R3下远程线程注入/IAT Hook
先上程序,然后慢慢解释
// remoteIATHook.cpp : Defines the entry point for the console application.
//
#include "stdafx.h"
#include <stdio.h>
#include <windows.h>
#include <tlhelp32.h>
#include <assert.h>
#pragma comment(lib,"user32.lib")
#define OPENPROCESSPROITY PROCESS_CREATE_THREAD|PROCESS_QUERY_INFORMATION|PROCESS_VM_OPERATION|PROCESS_VM_WRITE|PROCESS_VM_READ
typedef HMODULE (*load_GetModuleHandle)(char*);
typedef BOOL (*load_VirtualProtect)(LPVOID,SIZE_T,DWORD,PDWORD);
typedef SIZE_T (*load_VirtualQuery)(LPCVOID,PMEMORY_BASIC_INFORMATION,SIZE_T);
typedef struct InjCode
{
load_GetModuleHandle ldGetModuleHandle;
load_VirtualProtect ldVirtualProtect;
load_VirtualQuery ldVirtualQuery;
DWORD imageBase;
char dllName[32];
DWORD dllNameLen;
char funcName[32];
DWORD funcNameLen;
//用于计算RemotePrimeFunc与IATFuncLocate的距离
DWORD IATFuncLocateAddr;
//IAT中API函数原跳转地址
DWORD origFuncAddr;
//IAT中API函数新跳转地址
DWORD newFuncAddr;
DWORD currFuncAddr;
}InjCode;
DWORD* IATFuncLocate(DWORD procBaseAddr,char* targetDllName,DWORD dllLen,char* targetFuncName,DWORD funcLen);
//0x09
DWORD origFuncAddr;
DWORD myMessageBox()
{
DWORD distLab1,distLab2;
DWORD curLab1,curLab2;
DWORD currAddr;
__asm
{
//jmp跳转到标号到没事 用的是相对偏移
jmp Lab2;
}
//下面的无效指令预留一部分空间 由RemotePrimeFunc
//填入被Hook的API的入口
Lab1:
__asm
{
_emit 0x90;
_emit 0x90;
_emit 0x90;
_emit 0x90;
_emit 0x90;
_emit 0xcc;
_emit 0xcc;
}
Lab2:
/*Audit begin*/
int i=0;
int sum=0;
for(;i<10;i++)
{
sum += i;
}
//系统api要通过LoadLibrary加载,否则必然出错
/*Audit end*/
//准备返回 返回前要重定位Lab
//跳转到Hook以前的API代码内,保存在Lab1处4个字节
LabReloc:
__asm
{
lea eax,Lab1;
sub eax,myMessageBox;
mov distLab1,eax;
lea eax,Lab2;
sub eax,myMessageBox;
mov distLab2,eax;
//为了获得当前指令地址
_emit 0xe8;
_emit 0x00;
_emit 0x00;
_emit 0x00;
_emit 0x00;
//当前地址
pop eax;
//VirtualAllocEx分配的地址好像低2B都是0x00
and eax,0xFFFF0000
mov currAddr,eax;
}
curLab1 = currAddr+distLab1;
curLab2 = currAddr+distLab2;
__asm
{
mov eax,curLab1;
mov eax,[eax];
call eax;
}
}
DWORD myMessageBoxEnd()
{
return 0;
}
DWORD _stdcall RemotePrimeFunc(void* args)
{
DWORD dist;
char* funcName;
DWORD funcNameLen;
char* dllName;
DWORD dllNameLen;
DWORD distLab1,curLab1;
DWORD distLab2,curLab2;
InjCode* injCode = (InjCode*)args;
injCode->imageBase = (DWORD)(injCode->ldGetModuleHandle)(NULL);
funcName = injCode->funcName;
funcNameLen = injCode->funcNameLen;
dllName = injCode->dllName;
dllNameLen = injCode->dllNameLen;
DWORD currFuncAddr = injCode->currFuncAddr;
//函数IATFuncLocate
DWORD IATFuncLocateAddr = injCode->IATFuncLocateAddr;
PIMAGE_DOS_HEADER pDos;
//IAT表中的元素的地址
DWORD funcAddrInIAt=0;
//调用结束injCode->ret存放了主程序的imageBase:MZ...
