java封装AES加密算法
在实际coding中会经常遇到往数据库存入密码时加密,URL传参时的加密,由此简单封装了下java中的AES加密算法。
0、import类
import java.security.SecureRandom;
import javax.crypto.Cipher;
import javax.crypto.KeyGenerator;
import javax.crypto.SecretKey;
import javax.crypto.spec.SecretKeySpec;
import org.apache.axis.encoding.Base64; //非必须1、加密接口
/** * 加密 * @param content 待加密内容 * @param password 加密密钥 * @return */
public static byte[] encrypt(String content, String password) {
try {
KeyGenerator kgen = KeyGenerator.getInstance("AES");
kgen.init(128, new SecureRandom(password.getBytes()));
SecretKey secretKey = kgen.generateKey();
byte[] enCodeFormat = secretKey.getEncoded();
SecretKeySpec key = new SecretKeySpec(enCodeFormat, "AES");
Cipher cipher = Cipher.getInstance("AES");
byte[] byteContent = content.getBytes("utf-8");
cipher.init(Cipher.ENCRYPT_MODE, key);
byte[] result = cipher.doFinal(byteContent);
return result;
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
return null;
}2、解密接口
/**解密 * @param content 待解密内容 * @param password 解密密钥 * @return */
public static byte[] decrypt(byte[] content, String password) {
try {
KeyGenerator kgen = KeyGenerator.getInstance("AES");
kgen.init(128, new SecureRandom(password.getBytes()));
SecretKey secretKey = kgen.generateKey();
byte[] enCodeFormat = secretKey.getEncoded();
SecretKeySpec key = new SecretKeySpec(enCodeFormat, "AES");
Cipher cipher = Cipher.getInstance("AES");
cipher.init(Cipher.DECRYPT_MODE, key);
byte[] result = cipher.doFinal(content);
return result;
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
return null;
}3、编解码函数(非必须)
//编码函数
public static String encode(String content, String key) throws Exception {
byte[] encrypt = encrypt(content, key);
return Base64.encode(encrypt);
}
//解码函数
public static String decode(String encode, String key) throws Exception {
byte[] encrypt = Base64.decode(encode);
byte[] content = decrypt(encrypt, key);
return new String(content);
}4、测试
//0-正常使用
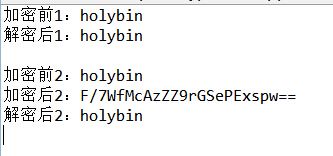
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception{
String content = "holybin";
String password = "12345678";
System.out.println("加密前1:" + content);
byte[] encryptResult1 = encrypt(content, password); //普通加密
byte[] decryptResult1 = decrypt(encryptResult1,password); //普通解密
System.out.println("解密后1:" + new String(decryptResult1));
System.out.println("\n加密前2:" + content);
String encryptResult2 = encode(content, password); //先编码再加密
System.out.println("加密后2:" + encryptResult2);
String decryptResult2 = decode(encryptResult2, password); //先解码再解密
System.out.println("解密后2:" + decryptResult2);
}5、问题与思考
(1)普通加密后将得到的byte数组直接转化为字符串用于输出,或者普通解密时从字符串转换为byte数组用于传参会发生什么?
//1-先测试加密
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception{
String content = "holybin";
String password = "12345678";
System.out.println("加密前1:" + content);
byte[] encryptResult1 = encrypt(content, password); //普通加密
System.out.println("加密后1:" + encryptResult1);
System.out.println("加密后1:" + new String(encryptResult1));
byte[] decryptResult1 = decrypt(encryptResult1,password); //普通解密
System.out.println("解密后1:" + new String(decryptResult1));
}结果1:

这里将加密后的byte数组直接转化成String输出,出现乱码。
//2-再测试解密
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception{
String content = "holybin";
String password = "12345678";
System.out.println("加密前1:" + content);
byte[] encryptResult1 = encrypt(content, password); //普通加密
String strEncryptResult1 = new String(encryptResult1,"UTF-8");
//System.out.println("加密后1:" + strEncryptResult1);
byte[] decryptResult1 = decrypt(strEncryptResult1.getBytes("UTF-8"),password); //普通解密
System.out.println("解密后1:" + new String(decryptResult1));
}结果2:
这里从加密后的String提取bytes数组用于解密,出现报错
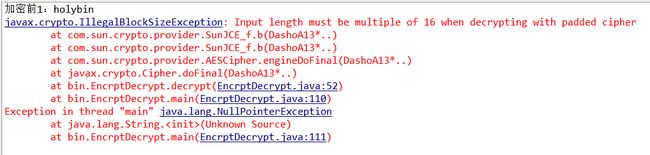
原因:主要是因为加密后的byte数组是不能强制转换成字符串的,加密过的字符串也不能直接提取bytes数组用于解密,解决方法有两个:一是像上面测试的例子一样先加密再编码,或先解码再解密(参考:4、测试);二是采用十六进制和二进制的相互转化函数(参考:下面的第(2)点)。
(2)十六进制和二进制相互转化函数
// 二进制转十六进制
public static String parseByte2HexStr(byte buf[]) {
StringBuffer sb = new StringBuffer();
for (int i = 0; i < buf.length; i++) {
String hex = Integer.toHexString(buf[i] & 0xFF);
if (hex.length() == 1) {
hex = '0' + hex;
}
sb.append(hex.toUpperCase());
}
return sb.toString();
}
// 十六进制转二进制
public static byte[] parseHexStr2Byte(String hexStr) {
if (hexStr.length() < 1)
return null;
byte[] result = new byte[hexStr.length() / 2];
for (int i = 0; i < hexStr.length() / 2; i++) {
int high = Integer.parseInt(hexStr.substring(i * 2, i * 2 + 1), 16);
int low = Integer.parseInt(hexStr.substring(i * 2 + 1, i * 2 + 2),
16);
result[i] = (byte) (high * 16 + low);
}
return result;
}使用示例:
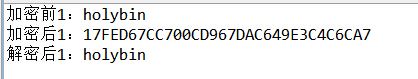
// 3-测试转化函数
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
String content = "holybin";
String password = "12345678";
//加密
System.out.println("加密前1:" + content);
byte[] encryptResult = encrypt(content, password); // 普通加密
String strEncryptResult = parseByte2HexStr(encryptResult);
System.out.println("加密后1:" + strEncryptResult);
//解密
byte[] byteDecryptResult = parseHexStr2Byte(strEncryptResult);
byte[] decryptResult = decrypt(byteDecryptResult, password); // 普通解密
System.out.println("解密后1:" + new String(decryptResult));
}测试代码:EncrptDecrypt.java