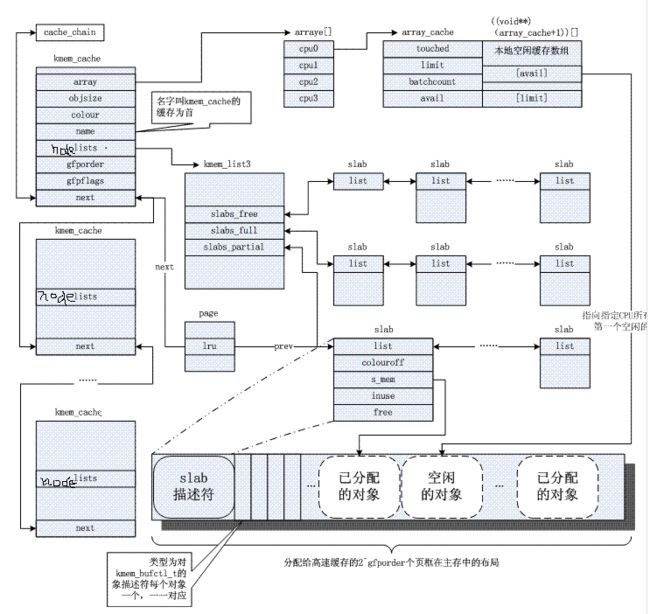
kmem_cache 初始化
kernel在启动会初始化后备高速缓存,解决了设备驱动中反复分配很多同一块大小内存的效率问题.
我是打算写一个内存管理系统的学习笔记. 从各个模块的初始化开始. 今天是kmem_cache 的初始流程.
/* * Set up kernel memory allocators */
static void __init mm_init(void)
{
/* * page_ext requires contiguous pages, * bigger than MAX_ORDER unless SPARSEMEM. */
page_ext_init_flatmem();
**mem_init**();
kmem_cache_init();
percpu_init_late();
pgtable_init();
vmalloc_init();
ioremap_huge_init();
}kmem_cache_init(); 在mm/slab.c 中实现.
/*
* Initialisation. Called after the page allocator have been initialised and
* before smp_init().
* 要在page callocator 初始化完成后调用该函数,并且要在多核初始化之前完成.
*/
void __init kmem_cache_init(void)
{
int i;
BUILD_BUG_ON(sizeof(((struct page *)NULL)->lru) <
sizeof(struct rcu_head));
kmem_cache = &kmem_cache_boot;
if (num_possible_nodes() == 1)
use_alien_caches = 0;
for (i = 0; i < NUM_INIT_LISTS; i++)
kmem_cache_node_init(&init_kmem_cache_node[i]);
/*
* Fragmentation resistance on low memory - only use bigger
* page orders on machines with more than 32MB of memory if
* not overridden on the command line.
*/
if (!slab_max_order_set && totalram_pages > (32 << 20) >> PAGE_SHIFT)
slab_max_order = SLAB_MAX_ORDER_HI;
/* Bootstrap is tricky, because several objects are allocated
* from caches that do not exist yet:
* 1) initialize the kmem_cache cache: it contains the struct
* kmem_cache structures of all caches, except kmem_cache itself:
* kmem_cache is statically allocated.
* Initially an __init data area is used for the head array and the
* kmem_cache_node structures, it's replaced with a kmalloc allocated
* array at the end of the bootstrap.
* 2) Create the first kmalloc cache.
* The struct kmem_cache for the new cache is allocated normally.
* An __init data area is used for the head array.
* 3) Create the remaining kmalloc caches, with minimally sized
* head arrays.
* 4) Replace the __init data head arrays for kmem_cache and the first
* kmalloc cache with kmalloc allocated arrays.
* 5) Replace the __init data for kmem_cache_node for kmem_cache and
* the other cache's with kmalloc allocated memory.
* 6) Resize the head arrays of the kmalloc caches to their final sizes.
*/
/* 1) create the kmem_cache */
/*
* struct kmem_cache size depends on nr_node_ids & nr_cpu_ids
*/
create_boot_cache(kmem_cache, "kmem_cache",
offsetof(struct kmem_cache, node) +
nr_node_ids * sizeof(struct kmem_cache_node *),
SLAB_HWCACHE_ALIGN);
list_add(&kmem_cache->list, &slab_caches);
slab_state = PARTIAL;
/*
* Initialize the caches that provide memory for the kmem_cache_node
* structures first. Without this, further allocations will bug.
