Python源码学习十--token的parse
in parsetok.c
static node * parsetok(struct tok_state *tok, grammar *g, int start, perrdetail *err_ret,
int *flags) 函数
step1 . parser_state * ps = PyParser_New(g, start);
--g is static grammar _PyParser_Grammar = {
6,
dfas,
{19, labels},
256
};
--start is predefined macro
#define Py_file_input 257
in Python.h
in parser_state *
PyParser_New(grammar *g, int start)
step 1.1 ps->p_grammar = p;
ps->p_tree = PyNode_New(start), start defines the 'type' of node
因为 node *PyNode_New(int type)
{
node *n = (node *) PyObject_MALLOC(1 * sizeof(node));
if (n == NULL)
return NULL;
n->n_type = type;
n->n_str = NULL;
n->n_lineno = 0;
n->n_nchildren = 0;
n->n_child = NULL;
return n;
}
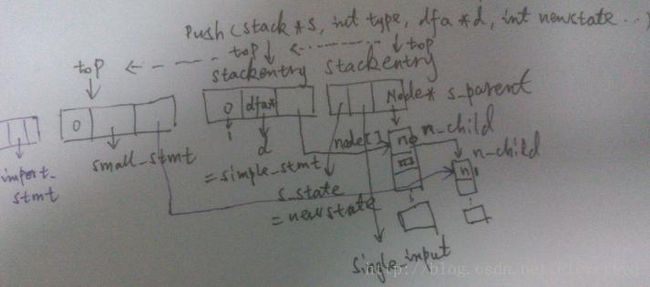
step1.2 s_reset(&ps->p_stack)
其中static void
s_reset(stack *s)
{
s->s_top = &s->s_base[MAXSTACK];
} 让stack的 s_top 指向s_base最后一个元素
step1.3 s_push(&ps->p_stack, PyGrammar_FindDFA(g, start), ps->p_tree);
其中dfa *
PyGrammar_FindDFA(grammar *g, register int type)
{
register dfa *d;
#if 1
/* Massive speed-up */
d = &g->g_dfa[type - NT_OFFSET]; //type = 257 as predefined, #define NT_OFFSET 256
//so d is one of static dfa dfas[81] member, dfas[1] in graminit.c
//dfas[1]'s type is 257,
assert(d->d_type == type);
return d;
#else
#endif
}
而static int
s_push(register stack *s, dfa *d, node *parent)
{
register stackentry *top;
top = --s->s_top;
top->s_dfa = d;
top->s_parent = parent;
top->s_state = 0;
return 0;
}
top指向前一个element, 赋值该element的s_dfa, s_parent
参见parser.h
typedef struct {
int s_state; /* State in current DFA */
dfa *s_dfa; /* Current DFA */
struct _node *s_parent; /* Where to add next node */
} stackentry;
step 2. for 循环中
step2.1 type = PyTokenizer_Get(tok, &a, &b);
PyParser_AddToken(ps, (int)type, str,
tok->lineno, col_offset,
&(err_ret->expected))
step2.1.1
/* Find out which label this token is */
ilabel = classify(ps, type, str); //for example type=1, str="a"
//it will search static label labels[168] , defined in graminit.c
//and find the pair (1, NULL), return the index of the element in array
step2.1.2
/* Loop until the token is shifted or an error occurred */
for (;;) {
/* Fetch the current dfa and state */
register dfa *d = ps->p_stack.s_top->s_dfa;
register state *s = &d->d_state[ps->p_stack.s_top->s_state];
/* Check accelerator */
if (s->s_lower <= ilabel && ilabel < s->s_upper) {
register int x = s->s_accel[ilabel - s->s_lower];
if (x != -1) {
if (x & (1<<7)) {
/* Push non-terminal */
int nt = (x >> 8) + NT_OFFSET;
int arrow = x & ((1<<7)-1);
dfa *d1 = PyGrammar_FindDFA(
ps->p_grammar, nt);
if ((err = push(&ps->p_stack, nt, d1, =======>push
arrow, lineno, col_offset)) > 0) {
D(printf(" MemError: push\n"));
return err;
}
D(printf(" Push ...\n"));
continue;
}
.....
return E_OK;
}
}
}
这段的关键是push函数,
static int
push(register stack *s, int type, dfa *d, int newstate, int lineno, int col_offset)
{
int err;
register node *n;
n = s->s_top->s_parent;
assert(!s_empty(s));
err = PyNode_AddChild(n, type, (char *)NULL, lineno, col_offset);
if (err)
return err;
s->s_top->s_state = newstate;
return s_push(s, d, CHILD(n, NCH(n)-1));
}
它建立起了一个复杂的数据如图