slab内存分配------内存池mempool
一:概述
采用伙伴算法分配内存时,每次至少分配一个页面。但当请求分配的内存大小为几十个字节或几百个字节时应该如何处理?如何在一个页面中分配小的内存区,小内存区的分配所产生的内碎片又如何解决?Linux采用Slab。
Linux 所使用的 slab 分配器的基础是 Jeff Bonwick 为 SunOS 操作系统首次引入的一种算法。Jeff 的分配器是围绕对象缓存进行的。在内核中,会为有限的对象集(例如文件描述符和其他常见结构)分配大量内存。Jeff 发现对内核中普通对象进行初始化所需的时间超过了对其进行分配和释放所需的时间。因此他的结论是不应该将内存释放回一个全局的内存池,而是将内存保持为针对特定目而初始化的状态。例如,如果内存被分配给了一个互斥锁,那么只需在为互斥锁首次分配内存时执行一次互斥锁初始化函数(mutex_init)即可。后续的内存分配不需要执行这个初始化函数,因为从上次释放和调用析构之后,它已经处于所需的状态中了
Linux slab 分配器使用了这种思想和其他一些思想来构建一个在空间和时间上都具有高效性的内存分配器。
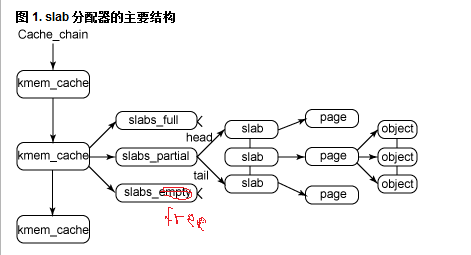
图 1 给出了 slab 结构的高层组织结构。在最高层是 cache_chain,这是一个 slab 缓存的链接列表。这对于 best-fit 算法非常有用,可以用来查找最适合所需要的分配大小的缓存(遍历列表)。cache_chain 的每个元素都是一个 kmem_cache 结构的引用(称为一个 cache)。它定义了一个要管理的给定大小的对象池。
每个缓存都包含了一个 slabs 列表,这是一段连续的内存块(通常都是页面)。存在 3 种 slab:
slabs_full:完全分配的 slab
slabs_partial:部分分配的 slab
slabs_free:空 slab,或者没有对象被分配
注意 slabs_free 列表中的 slab 是进行回收(reaping)的主要备选对象。正是通过此过程,slab 所使用的内存被返回给操作系统供其他用户使用。
slab 列表中的每个 slab 都是一个连续的内存块(一个或多个连续页),它们被划分成一个个对象。这些对象是从特定缓存中进行分配和释放的基本元素。注意 slab 是 slab 分配器进行操作的最小分配单位,因此如果需要对 slab 进行扩展,这也就是所扩展的最小值。通常来说,每个 slab 被分配为多个对象。
由于对象是从 slab 中进行分配和释放的,因此单个 slab 可以在 slab 列表之间进行移动。例如,当一个 slab 中的所有对象都被使用完时,就从 slabs_partial 列表中移动到 slabs_full 列表中。当一个 slab 完全被分配并且有对象被释放后,就从 slabs_full 列表中移动到 slabs_partial 列表中。当所有对象都被释放之后,就从 slabs_partial 列表移动到 slabs_free 列表中。
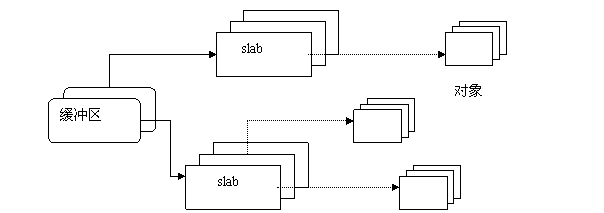
为了便于理解,在网上找了一个图,如下:
用于描述缓存的数据结构kmem_cache如下:
struct kmem_cache{
/* 1) per-cpu data, touched during every alloc/free */
struct array_cache *array[NR_CPUS];//array是一个指向数组的指针,每个数组项都对应于系统中的一个CPU。
每个数组项都包含了另一个指针,指向下文讨论的array_cache结构的实例
/* 2) Cache tunables. Protected by cache_chain_mutex */
unsigned int batchcount;
//指定了在每CPU列表为空的情况下,从缓存的slab中获取对象的数目。它还表示在缓存增长时分配的对象数目
unsigned int limit;
//limit指定了每CPU列表中保存的对象的最大数目,如果超出该值,内核会将batchcount个对象返回到slab
unsigned int shared;
unsigned int buffer_size;//指定了缓存中管理的对象的长度
