Configuring HBase Memstore: What You Should Know
In this post we discuss what HBase users should know about one of the internal parts of HBase: the Memstore. Understanding underlying processes related to Memstore will help to configure HBase cluster towards better performance.
HBase Memstore
Let’s take a look at the write and read paths in HBase to understand what Memstore is, where how and why it is used.
(picture was taken from Intro to HBase Internals and Schema Design presentation)
When RegionServer (RS) receives write request, it directs the request to specific Region. Each Region stores set of rows. Rows data can be separated in multiple column families (CFs). Data of particular CF is stored in HStore which consists of Memstore and a set of HFiles. Memstore is kept in RS main memory, while HFiles are written to HDFS. When write request is processed, data is first written into the Memstore. Then, when certain thresholds are met (obviously, main memory is well-limited) Memstore data gets flushed into HFile.
The main reason for using Memstore is the need to store data on DFS ordered by row key. As HDFS is designed for sequential reads/writes, with no file modifications allowed, HBase cannot efficiently write data to disk as it is being received: the written data will not be sorted (when the input is not sorted) which means not optimized for future retrieval. To solve this problem HBase buffers last received data in memory (in Memstore), “sorts” it before flushing, and then writes to HDFS using fast sequential writes. Note that in reality HFile is not just a simple list of sorted rows, it is much more than that.
Apart from solving the “non-ordered” problem, Memstore also has other benefits, e.g.:
- It acts as a in-memory cache which keeps recently added data. This is useful in numerous cases when last written data is accessed more frequently than older data
- There are certain optimizations that can be done to rows/cells when they are stored in memory before writing to persistent store. E.g. when it is configured to store one version of a cell for certain CF and Memstore contains multiple updates for that cell, only most recent one can be kept and older ones can be omitted (and never written to HFile).
Important thing to note is that every Memstore flush creates one HFile per CF.
On the reading end things are simple: HBase first checks if requested data is in Memstore, then goes to HFiles and returns merged result to the user.
What to Care about
There are number of reasons HBase users and/or administrators should be aware of what Memstore is and how it is used:
- There are number of configuration options for Memstore one can use to achieve better performance and avoid issues. HBase will not adjust settings for you based on usage pattern.
- Frequent Memstore flushes can affect reading performance and can bring additional load to the system
- The way Memstore flushes work may affect your schema design
Let’s take a closer look at these points.
Configuring Memstore Flushes
Basically, there are two groups of configuraion properties (leaving out region pre-close flushes):
- First determines when flush should be triggered
- Second determines when flush should be triggered and updates should be blocked during flushing
First group is about triggering “regular” flushes which happen in parallel with serving write requests. The properties for configuring flush thresholds are:
- hbase.hregion.memstore.flush.size
<property> <name>hbase.hregion.memstore.flush.size</name> <value>134217728</value> <description> Memstore will be flushed to disk if size of the memstore exceeds this number of bytes. Value is checked by a thread that runs every hbase.server.thread.wakefrequency. </description> </property>
- base.regionserver.global.memstore.lowerLimit
<property> <name>hbase.regionserver.global.memstore.lowerLimit</name> <value>0.35</value> <description>Maximum size of all memstores in a region server before flushes are forced. Defaults to 35% of heap. This value equal to hbase.regionserver.global.memstore.upperLimit causes the minimum possible flushing to occur when updates are blocked due to memstore limiting. </description> </property>
Note that the first setting is the size per Memstore. I.e. when you define it you should take into account the number of regions served by each RS. When number of RS grows (and you configured the setting when there were few of them) Memstore flushes are likely to be triggered by the second threshold earlier.
Second group of settings is for safety reasons: sometimes write load is so high that flushing cannot keep up with it and since we don’t want memstore to grow without a limit, in this situation writes are blocked unless memstore has “manageable” size. These thresholds are configured with:
- hbase.regionserver.global.memstore.upperLimit
<property> <name>hbase.regionserver.global.memstore.upperLimit</name> <value>0.4</value> <description>Maximum size of all memstores in a region server before new updates are blocked and flushes are forced. Defaults to 40% of heap. Updates are blocked and flushes are forced until size of all memstores in a region server hits hbase.regionserver.global.memstore.lowerLimit. </description> </property>
- hbase.hregion.memstore.block.multiplier
<property> <name>hbase.hregion.memstore.block.multiplier</name> <value>2</value> <description> Block updates if memstore has hbase.hregion.block.memstore time hbase.hregion.flush.size bytes. Useful preventing runaway memstore during spikes in update traffic. Without an upper-bound, memstore fills such that when it flushes the resultant flush files take a long time to compact or split, or worse, we OOME. </description> </property>
Blocking writes on particular RS on its own may be a big issue, but there’s more to that. Since in HBase by designone Region is served by single RS when write load is evenly distributed over the cluster (over Regions) having one such “slow” RS will make the whole cluster work slower (basically, at its speed).
Hint: watch for Memstore Size and Memstore Flush Queue size. Memstore Size ideally should not reach upper Memstore limit and Memstore Flush Queue size should not constantly grow.
Frequent Memstore Flushes
Since we want to avoid blocking writes it may seem a good approach to flush earlier when we are far from “writes-blocking” thresholds. However, this will cause too frequent flushes which can affect read performance and bring additional load to the cluster.
Every time Memstore flush happens one HFile created for each CF. Frequent flushes may create tons of HFiles. Since during reading HBase will have to look at many HFiles, the read speed can suffer.
To prevent opening too many HFiles and avoid read performance deterioration there’s HFiles compaction process. HBase will periodically (when certain configurable thresholds are met) compact multiple smaller HFiles into a big one. Obviously, the more files created by Memstore flushes, the more work (extra load) for the system. More to that: while compaction process is usually performed in parallel with serving other requests, when HBase cannot keep up with compacting HFiles (yes, there are configured thresholds for that too;)) it will block writes on RS again. As mentioned above, this is highly undesirable.
Hint: watch for Compaction Queue size on RSs. In case it is constantly growing you should take actions before it will cause problems.
More on HFiles creation & Compaction can be found here.
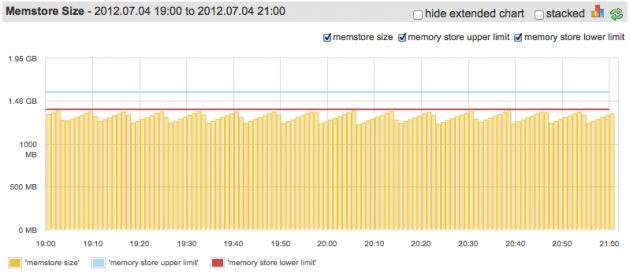
So, ideally Memstore should use as much memory as it can (as configured, not all RS heap: there are also in-memory caches), but not cross the upper limit. This picture (screenshot was taken from our SPM monitoring service) shows somewhat good situation:
“Somewhat”, because we could configure lower limit to be closer to upper, since we barely ever go over it.
Multiple Column Families & Memstore Flush
Memstores of all column families are flushed together (this might change). This means creating N HFiles per flush, one for each CF. Thus, uneven data amount in CF will cause too many HFiles to be created: when Memstore of one CF reaches threshold all Memstores of other CFs are flushed too. As stated above too frequent flush operations and too many HFiles may affect cluster performance.
Hint: in many cases having one CF is the best schema design.
Ref: http://blog.sematext.com/2012/07/16/hbase-memstore-what-you-should-know/