Regex - C++11, 6 of n
R"delim(...)delim", where delim is a character sequence of at most 16 basic characters except the backslash, whitespace and parentheses.
2) Note regex algorithm is greedy
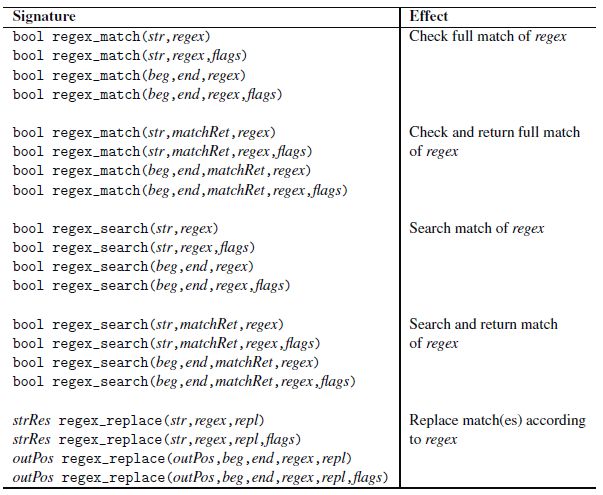
3) Main interfaces
a. basic_regex<> template: holds the regular expression pattern (predefined regex, wregex)
b. match_results<> template: carry back the match results (predefined s/c/ws/wcmatch, s for string, c for const char*)
c. regex_match(): checks whether the whole character sequence matches a regular expression
d. regex_search(): checks whether the character sequence partially matches a regular expression
f. regex_replace(): replace character sequences that match a regular expression.
4) Basic matching examples
regex reg1("<.*>.*</.*>");
bool found = regex_match ("<tag>value</tag>", reg1);
regex reg2("<(.*)>.*</\\1>"); // grouping and forward referencing
found = regex_match ("<tag>value</tag>", reg2);
// use grep grammer
regex reg3("<\\(.*\\)>.*</\\1>",regex_constants::grep);
found = regex_match ("<tag>value</tag>", reg3);
found = regex_match ("XML tag: <tag>value</tag>", regex(R"#<(.*)>.*</\1>#")); // fails to match
found = regex_search ("XML tag: <tag>value</tag>", regex(R"#<(.*)>.*</\1>#")); // match
5) match_results carry back the detail match result
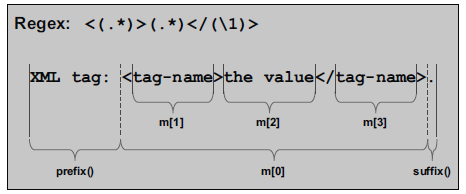
match_results object m has a state which provides the following interface:
In general, the match_results object contains:
– A sub_match object m[0] for all the matched characters
– A prefix(), a sub_match object that represents all characters before the first matched character
– A suffix(), a sub_match object that represents all characters after the last matched character
• In addition, for any capture group, you have access to a corresponding sub_match object m[n].
• size() yields the number of sub_match objects (including m[0]).
• All sub_match objects are derived from pair<> and have the position of the first character as
member first and the position after the last character as member second. In addition, str()
yields the characters as a string, length() yields the number of characters, operator << writes
the characters to a stream, and an implicit type conversion to a string is defined.