u32 reciprocal_buffer_size;//buffer_size的倒数值,为了克服出发运算对性能的影响
/* 3) touched by every alloc & free from the backend */
unsigned int flags;
//是一个标志寄存器,定义缓存的全局性质,当前只有一个标志位,用于标记slab头得管理数据是在slab内还是外
unsigned int num;//保存了可以放入slab的对象的最大数目
/* 4) cache_grow/shrink */
/* order of pgs per slab (2^n) */
unsigned int gfporder;//指定了slab包含的页数目以2为底得对数
/* force GFP flags, e.g. GFP_DMA */
gfp_t gfpflags;//与伙伴系统交互时所提供的分配标识
size_t colour;//指定了颜色的最大数目
unsigned int colour_off;//是基本偏移量乘以颜色值获得的绝对偏移量
struct kmem_cache *slabp_cache;/如果slab头部的管理数据存储在slab外部,则slabp_cache指向分配所需内存的一般性
缓存;如果slab头部在slab上,则其为NULL
unsigned int slab_size;//slab管理区的大小
unsigned int dflags;//另一个标志集合,描述slab的“动态性质”,但目前还没有定义标志
/* constructor func */
void (*ctor)(struct kmem_cache *, void *);//创建高速缓存时的构造函数指针
/* 5) cache creation/removal */
const char *name;//缓存的名称
struct list_head next;//用于将kmem_cache的所有实例保存在全局链表cache_chain上
/* 6) statistics */
#if STATS//统计数据字段
unsigned long num_active;
unsigned long num_allocations;
unsigned long high_mark;
unsigned long grown;
unsigned long reaped;
unsigned long errors;
unsigned long max_freeable;
unsigned long node_allocs;
unsigned long node_frees;
unsigned long node_overflow;
atomic_t allochit;
atomic_t allocmiss;
atomic_t freehit;
atomic_t freemiss;
#endif
#if DEBUG
/*
* If debugging is enabled, then the allocator can add additional
* fields and/or padding to every object. buffer_size contains the total
* object size including these internal fields, the following two
* variables contain the offset to the user object and its size.
*/
int obj_offset;
int obj_size;
#endif
/*
* We put nodelists[] at the end of kmem_cache, because we want to size
* this array to nr_node_ids slots instead of MAX_NUMNODES
* (see kmem_cache_init())
* We still use [MAX_NUMNODES] and not [1] or [0] because cache_cache
* is statically defined, so we reserve the max number of nodes.