pDos = (PIMAGE_DOS_HEADER)injCode->imageBase;//0x5a4d
__asm
{
lea eax,Lab1;
sub eax,RemotePrimeFunc;
mov distLab1,eax;
lea eax,Lab2;
sub eax,RemotePrimeFunc;
mov distLab2,eax;
}
curLab1 = injCode->currFuncAddr+distLab1;
curLab2 = injCode->currFuncAddr+distLab2;
__asm
{
mov eax,IATFuncLocateAddr;
//lea edx,Lab2; //日 不能随便用标号 标号是编译时的地址
mov edx,curLab2;
//取出call跳转到IATHook之间的差距
sub eax,edx;
//lea edx,Lab1; //日 不能随便用标号 标号是编译时的地址
mov edx,curLab1;
//求出差距后动态修改下面call 命令的偏移
mov [edx],eax;
//压入参数
push funcNameLen
push funcName;
push dllNameLen;
push dllName;
push pDos;
//这段代码的内存是可读写执行,因此可以动态修改跳转地址
_emit 0xE8;
Lab1:
_emit 0x90;
_emit 0x90;
_emit 0x90;
_emit 0x90;
//Lab2是call指令结束位置 Lab1和Lab2之间不能插入其他指令,会影响跳转距离
Lab2:
mov funcAddrInIAt,eax;
}
injCode->origFuncAddr = *(DWORD*)funcAddrInIAt;
MEMORY_BASIC_INFORMATION mbi;
/*
VirtualQuery((void*)funcAddrInIAt,&mbi,
sizeof(MEMORY_BASIC_INFORMATION));
VirtualProtect(mbi.BaseAddress,mbi.RegionSize,
PAGE_READWRITE,&mbi.Protect);
*/
//运行在远程进程中,API函数的IAT难免不同,必须要用目标进程的IAT表
(injCode->ldVirtualQuery)((void*)funcAddrInIAt,&mbi,
sizeof(MEMORY_BASIC_INFORMATION));
(injCode->ldVirtualProtect)(mbi.BaseAddress,mbi.RegionSize,
PAGE_READWRITE,&mbi.Protect);
*(DWORD*)(funcAddrInIAt) = injCode->newFuncAddr;
DWORD dwOldProtect;
(injCode->ldVirtualProtect)(mbi.BaseAddress,mbi.RegionSize,
mbi.Protect,&dwOldProtect);
//添加审计代码后此处的硬编码0x47需要修改
*(DWORD*)(injCode->newFuncAddr+0x0b) = injCode->origFuncAddr;
//测试Hook函数
//DWORD res = (DWORD)(injCode->ldGetModuleHandle)(NULL);
__asm
{
//模拟call [Mem] 在远程进程中调用GetModuleHandle
//跳转地址在IAT表中 因此是FF 15 32bit address
_emit 0xff;
_emit 0x15;
_emit 0x40;
_emit 0x10;
_emit 0x00;
_emit 0x01;
}
_asm jmp $
}
//定位指定函数名在IAT表中的地址
DWORD* IATFuncLocate(DWORD procBaseAddr,char* targetDllName,DWORD dllLen,char* targetFuncName,DWORD funcLen)
{
DWORD* lpAddr;
IMAGE_DOS_HEADER *pDosHeader = (IMAGE_DOS_HEADER*)procBaseAddr;
IMAGE_OPTIONAL_HEADER *pOptHeader = (IMAGE_OPTIONAL_HEADER*)((BYTE*)procBaseAddr + pDosHeader->e_lfanew + 24);
IMAGE_IMPORT_DESCRIPTOR *pImportDesc = (IMAGE_IMPORT_DESCRIPTOR*)((BYTE*)procBaseAddr + pOptHeader->DataDirectory[IMAGE_DIRECTORY_ENTRY_IMPORT].VirtualAddress);
while(pImportDesc->FirstThunk)
{
char *pszDllName = (char*)((BYTE*)procBaseAddr + pImportDesc->Name);
__asm
{
mov esi,pszDllName;
mov edi,targetDllName;
mov ecx,dllLen;
repz cmpsb;
test ecx,ecx;
jnz NotThisDll;
}
IMAGE_THUNK_DATA *pThunk = (IMAGE_THUNK_DATA *)((BYTE *)procBaseAddr + pImportDesc->OriginalFirstThunk);
