But how to draw an arrowed line? We have to come back at school days, when we learn trigonometry.
Basics
With the function atan2 we can obtain the angle of the source line. Adding to this angle a defined sub-angle (arrow_degrees_) we can get the left and right angle of the arrow arms. With this two angles and using a defined lenght for the arrow arms (arrow_lenght_) we can finally achieve two points to use for perform drawing operations.
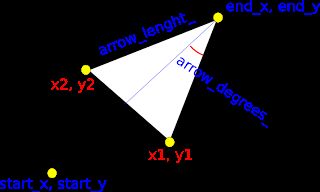
Now return to the future...we need to transform this on c++ code.
void calcVertexes(double start_x, double start_y, double end_x, double end_y, double& x1, double& y1, double& x2, double& y2) { double angle = atan2 (end_y - start_y, end_x - start_x) + M_PI; x1 = end_x + arrow_lenght_ * cos(angle - arrow_degrees_); y1 = end_y + arrow_lenght_ * sin(angle - arrow_degrees_); x2 = end_x + arrow_lenght_ * cos(angle + arrow_degrees_); y2 = end_y + arrow_lenght_ * sin(angle + arrow_degrees_); } Effective arrow object
We want to offer many kinds of arrows to the user, like on the wikipedia page for the symbol Arrow. I start to define this kind of arrows:
enum ArrowStyle { ARROW_OPEN, ARROW_SOLID, ARROW_SOLID_FILLED, ARROW_DIAMOND, ARROW_DIAMOND_FILLED, ARROW_CIRCLE, ARROW_CIRCLE_FILLED }; But we do not like to put an if-then-else evry time we need to draw the arrow. Is better to define an ArrowHead base class with an abstract method draw, and implements all different styles inheriting from the ArrowHead class.
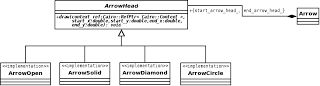
The ArrowHead class is the base class.
class ArrowHead { public: enum ArrowStyle { ARROW_OPEN, ARROW_SOLID, ARROW_SOLID_FILLED, ARROW_DIAMOND, ARROW_DIAMOND_FILLED, ARROW_CIRCLE, ARROW_CIRCLE_FILLED }; ArrowHead() : arrow_lenght_( 15 ), arrow_degrees_( 0.5 ) { } virtual ~ArrowHead() { } void calcVertexes(double start_x, double start_y, double end_x, double end_y, double& x1, double& y1, double& x2, double& y2) { double angle = atan2 (end_y - start_y, end_x - start_x) + M_PI; x1 = end_x + arrow_lenght_ * cos(angle - arrow_degrees_); y1 = end_y + arrow_lenght_ * sin(angle - arrow_degrees_); x2 = end_x + arrow_lenght_ * cos(angle + arrow_degrees_); y2 = end_y + arrow_lenght_ * sin(angle + arrow_degrees_); } virtual void draw(Cairo::RefPtr< Cairo::Context > context_ref, double start_x, double start_y, double end_x, double end_y) = 0; protected: double arrow_lenght_; double arrow_degrees_; }; The Arrow object has two arrow head, for draw the begin and the end arrow.
std::auto_ptr< ArrowHead > start_arrow_head_ptr_; std::auto_ptr< ArrowHead > end_arrow_head_ptr_; we can use this object for draw the arrow:
start_arrow_head_ptr_->draw (context_ref, x2, y2, x1, y1); end_arrow_head_ptr_->draw (context_ref, x1, y1, x2, y2); Now we need to implements all classes for the effective renderering. We can start with the ARROW_OPEN, like this:
We simply need to draw two lines, the first line from end_x, end_y to x1, y1 the second line from end_x, end_y to x2, y2.
class ArrowOpen : public ArrowHead { public: ArrowOpen() : ArrowHead(), line_color_( "black" ) { } virtual ~ArrowOpen() { } void draw(Cairo::RefPtr< Cairo::Context > context_ref, double start_x, double start_y, double end_x, double end_y) { double x1; double y1; double x2; double y2; calcVertexes (start_x, start_y, end_x, end_y, x1, y1, x2, y2); context_ref->set_source_rgb (line_color_.get_red_p(), line_color_.get_blue_p(), line_color_.get_green_p()); context_ref->move_to (end_x, end_y); context_ref->line_to (x1, y1); context_ref->stroke(); context_ref->move_to (end_x, end_y); context_ref->line_to (x2, y2); context_ref->stroke(); } protected: Gdk::Color line_color_; }; We can implement the ARROW_SOLID, like this:
In this case we need to draw a triangle using the three vertexes: end_x, end_y; x1, y1 and x2, y2.