*/
struct kmem_list3 *nodelists[MAX_NUMNODES];
//nodelists是一个数组,每个数组对应于系统中一个可能的内存结点。每个数组项都包含kmem_list3的一个实例
/*
* Do not add fields after nodelists[]
*/
} |
array_cache数据结构描述:
struct array_cache {
unsigned int avail;//本地高速缓存中可用的空闲对象数
unsigned int limit;//空闲对象的上限
unsigned int batchcount;//一次转入和转出的对象数量
unsigned int touched;//标识本地CPU最近是否被使用
spinlock_t lock;
void *entry[];//这是一个伪数组,便于对后面用于跟踪空闲对象的指针数组的访问
}; |
kmem_list3数据结构描述:
struct kmem_list3 {
struct list_head slabs_partial;//部分空闲的slab链表
struct list_head slabs_full;//非空闲的slab链表
struct list_head slabs_free;//完全空闲的slab链表
unsigned long free_objects;//部分空闲的slab链表和完全空闲的slab链表中空闲对象的总数
unsigned int free_limit;//指定了所有slab上容许未使用对象的最大数目
unsigned int colour_next;//内核建立的下一个slab的颜色
spinlock_t list_lock;
struct array_cache *shared;//结点内共享
struct array_cache **alien;//在其他结点上
unsigned long next_reap;//定义了内核在两次尝试收缩缓存之间,必须经过的时间间隔
int free_touched;//表示缓存是否是活动的
}; |
slab数据结构描述:
struct slab {
struct list_head list;
unsigned long colouroff;//该Slab上着色区的大小
void *s_mem;//指向对象区的起点
unsigned int inuse;//Slab中所分配对象的个数
kmem_bufctl_t free;//指明了空闲对象链中的第一个对象,kmem_bufctl_t其实是一个整数
unsigned short nodeid;//结点标识号
}; |
其实slab机制的简介表示如下图所示:
slab内的结构如下图所示:
每个Slab的首部都有一个小小的区域是不用的,称为“着色区(coloring area)”。着色区的大小使Slab中的每个对象的起始地址都按高速缓存中的”缓存行(cache line)”大小进行对齐(80386的一级高速缓存行大小为16字节,Pentium为32字节)。因为Slab是由1个页面或多个页面(最多为32)组成,因此,每个Slab都是从一个页面边界开始的,它自然按高速缓存的缓冲行对齐。但是,Slab中的对象大小不确定,设置着色区的目的就是将Slab中第一个对象的起始地址往后推到与缓冲行对齐的位置。因为一个缓冲区中有多个Slab,因此,应该把每个缓冲区中的各个Slab着色区的大小尽量安排成不同的大小,这样可以使得在不同的Slab中,处于同一相对位置的对象,让它们在高速缓存中的起始地址相互错开,这样就可以改善高速缓存的存取效率。
每个Slab上最后一个对象以后也有个小小的废料区是不用的,这是对着色区大小的补偿,其大小取决于着色区的大小,以及Slab与其每个对象的相对大小。但该区域与着色区的总和对于同一种对象的各个Slab是个常数。
每个对象的大小基本上是所需数据结构的大小。只有当数据结构的大小不与高速缓存中的缓冲行对齐时,才增加若干字节使其对齐。所以,一个Slab上的所有对象的起始地址都必然是按高速缓存中的缓冲行对齐的。
与传统的内存管理模式相比, slab 缓存分配器提供了很多优点。首先,内核通常依赖于对小对象的分配,它们会在系统生命周期内进行无数次分配。slab 缓存分配器通过对类似大小的对象进行缓存而提供这种功能,从而避免了常见的碎片问题。slab 分配器还支持通用对象的初始化,从而避免了为同一目而对一个对象重复进行初始化。最后,slab 分配器还可以支持硬件缓存对齐和着色,这允许不同缓存中的对象占用相同的缓存行,从而提高缓存的利用率并获得更好的性能。
二:初始化
初看起来,slab系统的初始化不是特别麻烦,因为伙伴系统已经完全启用,内核没有受到其他特别的限制。尽管如此,由于slab分配器的结构所致,这里有一个鸡与蛋的问题。为初始化slab数据结构,内核需要若干远小于一整页的内存块,这些最适合由kmalloc分配。这里是关键所在:只有在slab系统已经启用之后,才能使用kmalloc。更确切的说,该问题涉及kmalloc的Per-CPU缓存的初始化。在这些缓存能初始化之前,kmalloc必须可以用来分配所需的内存空间,而kmalloc自身也处于初始化的过程中,所以这是一个不可能完成的场景,内核必须借助一些技巧。内核中使用kmem_cache_init函数用于初始化slab分配器。它在内核初始化阶段(start_kernel)、伙伴系统启用之后调用。kmem_cache_init采用了一个多步骤的过程,逐步激活slab分配器。
kmem_cache_init可以分为六个阶段:
第一个阶段:是根据kmem_cache来设置cache_cache的字段值;
第二个阶段:首先是创建arraycache_init对应的高速缓存,同时也是在这个kmem_cache_create的调用过程中,创建了用于保存cache的kmem_cache的slab,并初始化了slab中的各个对象;