In addition, the match_results object as a whole provides:
– member function str() to yield the matched string as a whole (calling str() or str(0))
or the nth matched substring (calling str(n)), which is empty if no matched substring exists
(thus, passing an n greater than size() is valid)
– member function length() to yield the length of the matched string as a whole (calling
length() or length(0)) or the length of the nth matched substring (calling length(n)),
which is 0 if no matched substring exists (thus, passing an n greater than size() is valid)
– member function position() to yield the position of the matched string as a whole (calling
position() or position(0)) or the position of the nth matched substring (calling
length(n))
– member functions begin(), cbegin(), end(), and cend() to iterate over the sub_match
objects m[0] to m[n]
6) regex_iterator<>, predefinesare s/c/w/wc regex_iterator
Examples:
string data = "<person>\n"
" <first>Nico</first>\n"
" <last>Josuttis</last>\n"
"</person>\n";
regex reg("<(.*)>(.*)</(\\1)>");
// iterate over all matches (using a regex_iterator):
sregex_iterator pos(data.cbegin(),data.cend(),reg);
sregex_iterator end;
for ( ; pos != end ; ++pos ) {
cout << "match: " << pos->str() << endl;
cout << " tag: " << pos->str(1) << endl;
cout << " value: " << pos->str(2) << endl;
}
// use a regex_iterator to process each matched substring as element in an algorithm:
sregex_iterator beg(data.cbegin(),data.cend(),reg);
for_each (beg,end,[](const smatch& m) {
cout << "match: " << m.str() << endl;
cout << " tag: " << m.str(1) << endl;
cout << " value: " << m.str(2) << endl;
});
7) regex_token_iterator<> tokenizer, predefines are s/c/w/wc regex_token_iterator
Example:
string data = "<person>\n"
"<first>Nico</first>\n"
"<last>Josuttis</last>\n"
"</person>\n";
regex reg("<(.*)>(.*)</(\\1)>");
// iterate over all matches (using a regex_token_iterator):
sregex_token_iterator pos(data.cbegin(),data.cend(), // sequence
reg, // token separator
{0,2}); // 0: full match, 2: second substring
sregex_token_iterator end;
for ( ; pos != end ; ++pos ) {
cout << "match: " << pos->str() << endl;
}
cout << endl;
string names = "nico, jim, helmut, paul, tim, john paul, rita";
regex sep("[ \t\n]*[,;.][ \t\n]*"); // separated by , ; or . and spaces
sregex_token_iterator p(names.cbegin(),names.cend(), // sequence
sep, // separator
-1); // -1: values between separators
sregex_token_iterator e;
for ( ; p != end ; ++p ) {
cout << "name: " << *p << endl;
}
8) regex_replace
string data = "<person>\n"
"<first>Nico</first>\n"
"<last>Josuttis</last>\n"
"</person>\n";
regex reg("<(.*)>(.*)</(\\1)>");
// print data with replacement for matched patterns
cout << regex_replace (data, // data
reg, // regular expression
"<$1 value=\"$2\"/>") // replacement
<< endl;
// same using sed syntax
cout << regex_replace (data, // data
reg, // regular expression
"<\\1 value=\"\\2\"/>", // replacement
regex_constants::format_sed) // format flag
<< endl;
// use iterator interface, and
// - format_no_copy: don’t copy characters that don’t match
// - format_first_only: replace only the first match found
string res2;
regex_replace (back_inserter(res2), // destination
data.begin(), data.end(), // source range
reg, // regular expression
"<$1 value=\"$2\"/>", // replacement
regex_constants::format_no_copy | regex_constants::format_first_only);// format flags
cout << res2 << endl;

Regex Replacement Symbols
9) Regex flags
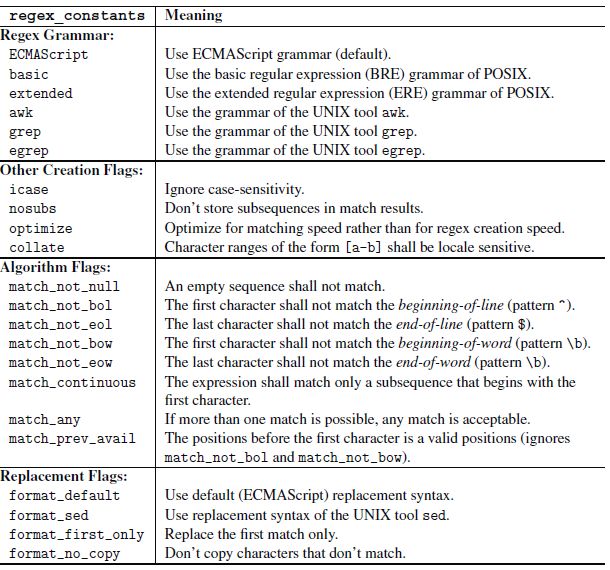
Examples:
// case-insensitive find LaTeX index entries
string pat1 = R"(\\.*index\{([^}]*)\})"; // first capture group
string pat2 = R"(\\.*index\{(.*)\}\{(.*)\})"; // 2nd and 3rd capture group
// grep and egrep can search for multiple regular expressions separated by '\n' at the same time
regex pat (pat1+"\n"+pat2, regex_constants::egrep|regex_constants::icase);
// initialize string with characters from standard input:
string data((istreambuf_iterator<char>(cin)), istreambuf_iterator<char>());
// search and print matching index entries:
smatch m;
auto pos = data.cbegin();
auto end = data.cend();
for ( ; regex_search (pos,end,m,pat); pos = m.suffix().first) {
cout << "match: " << m.str() << endl;
cout << " val: " << m.str(1)+m.str(2) << endl;
cout << " see: " << m.str(3) << endl;
}
Input samples:
\chapter{The Standard Template Library}
\index{STL}%
\MAININDEX{standard template library}%
\SEEINDEX{standard template library}{STL}%
This is the basic chapter about the STL.