int n = 0;
char *pszFunName = NULL;
while(pThunk->u1.Function)
{
pszFunName = (char *)((BYTE *)procBaseAddr + (DWORD)pThunk->u1.AddressOfData + 2);
__asm
{
mov esi,pszFunName;
mov edi,targetFuncName;
mov ecx,funcLen;
repz cmpsb;
test ecx,ecx;
jnz NotThisFunc;
}
lpAddr = (DWORD*)((BYTE *)procBaseAddr + pImportDesc->FirstThunk) + n;
NotThisFunc:
n++;
pThunk++;
}
NotThisDll:
pImportDesc++;
}
return lpAddr;
}
DWORD _stdcall RemotePrimeFuncEnd()
{
return 0;
}
#define FIND(structTest,e) (size_t)&(((structTest*)0)->e)
int main(int argc, char* argv[])
{
DWORD origProct;
InjCode injCode;
strcpy(injCode.funcName,"GetModuleHandleA");
injCode.funcNameLen = strlen(injCode.funcName);
strcpy(injCode.dllName,"KERNEL32.dll");
injCode.dllNameLen = strlen(injCode.dllName);
#if 0
//真实注入时 injCode.IATFuncLocateAddr要换成通过VirtualAllocEx分配的地址
injCode.IATFuncLocateAddr = (DWORD)&IATFuncLocate;
//真实注入时 injCode.newFuncAddr要换成通过VirtualAllocEx分配的地址
injCode.newFuncAddr = (DWORD)&myMessageBox;
//真实注入时VirtualProtect的起止也要修改
VirtualProtect(RemotePrimeFunc,((DWORD)&RemotePrimeFuncEnd-(DWORD)&RemotePrimeFunc),PAGE_EXECUTE_READWRITE,&origProct);
VirtualProtect(myMessageBox,((DWORD)&myMessageBoxEnd-(DWORD)&myMessageBox),PAGE_EXECUTE_READWRITE,&origProct);
//RemotePrimeFunc(&injCode);
#endif
HANDLE hProcessSnap;
PROCESSENTRY32 pe32;
HANDLE remoteProgHd;
DWORD targetPid,writtenNum;
DWORD dwThreadId;
DWORD codeLen;
void* remoteMainFuncAddr, *remoteAuditAddr;
void* remoteArg;
FILE* pidFp = fopen("c:\\pid.txt","r+");
fscanf(pidFp,"%d",&targetPid);
fclose(pidFp);
//sscanf(,"%d",&targetPid);
hProcessSnap = CreateToolhelp32Snapshot(TH32CS_SNAPPROCESS, 0);
if( hProcessSnap == INVALID_HANDLE_VALUE )
{
assert(false);
}
pe32.dwSize = sizeof( PROCESSENTRY32 );
if( !Process32First( hProcessSnap, &pe32 ) )
{
assert(false);
}
do
{
if(pe32.th32ProcessID == targetPid)
{
remoteProgHd = OpenProcess( OPENPROCESSPROITY, FALSE, pe32.th32ProcessID );
if(remoteProgHd == NULL)
{
assert(false);
}
break;
}
}while(Process32Next( hProcessSnap, &pe32));
HMODULE moduleBase = GetModuleHandle("kernel32.dll");
injCode.ldGetModuleHandle = (load_GetModuleHandle)GetProcAddress(moduleBase,"GetModuleHandleA");
injCode.ldVirtualProtect = (load_VirtualProtect)GetProcAddress(moduleBase,"VirtualProtect");
injCode.ldVirtualQuery = (load_VirtualQuery)GetProcAddress(moduleBase,"VirtualQuery");