第三个阶段:创建kmem_list3对应的高速缓存,在这里要注意的一点是,如果sizeof(arraycache_t)和sizeof(kmem_list3)的大小一样大,那么就不再使用kmem_cache_create来为kmem_list3创建cache了,因为如果两者相等的话,两者就可以使用同一个cache;
第四个阶段:创建并初始化所有的通用cache和dma cache;
第五个阶段:创建两个arraycache_init对象,分别取代cache_cache中的array字段和malloc_sizes[INDEX_AC].cs_cachep->array字段;
第六个阶段:创建两个kmem_list3对象,取代cache_cache中的kmem_list3字段和malloc_sizes[INDEX_AC].cs_cachep->nodelist3字段.如此一来,经过上面的六个阶段后,所有的初始化工作基本完成了。
kmem_cache_init源代码详细分析如下:
void __init kmem_cache_init(void)
{
size_t left_over;
struct cache_sizes *sizes;
struct cache_names *names;
int i;
int order;
int node;
/* 在slab初始化好之前,无法通过kmalloc分配初始化过程中必要的一些对象 ,只能使用静态的全局变量
,待slab初始化后期,再使用kmalloc动态分配的对象替换全局变量 */
/* 如前所述,先借用全局变量initkmem_list3表示的slab三链
,每个内存节点对应一组slab三链。initkmem_list3是个slab三链数组,对于每个内存节点,包含三组
:struct kmem_cache的slab三链、struct arraycache_init的slab 三链、struct kmem_list3的slab三链 。
这里循环初始化所有内存节点的所有slab三链 */
if (num_possible_nodes() == 1) {
use_alien_caches = 0;
numa_platform = 0;
}
for (i = 0; i < NUM_INIT_LISTS; i++) {//初始化所有node的所有slab中的三个链表
kmem_list3_init(&initkmem_list3[i]);
if (i < MAX_NUMNODES)
cache_cache.nodelists[i] = NULL;//全局静态变量cache_cache,这个变量是用来管理所有缓存的kmem_cache的,
也就是说,在初始化阶段,将会创建一个slab,用来存放所有缓存的kmem_cache
}
/*
* Fragmentation resistance on low memory - only use bigger
* page orders on machines with more than 32MB of memory.
*/
if (num_physpages > (32 << 20) >> PAGE_SHIFT)//num_physpages是记录系统实际存在物理内存的总页数,如果大于32M
slab_break_gfp_order = BREAK_GFP_ORDER_HI;//才可以创建高阶指数内存页数的高速缓存内存对象
/* Bootstrap is tricky, because several objects are allocated
* from caches that do not exist yet:
* 1) initialize the cache_cache cache: it contains the struct
* kmem_cache structures of all caches, except cache_cache itself:
* cache_cache is statically allocated.
* Initially an __init data area is used for the head array and the
* kmem_list3 structures, it's replaced with a kmalloc allocated
* array at the end of the bootstrap.
* 2) Create the first kmalloc cache.
* The struct kmem_cache for the new cache is allocated normally.
* An __init data area is used for the head array.
* 3) Create the remaining kmalloc caches, with minimally sized
* head arrays.
* 4) Replace the __init data head arrays for cache_cache and the first
* kmalloc cache with kmalloc allocated arrays.
* 5) Replace the __init data for kmem_list3 for cache_cache and
* the other cache's with kmalloc allocated memory.
* 6) Resize the head arrays of the kmalloc caches to their final sizes.