class ArrowSolid : public ArrowHead { public: ArrowSolid() : ArrowHead(), line_color_( "black" ), fill_color_( "white" ) { } virtual ~ArrowSolid() { } void draw(Cairo::RefPtr< Cairo::Context > context_ref, double start_x, double start_y, double end_x, double end_y) { double x1; double y1; double x2; double y2; calcVertexes (start_x, start_y, end_x, end_y, x1, y1, x2, y2); context_ref->move_to (end_x, end_y); context_ref->line_to (x1, y1); context_ref->line_to (x2, y2); context_ref->close_path(); context_ref->set_source_rgb (line_color_.get_red_p(), line_color_.get_blue_p(), line_color_.get_green_p()); context_ref->stroke_preserve(); context_ref->set_source_rgb (fill_color_.get_red_p(), fill_color_.get_blue_p(), fill_color_.get_green_p()); context_ref->fill(); } protected: Gdk::Color line_color_; Gdk::Color fill_color_; }; We can implement the ARROW_DIAMOND, like this:
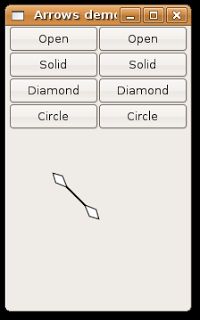
In this case we need four vertexes, but for now we have only three vertexes. The fourth vertex is also a point on the source line (so for the same angle of the source line), I use this method:
class ArrowDiamond : public ArrowHead { public: ArrowDiamond() : ArrowHead(), line_color_( "black" ), fill_color_( "white" ) { arrow_lenght_ = 10.0; } virtual ~ArrowDiamond() { } void draw(Cairo::RefPtr< Cairo::Context > context_ref, double start_x, double start_y, double end_x, double end_y) { double angle = atan2 (end_y - start_y, end_x - start_x) + M_PI; double x1 = end_x + arrow_lenght_ * cos(angle - arrow_degrees_); double y1 = end_y + arrow_lenght_ * sin(angle - arrow_degrees_); double x2 = end_x + arrow_lenght_ * cos(angle + arrow_degrees_); double y2 = end_y + arrow_lenght_ * sin(angle + arrow_degrees_); double x3 = end_x + arrow_lenght_ * 2 * cos(angle); double y3 = end_y + arrow_lenght_ * 2 * sin(angle); context_ref->move_to (end_x, end_y); context_ref->line_to (x1, y1); context_ref->line_to (x3, y3); context_ref->line_to (x2, y2); context_ref->close_path(); context_ref->set_source_rgb (line_color_.get_red_p(), line_color_.get_blue_p(), line_color_.get_green_p()); context_ref->stroke_preserve(); context_ref->set_source_rgb (fill_color_.get_red_p(), fill_color_.get_blue_p(), fill_color_.get_green_p()); context_ref->fill(); } protected: Gdk::Color line_color_; Gdk::Color fill_color_; }; The last implementation is the ARROW_CIRCLE, like this:
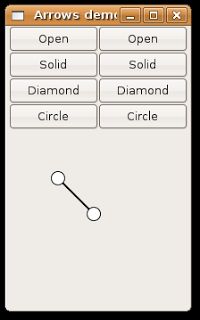
For draw a circle we need to have the center and the radius. We can define a radius (using arrow_lenght_) and then put the center on the source line.
class ArrowCircle : public ArrowHead { public: ArrowCircle() : ArrowHead(), line_color_( "black" ), fill_color_( "white" ) { arrow_lenght_ = 7.0; } virtual ~ArrowCircle() { } void draw(Cairo::RefPtr< Cairo::Context > context_ref, double start_x, double start_y, double end_x, double end_y) { double angle = atan2 (end_y - start_y, end_x - start_x) + M_PI; double xc = end_x + arrow_lenght_ * cos(angle); double yc = end_y + arrow_lenght_ * sin(angle); context_ref->arc (xc, yc, arrow_lenght_, 0.0, 2 * M_PI); context_ref->set_source_rgb (line_color_.get_red_p(), line_color_.get_blue_p(), line_color_.get_green_p()); context_ref->stroke_preserve(); context_ref->set_source_rgb (fill_color_.get_red_p(), fill_color_.get_blue_p(), fill_color_.get_green_p()); context_ref->fill(); } protected: Gdk::Color line_color_; Gdk::Color fill_color_; }; Now we need only two functions for set the begin and end arrow style:
void CairoArea::setStartArrowStyle(ArrowHead::ArrowStyle style) { switch (style) { case ArrowHead::ARROW_OPEN: start_arrow_head_ptr_ = std::auto_ptr< ArrowHead >( new ArrowOpen() ); break; case ArrowHead::ARROW_SOLID_FILLED: start_arrow_head_ptr_ = std::auto_ptr< ArrowHead >( new ArrowSolid() ); break; case ArrowHead::ARROW_DIAMOND_FILLED: start_arrow_head_ptr_ = std::auto_ptr< ArrowHead >( new ArrowDiamond() ); break; case ArrowHead::ARROW_CIRCLE_FILLED: start_arrow_head_ptr_ = std::auto_ptr< ArrowHead >( new ArrowCircle() ); break; } } void CairoArea::setEndArrowStyle(ArrowHead::ArrowStyle style) { switch (style) { case ArrowHead::ARROW_OPEN: end_arrow_head_ptr_ = std::auto_ptr< ArrowHead >( new ArrowOpen() ); break; case ArrowHead::ARROW_SOLID_FILLED: end_arrow_head_ptr_ = std::auto_ptr< ArrowHead >( new ArrowSolid() ); break; case ArrowHead::ARROW_DIAMOND_FILLED: end_arrow_head_ptr_ = std::auto_ptr< ArrowHead >( new ArrowDiamond() ); break; case ArrowHead::ARROW_CIRCLE_FILLED: end_arrow_head_ptr_ = std::auto_ptr< ArrowHead >( new ArrowCircle() ); break; } }