codeLen = ((DWORD)&RemotePrimeFuncEnd-(DWORD)&RemotePrimeFunc);
//codeLen = (codeLen+0xFFF)&0x1000;
remoteMainFuncAddr = VirtualAllocEx(remoteProgHd,0,(codeLen+0xFFF)&0x1000,MEM_COMMIT, PAGE_EXECUTE_READWRITE);
assert(remoteMainFuncAddr);
WriteProcessMemory(remoteProgHd,remoteMainFuncAddr,&RemotePrimeFunc,codeLen,&writtenNum);
//重新计算IATFuncLocate函数在远程进程中的地址:基址+偏移
injCode.IATFuncLocateAddr = (DWORD)((char*)remoteMainFuncAddr+((DWORD)&IATFuncLocate - (DWORD)&RemotePrimeFunc));
injCode.currFuncAddr = (DWORD)remoteMainFuncAddr;
//创建远程挂钩函数
codeLen = ((DWORD)&myMessageBoxEnd-(DWORD)&myMessageBox);
//codeLen = (codeLen+0xFFF)&0x1000;
remoteAuditAddr = VirtualAllocEx(remoteProgHd,0,(codeLen+0xFFF)&0x1000,MEM_COMMIT, PAGE_EXECUTE_READWRITE);
assert(remoteAuditAddr);
WriteProcessMemory(remoteProgHd,remoteAuditAddr,&myMessageBox,codeLen,&writtenNum);
injCode.newFuncAddr = (DWORD)remoteAuditAddr;
//创建远程参数块
remoteArg = VirtualAllocEx(remoteProgHd,0,(sizeof(InjCode)+0xFFF)&0x1000,MEM_COMMIT, PAGE_READWRITE);
assert(remoteArg);
WriteProcessMemory(remoteProgHd,remoteArg,&injCode,sizeof(InjCode),&writtenNum);
//还要把injCode!funcName拷贝过去,要不然远程空间中的injCode!funcName没有值
DWORD offset = FIND(InjCode,funcName);
WriteProcessMemory(remoteProgHd,((char*)remoteArg+offset),injCode.funcName,32,&writtenNum);
offset = FIND(InjCode,dllName);
WriteProcessMemory(remoteProgHd,((char*)remoteArg+offset),injCode.dllName,32,&writtenNum);
//此后直接对remoteArg的域修改全是无效的 要用WriteProcessMemory修改远程进程中的remoteArg
HANDLE hThd = CreateRemoteThread(remoteProgHd,NULL,0,(LPTHREAD_START_ROUTINE)remoteMainFuncAddr,remoteArg,0,&dwThreadId);
WaitForSingleObject(remoteProgHd, INFINITE);
CloseHandle(remoteProgHd);
return 0;
}
整个代码分4部分main函数是注入部分,往远程进程中创建Hook函数的运行空间和函数参数;IATFuncLocate搜索目标进程的IAT表,定位指定函数的入口地址;myMessageBox是一个Hook函数,IAT表中函数入口被替换为这个函数的入口地址,当进程调用指定函数后将进入myMessageBox,myMessageBox函数退出前还要重新调用被Hook的函数;最后RemotePrimeFunc是一个载体,负责调用IATFuncLocate和安装myMessageBox
注入和IAT搜索本身不是很难,CSDN上可以搜到。本文主要涉及RemotePrimeFunc的调试过程。
1).注入最重要的是注入后能load被注入进程中原本没有的dll,因此加载kernel32.dll很重要。xp虚拟机上每次一重启kernel32.dll的加载地址就发生了改变,因此不能硬编码。不过好在在一次系统运行期间kernel32.dll的加载地址是固定的,并且在每个进程中都相同,因此在注入前先确定一下当前kernel32.dll的地址还是有所帮助的。要修改目标进程IAT表项,难免要用到VirtualQuery/VirtualProtect,因此还要在注入前获得VirtualQuery/VirtualProtect的入口地址。VirtualQuery/VirtualProtect的实现在kernel32.dll中,由于kernel32.dll的加载地址已经固定下来,VirtualQuery/VirtualProtect的入口地址也因此固定下来。
可能你会问我,为什么不能在RemotePrimeFunc函数中直接调用VirtualQuery/VirtualProtect两个函数,还是一定要搜索他们的入口地址,然后跳转过去?