*/
node = numa_node_id();//获取当前的内存结点号
//第一步,创建struct kmem_cache所在的cache,由全局变量cache_cache指向,这里只是初始化数据结构,并未真正创建这些
对象,要待分配时才创建。全局变量cache_chain是内核slab cache链表的表头
INIT_LIST_HEAD(&cache_chain);//初始化保存所有slab cache的全局链表cache_chain
list_add(&cache_cache.next, &cache_chain);//将cache_cache加入到slab cache链表
cache_cache.colour_off = cache_line_size();//设置cache着色基本单位为cache line的大小:32字节
cache_cache.array[smp_processor_id()] = &initarray_cache.cache;
//初始化cache_cache的local cache,同样这里也不能使用kmalloc,需要使用静态分配的全局变量initarray_cache
cache_cache.nodelists[node] = &initkmem_list3[CACHE_CACHE];//初始化slab链表 ,用全局变量
/*
* struct kmem_cache size depends on nr_node_ids, which
* can be less than MAX_NUMNODES.
*/
cache_cache.buffer_size = offsetof(struct kmem_cache, nodelists) + nr_node_ids * sizeof(struct kmem_list3 *);
//buffer_size保存slab中对象的大小,这里是计算struct kmem_cache的大小,nodelists是最后一个成员,nr_node_ids
保存内存节点个数,UMA为1,所以nodelists偏移加上1个struct kmem_list3 的大小即为struct kmem_cache的大小
#if DEBUG
cache_cache.obj_size = cache_cache.buffer_size;
#endif
cache_cache.buffer_size = ALIGN(cache_cache.buffer_size,
cache_line_size());//将对象大小与cache line大小对齐
cache_cache.reciprocal_buffer_size =
reciprocal_value(cache_cache.buffer_size);//计算对象大小的倒数,用于计算对象在slab中的索引
for (order = 0; order < MAX_ORDER; order++) {
cache_estimate(order, cache_cache.buffer_size,
cache_line_size(), 0, &left_over, &cache_cache.num);//计算cache_cache中的对象数目
if (cache_cache.num)//num不为0意味着创建struct kmem_cache对象成功,退出
break;
}
BUG_ON(!cache_cache.num);
cache_cache.gfporder = order;//gfporder表示本slab包含2^gfporder个页面
cache_cache.colour = left_over / cache_cache.colour_off;//着色区的大小,以colour_off为单位
cache_cache.slab_size = ALIGN(cache_cache.num * sizeof(kmem_bufctl_t) +
sizeof(struct slab), cache_line_size());//slab管理对象的大小
/* 2+3) create the kmalloc caches */
sizes = malloc_sizes;//malloc_sizes保存大小
names = cache_names;//cache_names保存cache名
/*
* Initialize the caches that provide memory for the array cache and the
* kmem_list3 structures first. Without this, further allocations will
* bug.
*/
//首先创建struct array_cache和struct kmem_list3所用的general cache,它们是后续初始化动作的基础
sizes[INDEX_AC].cs_cachep = kmem_cache_create(names[INDEX_AC].name,
sizes[INDEX_AC].cs_size,
ARCH_KMALLOC_MINALIGN,
ARCH_KMALLOC_FLAGS|SLAB_PANIC,
NULL);//INDEX_AC是计算local cache所用的struct arraycache_init对象在kmalloc size中的索引,
即属于哪一级别大小的general cache,创建此大小级别的cache为local cache所用
if (INDEX_AC != INDEX_L3) {//如果struct kmem_list3和struct arraycache_init对应的kmalloc size索引不同,
即大小属于不同的级别,则创建struct kmem_list3所用的cache,否则共用一个cache
sizes[INDEX_L3].cs_cachep =
kmem_cache_create(names[INDEX_L3].name,
sizes[INDEX_L3].cs_size,
ARCH_KMALLOC_MINALIGN,
ARCH_KMALLOC_FLAGS|SLAB_PANIC,
NULL);
}
slab_early_init = 0;//创建完上述两个general cache后,slab early init阶段结束,在此之前,不允许创建外置式slab
while (sizes->cs_size != ULONG_MAX) {//循环创建kmalloc各级别的general cache
/*
* For performance, all the general caches are L1 aligned.
* This should be particularly beneficial on SMP boxes, as it
* eliminates "false sharing".
* Note for systems short on memory removing the alignment will
* allow tighter packing of the smaller caches.
