javascript之window对象
1、全局的window对象
JavaScript中的任何一个全局函数或变量都是window的属性。
<script type="text/javascript"> var name="撼地神牛"; document.write(window.name); </script>
2、window与self对象
self对象与window对象完全相同,self通常用于确认就是在当前的窗体内。
<script type="text/javascript"> document.write(window == self); //必须相等,永远都相等 document.write(window.Top == window.self); //判断当前框架是否是主框架 </script>
window、self、window.self三者是等价的。
3、window的子对象
window的主对象主要有如下几个:
- JavaScript document 对象
- JavaScript frames 对象
- JavaScript history 对象
- JavaScript location 对象
- JavaScript navigator 对象
- JavaScript screen 对象
4、window函数索引(仅对IE有效)
窗体控制函数:
- JavaScript moveBy() 函数:从当前位置水平移动窗体x个像素,垂直移动窗体y个像素,x为负数,将向左移动窗体,y为负数,将向上移动窗体。
- JavaScript moveTo() 函数:移动窗体左上角到相对于屏幕左上角的(x,y)点,当使用负数做为参数时会把窗体移出屏幕的可视区域。
- JavaScript resizeBy() 函数:相对窗体当前的大小,宽度调整w个像素,高度调整h个像素。如果参数为负值,将缩小窗体,反之扩大窗体。
- JavaScript resizeTo() 函数:把窗体宽度调整为w个像素,高度调整为h个像素。
<body> <input type="button" id="btn1" value="先设置窗体固定大小!" onclick="window.resizeTo(500,500);" /> <input type="button" id="btn2" value="再缩小10像素!" onclick="window.resizeBy(-10,-10);" /> <input type="button" id="btn2" value="上!" onclick="window.moveBy(0,-5);" /> <input type="button" id="btn2" value="下!" onclick="window.moveBy(0, 5);" /> <input type="button" id="btn2" value="左!" onclick="window.moveBy(-5, 0);" /> <input type="button" id="btn2" value="右!" onclick="window.moveBy(5, 0);" /> <input type="button" id="btn2" value="距离左上角左边100像素,顶部200像素" onclick="window.moveTo(100, 200);" /> </body>
窗体滚动轴控制函数:
- JavaScript scrollTo() 函数:在窗体中如果有滚动条,将横向滚动条移动到相对于窗体宽度为x个像素的位置,将纵向滚动条移动到相对于窗体高度为y个像素的位置。
- JavaScript scrollBy() 函数:如果有滚动条,将横向滚动条移动到相对于当前横向滚动条的x个像素的位置(就是向左移动x像素),将纵向滚动条移动到相对于当前纵向滚动条高度为y个像素的位置(就是向下移动y像素)。
注意区别,一个是相对当前窗口,一个是相当现在滚动条的位置。
<div style="height:150%; width:150%; background-color:#ddd"> <input type="button" id="btn1" value="移动滚动条!" onclick="window.scrollTo(100,100);" /> //相当于设置绝对位置 <input type="button" id="btn1" value="移动滚动条!" onclick="window.scrollBy(100,100);" /> //相当于累加 </div>
窗体焦点控制函数:
- JavaScript focus() 函数:使窗体或空间获得焦点
- JavaScript blur() 函数:使窗体或控件失去焦点
<div> <input type="button" value="获得焦点" onclick="document.getElementById('testInput').focus()" /> <input type="button" value="失去焦点" onclick="document.getElementById('testInput').blur()" /> <input type="text" value="text" id="testInput" onblur="alert('我已失去焦点')" /> </div>
新建窗体函数:
- JavaScript open() 函数:打开(弹出)一个新的窗体
- JavaScript close() 函数:关闭窗体
- JavaScript opener 属性:通过opener可以实现跨窗体之间的通讯,但是要保证是在同一域名下,而且一个窗体要包含另一个窗体的opener。
window.open(url, name, features, replace);
open函数参数说明:
- url -- 要载入窗体的URL;
- name -- 新建窗体的名称(也可以是HTML target属性的取值,目标);
- features -- 代表窗体特性的字符串,字符串中每个特性使用逗号分隔;
- replace -- 一个布尔值,说明新载入的页面是否替换当前载入的页面,此参数通常不用指定。
open方法示例:
<a href="2.html" target="2">在新窗口打开连接</a> <a href="#" onclick="window.open('http://www.google.com','2');">在已建立连接的页面打开新地址</a>
首先使用普通HTML链接打开一个页面(target名为dreamdu),之后使用open函数打开另一个页面,浏览器首先要查找是否有名称为dreamdu的窗体,如果有,就在这个窗体中加载open的地址。
经过设置的open
window.open ('page.html', 'newwindow', 'height=100, width=400, top=0,left=0, toolbar=no, menubar=no, scrollbars=no, resizable=no,location=no, status=no')
弹窗方法:
方法一:<body onload="openwin()"> 浏览器读页面时弹出窗口;
方法二:<body onunload="openwin()"> 浏览器离开页面时弹出窗口;
open函数第三个参数features说明:
| 参数名称 | 类型 | 说明 |
|---|---|---|
| height | Number | 设置窗体的高度,不能小于100 |
| left | Number | 说明创建窗体的左坐标,不能为负值 |
| location | Boolean | 窗体是否显示地址栏,默认值为no |
| resizable | Boolean | 窗体是否允许通过拖动边线调整大小,默认值为no |
| scrollable | Boolean | 窗体中内部超出窗口可视范围时是否允许拖动,默认值为no |
| toolbar | Boolean | 窗体是否显示工具栏,默认值为no |
| top | Number | 说明创建窗体的上坐标,不能为负值 |
| status | Boolean | 窗体是否显示状态栏,默认值为no |
| width | Number | 创建窗体的宽度,不能小于100 |
特性字符串中的每个特性使用逗号分隔,每个特性之间不允许有空格。