*/
kmalloc_caches[INDEX_NODE] = create_kmalloc_cache("kmalloc-node",
kmalloc_size(INDEX_NODE), ARCH_KMALLOC_FLAGS);
slab_state = PARTIAL_NODE;
setup_kmalloc_cache_index_table();
slab_early_init = 0;
/* 5) Replace the bootstrap kmem_cache_node */
{
int nid;
for_each_online_node(nid) {
init_list(kmem_cache, &init_kmem_cache_node[CACHE_CACHE + nid], nid);
init_list(kmalloc_caches[INDEX_NODE],
&init_kmem_cache_node[SIZE_NODE + nid], nid);
}
}
create_kmalloc_caches(ARCH_KMALLOC_FLAGS);
}
创建完后背高速缓存 机制.
下面举例使用.
JFFS2 文件系统
static struct kmem_cache *full_dnode_slab;
struct jffs2_full_dnode *jffs2_alloc_full_dnode(void)
{
struct jffs2_full_dnode *ret;
ret = **kmem_cache_alloc**(full_dnode_slab, GFP_KERNEL);// kmem_cache_alloc分配kmem_cache
dbg_memalloc("%p\n", ret);
return ret;
}
kmem_cache_alloc 从高速缓存中分配object
/** * kmem_cache_alloc - Allocate an object * @cachep: The cache to allocate from. * @flags: See kmalloc(). * * Allocate an object from this cache. The flags are only relevant * if the cache has no available objects. */
void *kmem_cache_alloc(struct kmem_cache *cachep, gfp_t flags)
{
void *ret = ***slab_alloc***(cachep, flags, _RET_IP_);
trace_kmem_cache_alloc(_RET_IP_, ret,
cachep->object_size, cachep->size, flags);
return ret;
}
EXPORT_SYMBOL(kmem_cache_alloc);
static __always_inline void *
**slab_alloc**(struct kmem_cache *cachep, gfp_t flags, unsigned long caller)
{
unsigned long save_flags;
void *objp;
flags &= gfp_allowed_mask;
cachep = slab_pre_alloc_hook(cachep, flags);
if (unlikely(!cachep))
return NULL;
cache_alloc_debugcheck_before(cachep, flags);
local_irq_save(save_flags);
objp = __do_cache_alloc(cachep, flags);
local_irq_restore(save_flags);
objp = cache_alloc_debugcheck_after(cachep, flags, objp, caller);
prefetchw(objp);
if (unlikely(flags & __GFP_ZERO) && objp)
memset(objp, 0, cachep->object_size);
slab_post_alloc_hook(cachep, flags, 1, &objp);
return objp;
}
static __always_inline void *
__do_cache_alloc(struct kmem_cache *cachep, gfp_t flags)
{
return ____cache_alloc(cachep, flags);
}
static inline void *____cache_alloc(struct kmem_cache *cachep, gfp_t flags)
{
void *objp;
struct array_cache *ac;
check_irq_off();
ac = cpu_cache_get(cachep);
if (likely(ac->avail)) {
ac->touched = 1;
objp = ac->entry[--ac->avail];
STATS_INC_ALLOCHIT(cachep);
goto out;
}
STATS_INC_ALLOCMISS(cachep);
objp = cache_alloc_refill(cachep, flags);
/*
* the 'ac' may be updated by cache_alloc_refill(),
* and kmemleak_erase() requires its correct value.
*/
ac = cpu_cache_get(cachep);
out:
/*
* To avoid a false negative, if an object that is in one of the
* per-CPU caches is leaked, we need to make sure kmemleak doesn't
* treat the array pointers as a reference to the object.
*/
if (objp)
kmemleak_erase(&ac->entry[ac->avail]);
return objp;
}
kmem_cache 的定义如下;
struct kmem_cache {
unsigned int object_size;/* The original size of the object */
unsigned int size; /* The aligned/padded/added on size */
unsigned int align; /* Alignment as calculated */
unsigned long flags; /* Active flags on the slab */
const char *name; /* Slab name for sysfs */
int refcount; /* Use counter */
void (*ctor)(void *); /* Called on object slot creation */
struct list_head list; /* List of all slab caches on the system */
};