\section{STL Components}
\hauptindex{STL, introduction}%
The \stl{} is based on the cooperation of
...
10) The regex ECMAScript grammar and special chars
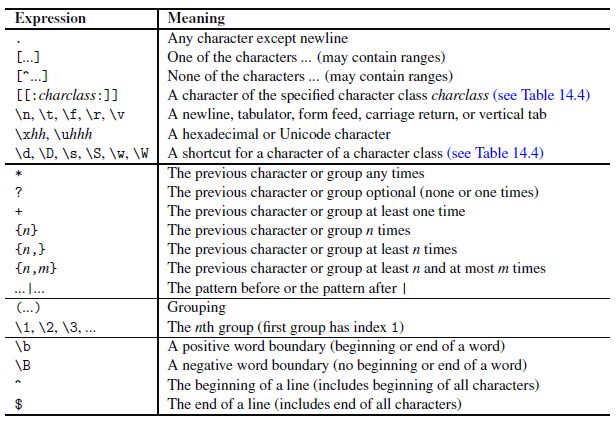
ECMAScript grammar
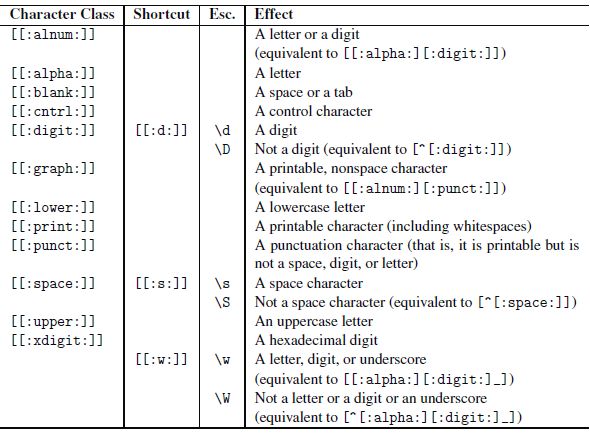
Character classes in ECMAScript
(11) Grammar differences

(12) Regex exception
exception code to explanation string for debugging
template <typename T>
std::string regexCode (T code)
{
switch (code) {
case std::regex_constants::error_collate:
return "error_collate: regex has invalid collating element name";
case std::regex_constants::error_ctype:
return "error_ctype: regex has invalid character class name";
case std::regex_constants::error_escape:
return "error_escape: regex has invalid escaped char. or trailing escape";
case std::regex_constants::error_backref:
return "error_backref: regex has invalid back reference";
case std::regex_constants::error_brack:
return "error_brack: regex has mismatched ’[’ and ’]’";
case std::regex_constants::error_paren:
return "error_paren: regex has mismatched ’(’ and ’)’";
case std::regex_constants::error_brace:
return "error_brace: regex has mismatched ’{’ and ’}’";
case std::regex_constants::error_badbrace:
return "error_badbrace: regex has invalid range in {} expression";
case std::regex_constants::error_range:
return "error_range: regex has invalid character range, such as ’[b-a]’";
case std::regex_constants::error_space:
return "error_space: insufficient memory to convert regex into finite state";
case std::regex_constants::error_badrepeat:
return "error_badrepeat: one of *?+{ not preceded by valid regex";
case std::regex_constants::error_complexity:
return "error_complexity: complexity of match against regex over pre-set level";
case std::regex_constants::error_stack:
return "error_stack: insufficient memory to determine regex match";
}
return "unknown/non-standard regex error code";
}
int main()
{
try {
// initialize regular expression with invalid syntax:
regex pat ("\\\\.*index\\{([^}]*)\\}",
regex_constants::grep|regex_constants::icase);
...
}
catch (const regex_error& e) {
cerr << "regex_error: \n"
<< " what(): " << e.what() << "\n"
<< " code(): " << regexCode(e.code()) << endl;
}
}