*/
if (!sizes->cs_cachep) {
//某级别的kmalloc cache还未创建,创建之,struct kmem_list3和struct arraycache_init对应的cache已经创建过了
sizes->cs_cachep = kmem_cache_create(names->name,
sizes->cs_size,
ARCH_KMALLOC_MINALIGN,
ARCH_KMALLOC_FLAGS|SLAB_PANIC,
NULL);
}
#ifdef CONFIG_ZONE_DMA
sizes->cs_dmacachep = kmem_cache_create(
names->name_dma,
sizes->cs_size,
ARCH_KMALLOC_MINALIGN,
ARCH_KMALLOC_FLAGS|SLAB_CACHE_DMA|
SLAB_PANIC,
NULL);
#endif
sizes++;
names++;
}//至此,kmalloc general cache已经创建完毕,可以拿来使用了
/* 4) Replace the bootstrap head arrays */
{//第四步,用kmalloc对象替换静态分配的全局变量。到目前为止一共使用了两个全局local cache,一个是cache_cache的
local cache指向initarray_cache.cache,另一个是malloc_sizes[INDEX_AC].cs_cachep的local cache指向
initarray_generic.cache,参见setup_cpu_cache函数。这里替换它们。
struct array_cache *ptr;
ptr = kmalloc(sizeof(struct arraycache_init), GFP_KERNEL);//申请cache_cache所用local cache的空间
local_irq_disable();
BUG_ON(cpu_cache_get(&cache_cache) != &initarray_cache.cache);
memcpy(ptr, cpu_cache_get(&cache_cache),
sizeof(struct arraycache_init));//复制原cache_cache的local cache,即initarray_cache,到新的位置
/*
* Do not assume that spinlocks can be initialized via memcpy:
*/
spin_lock_init(&ptr->lock);
cache_cache.array[smp_processor_id()] = ptr;//cache_cache的local cache指向新的位置
local_irq_enable();
ptr = kmalloc(sizeof(struct arraycache_init), GFP_KERNEL);
//申请malloc_sizes[INDEX_AC].cs_cachep所用local cache的空间
local_irq_disable();
BUG_ON(cpu_cache_get(malloc_sizes[INDEX_AC].cs_cachep)
!= &initarray_generic.cache);
memcpy(ptr, cpu_cache_get(malloc_sizes[INDEX_AC].cs_cachep),
sizeof(struct arraycache_init));//复制原local cache到新分配的位置,注意此时local cache的大小是固定的
/*
* Do not assume that spinlocks can be initialized via memcpy:
*/
spin_lock_init(&ptr->lock);
malloc_sizes[INDEX_AC].cs_cachep->array[smp_processor_id()] =
ptr;
local_irq_enable();
}
/* 5) Replace the bootstrap kmem_list3's */
{//第五步,与第四步类似,用kmalloc的空间替换静态分配的slab三链
int nid;
/* Replace the static kmem_list3 structures for the boot cpu */
init_list(&cache_cache, &initkmem_list3[CACHE_CACHE], node);//复制struct kmem_cache的slab三链
for_each_online_node(nid) {
init_list(malloc_sizes[INDEX_AC].cs_cachep,
&initkmem_list3[SIZE_AC + nid], nid);//复制struct arraycache_init的slab三链
if (INDEX_AC != INDEX_L3) {
init_list(malloc_sizes[INDEX_L3].cs_cachep,
&initkmem_list3[SIZE_L3 + nid], nid);//复制struct kmem_list3的slab三链
}
}
}
/* 6) resize the head arrays to their final sizes */
{//初始化阶段local cache的大小是固定的,要根据对象大小重新计算
struct kmem_cache *cachep;
mutex_lock(&cache_chain_mutex);
list_for_each_entry(cachep, &cache_chain, next)
if (enable_cpucache(cachep))
BUG();
mutex_unlock(&cache_chain_mutex);
}
/* Annotate slab for lockdep -- annotate the malloc caches */
init_lock_keys();
/* Done! */
g_cpucache_up = FULL;//大功告成,general cache终于全部建立起来了
/*
* Register a cpu startup notifier callback that initializes
* cpu_cache_get for all new cpus
*/
register_cpu_notifier(&cpucache_notifier);//注册cpu up回调函数,cpu up时配置local cache
/*
* The reap timers are started later, with a module init call: That part
* of the kernel is not yet operational.