其实,开始时我也没想到这个,运行时遇到了异常调试时在发现的:
程序编译时,编译器并不知道RemotePrimeFunc这段代码将要在哪运行,因此把RemotePrimeFunc中对VirtualQuery的调用编译为:
FF 25 [32bit Mem]
[32bit Mem]中的内容是啥?当然是VirtualQuery在注入进程IAT表中的地址。我在编译代码时,指定注入进程加载基址是0x400000。因此IAT表至少在0x400000之后。看一下反汇编结果:
MEMORY_BASIC_INFORMATION mbi; VirtualQuery((void*)0,&mbi, sizeof(MEMORY_BASIC_INFORMATION)); 004012FC push 1Ch 004012FE lea eax,[mbi] 00401301 push eax 00401302 push 0 00401304 call dword ptr [__imp__VirtualQuery@12 (44402Ch)] return 0;可以看到注入进程会去0x44402c处寻找API入口。但是程序注入到其他进程后,不保证被注入的进程也是从0x400000出加载,进一步说0x44402c处未必就是VirtualQuery再IAT表中的入口地址。因此需要在注入之前获得VirtualQuery的地址,以后直接call这个地址。
2).创建远程参数块,调用remoteArg = VirtualAllocEx(remoteProgHd,0,(sizeof(InjCode)+0xFFF)&0x1000,MEM_COMMIT, PAGE_READWRITE);之后remoteArg就是的地址是远程线程的地址,直接修改里面的内容很可能失败(因为本进程空间中可能并没有分配这段虚拟地址,写一段不存在的虚拟地址将引起保护异常)。因此往remoteArg拷贝内容要用到WriteProcessMemory。并且,如果只修改injCode的内容,而不调用WriteProcessMemory,remoteArg指向的远程空间中什么都不会发生。我有段代码是WriteProcessMemory之后,往injCode->targetFuncName中拷贝函数名,等到注入后,远程进程InjCode结构对应域中什么都么得~
3).关于远程线程创建后调试代码的问题。源码级的调试,估计是不可能了,只有汇编级的调试。可是怎么查找远程进程中运行的汇编语句对应哪条语句?我的办法是:编译源码时,使编译器生成list文件,里面有源码在连接前相对于文件头的偏移。然后,根据函数在远程进程中加载的位置+相对偏移定位源码位置:
在我机器上生成的cod文件显示,RemotePrimeFunc偏移为0xb0:
?RemotePrimeFunc@@YGKPAX@Z PROC ; RemotePrimeFunc
; 115 : {
000b0 55 push ebp
000b1 8b ec mov ebp, esp
000b3 81 ec 98 00 00
00 sub esp, 152 ; 00000098H
000b9 53 push ebx
000ba 56 push esi
000bb 57 push edi
; 116 : DWORD dist;
; 117 : char* funcName;
; 118 : DWORD funcNameLen;
; 119 : char* dllName;
; 120 : DWORD dllNameLen;
; 121 : DWORD distLab1,curLab1;
; 122 : DWORD distLab2,curLab2;
; 123 :
; 124 : InjCode* injCode = (InjCode*)args;
而remoteMainFuncAddr分配到的远程地址是0xb50000
dd remoteMainFuncAddr 0012fdbc 00b50000 00000090 02480200 00000020 0012fdcc 00000a78 000007e4 00000128 00000000即RemotePrimeFunc的运行地址从0xb50000开始,那么0xb50000对应了Cod文件中的000B0,计算远程进程中其他指令的在Cod文件中的位置只要都先减去0xB50000然后加上b0即可。
4).从RemotePrimeFunc跳转到IATFuncLocate。
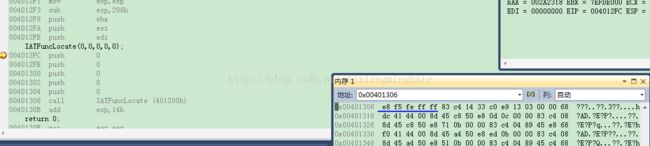
这是一段相对偏移跳转,无所谓是在注入进程还是被注入进程,都能正确的调用。
同样的从一个偏移地址跳转到另一个偏移地址也是没问题的,因为也是相对偏移的跳转。但是用到lea eax,Lab时就需要注意了,取出的是Lab在连接时指定的地址,也就是运行在注入进程中的地址。因此如果要取某一处地址的内容,应该要用位置无关代码,如何写出位置无关代码?
以取Lab地址处指令为例:
(Lab-RemotePrimeFunc)获得Lab相对于RemotePrimeFunc的偏移,这个偏移只要不修改代码,不管在哪运行都不会改变。然后获得RemotePrimeFunc的基址,这是通过远程参数传递过来的。两者相加即可得到Lab运行时的地址。如果RemotePrimeFunc的基址无法获得,怎么办,如这里的myMessageBox函数?
首先myMessageBox是通过VirtuallAllocate分配的,VirtuallAllocate分配的,低16bit在xp上全0。其次,如何获得myMessageBox当前地址?
可以用call $ pop eax;获得当前地址,这个操作结束eax中就是当前地址,同时还堆栈平衡~最后eax&0xFFFF0000就可获得myMessageBox的基址。
5).在myMessageBox动态修改返回地址。myMessageBox是代码段,RE的权限。修改返回地址前要修改代码段权限位RWE