window.open函数新建立窗体后会返回新建窗体的window对象,通过此对象可以控制窗体(移动,改变大小,关闭)。
close函数:
<input type="button" value="关闭已经打开的窗体!" onclick="window.close();" />
self.close();配合上setTimeout()可以实现,打开的窗口定时关闭的效果。
对话框函数:
- JavaScript alert() 函数:弹出消息对话框(对话框中有一个OK按钮)
- JavaScript confirm() 函数:弹出消息对话框(对话框中包含一个OK按钮与Cancel按钮)
- JavaScript prompt() 函数:弹出消息对话框(对话框中包含一个OK按钮、Cancel按钮与一个文本输入框)
alert();
不说。
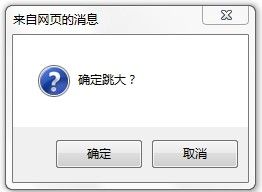
confirm(str);
confirm()消息对话框是排它的,也就是在用户点击对话框的按钮前,不能进行任何其它操作。
if(confirm("确定跳大?")) { alert("果断跳大"); } else { alert("猥琐打钱"); }
显示如下:
prompt(str1, str2);
函数有两个参数
- str1 -- 要显示在消息对话框中的文本,不可修改
- str2 -- 文本框中的内容,可以修改
var sResult=prompt("请在下面输入你的姓名", "撼地神牛"); if(sResult!=null) { alert(sResult + "已经超越神的杀戮"); } else { alert("无名氏已经超越神的杀戮"); }
显示如下:
时间等待与间隔函数:
- JavaScript setTimeout() 函数
- JavaScript clearTimeout() 函数
- JavaScript setInterval() 函数
- JavaScript clearInterval() 函数
1、setTimeout()、clearTimeout() 在指定的时间后调用函数
语法:
- setTimeout(fun,time); fun:函数体或函数名,time指定时间,单位为毫秒。
- clearTimeout(id); 取消指定的setTimeout函数将要执行的代码
setTimeout(function () { document.write("隔3秒后触发"); }, 3000) //在3秒后输出 setTimeout(fun1, 5000); //在5秒后输出 function fun1() { document.write("函数名的方式5秒后触发"); }
2、setInterval()、clearInterval(value) 在间隔指定的事件后重复调用函数
语法:
- setInterval(fun1,time) fun:函数体或函数名,time指定的时间,单位为毫秒。会返回一个值,这个值是统计该函数的个数用的,第一个是1,第二个就是2,指明是第几个setInterval函数。
- clearInterval(value) value:setInterval()函数返回的值,根据这个值可以停止setInterval()的重复。
var i = 0; var h = setInterval(function () { document.write("3秒输出一次<br/>"); i++; if (i >= 3) { clearInterval(h); document.write("停止输出"); } }, 3000);
注意,javascript是单线程的,因此,这个定时函数实际上是通过插入执行队列的方式来实现。
如下面的代码:
function fn() { setTimeout(function(){alert('can you see me?');},1000); while(true) {} }
alert();永远都不会执行,因为线程一直被死循环占用了。
window.location子对象
解析URL对象location
location对象的属性有:href,protocal,host,hostname,port,pathname,search,hash
document.write(location.href + "<br/>"); // http://localhost:4889/javascriptTest.html
document.write(location.protocol + "<br/>"); // http:
document.write(location.host + "<br/>"); // localhost:4889
document.write(location.hostname + "<br/>"); // localhost
document.write(location.port + "<br/>"); // 4889
document.write(location.pathname + "<br/>"); // /javascriptTest.html
document.write(location.search + "换行<br/>"); //http://localhost:4889/javascriptTest.html?id=1&name=张三 如果路径是这样,则输出 ?id=1&name=%E5%BC%A0%E4%B8%89
document.write(location.hash); //http: //localhost:4889/javascriptTest.html#kk=你好?id=1&name=张三 如果路径是这样,则输出 #kk=你好?id=1&name=张三
载入新文档
location.reload() 重新加载页面
location.replace() 本窗口载入新文档
location.assign() 本窗口载入新文档
location = "http://www.baidu.com" //跳转到指定网址
location = "search.html" //相对路径跳转
location = "#top" //跳转到页面顶部
浏览历史
History()对象的back()与forward() 与浏览器的“后退”,"前进"功能一样。
history.go(-2); 后退两个历史记录
浏览器和屏幕信息
navigator.appName Web浏览器全称
navigator.appVersion Web浏览器厂商和版本的详细字符串
navigator.userAgent 客户端绝大部分信息
navagator.platform 浏览器运行所在的操作系统
document.write(navigator.userAgent + "<br/>"); // Mozilla/5.0 (Windows NT 6.1) AppleWebKit/537.11 (KHTML, like Gecko) Chrome/23.0.1271.97 Safari/537.11
document.write(navigator.appName + "<br/>"); //Netscape
document.write(navigator.appVersion + "<br/>"); //5.0 (Windows NT 6.1) AppleWebKit/537.11 (KHTML, like Gecko) Chrome/23.0.1271.97 Safari/537.11
document.write(navigator.platform); //Win32
窗口的关系
parent == self 只有顶级窗口才返回true
parent和top属性允许脚本引用它的窗体的祖先,通常窗体是通过<iframe>元素创建的,可以用来获取顶级窗口。
5、event事件对象
最有用的两个操作:阻止事件冒泡。有时return false;不管用,这个或许就管用了。
//IE: window.event.cancelBubble = true;//停止冒泡 window.event.returnValue = false;//阻止事件的默认行为 //Firefox: event.preventDefault();// 取消事件的默认行为 event.stopPropagation(); // 阻止事件的传播