*/
} |
内存池:mempool
内存池(Memery Pool)技术是在真正使用内存之前,先申请分配一定数量的、大小相等(一般情况下)的内存块留作备用。当有新的内存需求时,就从内存池中分出一部分内存块,若内存块不够再继续申请新的内存。这样做的一个显著优点是尽量避免了内存碎片,使得内存分配效率得到提升。
- typedef struct mempool_s {
- spinlock_t lock; /*保护内存池的自旋锁*/
- int min_nr; /*内存池中最少可分配的元素数目*/
- int curr_nr; /*尚余可分配的元素数目*/
- void **elements; /*指向元素池的指针*/
- void *pool_data; /*内存源,即池中元素真实的分配处*/
- mempool_alloc_t *alloc; /*分配元素的方法*/
- mempool_free_t *free; /*回收元素的方法*/
- wait_queue_head_t wait; /*被阻塞的等待队列*/
- } mempool_t;
- mempool_t *mempool_create(int min_nr, mempool_alloc_t *alloc_fn,
- mempool_free_t *free_fn, void *pool_data)
- {
- return mempool_create_node(min_nr,alloc_fn,free_fn, pool_data,-1);
- }
- void mempool_destroy(mempool_t *pool)
- {
- while (pool->curr_nr) {
- void *element = remove_element(pool);
- pool->free(element, pool->pool_data);
- }
- kfree(pool->elements);
- kfree(pool);
- }
- void * mempool_alloc(mempool_t *pool, gfp_t gfp_mask){
- ......
- element = pool->alloc(gfp_temp, pool->pool_data);
- if (likely(element != NULL))
- return element;
-
- spin_lock_irqsave(&pool->lock, flags);
- if (likely(pool->curr_nr)) {
- element = remove_element(pool);/*从内存池中提取一个对象*/
- spin_unlock_irqrestore(&pool->lock, flags);
- /* paired with rmb in mempool_free(), read comment there */
- smp_wmb();
- return element;
- }
- ......
- }
- init_wait(&wait);
- prepare_to_wait(&pool->wait, &wait, TASK_UNINTERRUPTIBLE);
- spin_unlock_irqrestore(&pool->lock, flags);
- io_schedule_timeout(5*HZ);
- finish_wait(&pool->wait, &wait);
- void mempool_free(void *element, mempool_t *pool)
- {
- if (pool->curr_nr < pool->min_nr) {
- spin_lock_irqsave(&pool->lock, flags);
- if (pool->curr_nr < pool->min_nr) {
- add_element(pool, element);
- spin_unlock_irqrestore(&pool->lock, flags);
- wake_up(&pool->wait);
- return;
- }
- spin_unlock_irqrestore(&pool->lock, flags);
- }
- pool->free(element, pool->pool_data);
- }
- void *mempool_alloc_slab(gfp_t gfp_mask, void *pool_data)
- {
- struct kmem_cache *mem = pool_data;
- return kmem_cache_alloc(mem, gfp_mask);
- }
- void mempool_free_slab(void *element, void *pool_data)
- {
- struct kmem_cache *mem = pool_data;
- kmem_cache_free(mem, element);
- }
-
- void *mempool_kmalloc(gfp_t gfp_mask, void *pool_data)
- {
- size_t size = (size_t)pool_data;
- return kmalloc(size, gfp_mask);
- }
- void mempool_kfree(void *element, void *pool_data)
- {
- kfree(element);
- }
-
- void *mempool_alloc_pages(gfp_t gfp_mask, void *pool_data)
- {
- int order = (int)(long)pool_data;
- return alloc_pages(gfp_mask, order);
- }
- void mempool_free_pages(void *element, void *pool_data)
- {
- int order = (int)(long)pool_data;
- __free_pages(element, order);
- }