android布局属性之weight
先给出一些布局以及其效果,然后分析其原因
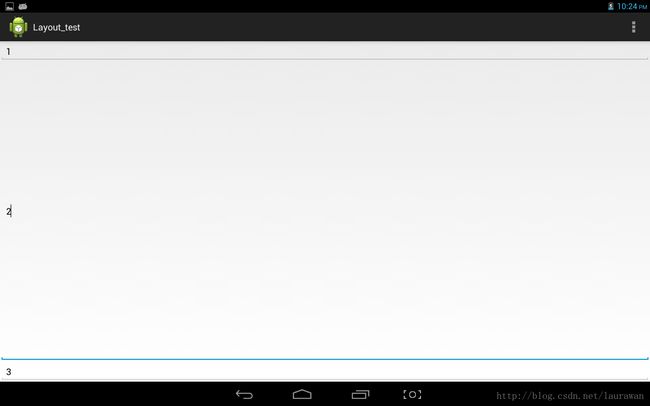
例一:
<LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:orientation="vertical"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:layout_width="match_parent">
<EditText
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="@string/one"
/>
<EditText
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="@string/two"
android:layout_weight="1.0"
/>
<EditText
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="@string/three"
/>
</LinearLayout>
结果:
只有EditText2使用了layout_weight属性,并赋值为1(设置为>0的值都是一样的效果),根据API,其他两个没有使用layout _weight的EditText,
其实其layout_weight默认为0
EditText2的layout_height可设置为0dip,同样的效果。
例二
<LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:orientation="horizontal"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_width="match_parent">
<EditText
android:layout_width="0dip"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="@string/one"
android:background="#ff0000"
android:layout_weight="1.0"
/>
<EditText
android:layout_width="0dip"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="@string/two"
android:background="#cccc"
android:layout_weight="2.0"
/>
<EditText
android:layout_width="0dip"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="@string/three"
android:background="#ddaacc"
android:layout_weight="3.0"
/>
</LinearLayout>
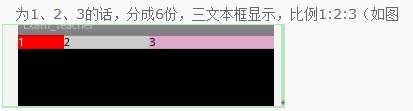
例三
将例二中的android:layout_width="match_parent",比例为1:2:3
例四:
将例二中的android:layout_width="match_parent",比例为1:2:2
之所以会出现上述记过,其实质是:
首先分配layout_height或layout_width中指定的宽度,然后把剩余空间按照权重分配给各个view。
比如例四,layout_width为match_parent,首先给每个edittext分配1个屏宽,这样就用去了3个屏宽,
剩余空间为s=1-3=-2
比例为1:2:2,所以
edittext1:1+(-2*1/5)=3/5
edittext2:1+(-2*2/5)=1/5
edittext3:1+(-2*2/5)=1/5
所以,显示比例为3:1:1
有人说,岂不是每次都要去计算,好麻烦,但是我们一般使用时,把layout_height或layout_width置为0dip
如例二
这样剩余空间就为1
edittext1:0+(1*1/5)=1/5
edittext2:0+(1*2/5)=2/5
edittext3:0+(1*3/5)=3/5
这种情况就是按照我们设置的1:2:3了,一目了然。
在android中的应用
android\frameworks\base\core\res\res\layout\preference_list_content.xml
这个布局是PreferenceActivity.java的布局,Setting应用中的Settings.java为其子类。
所以Setting的布局为该布局。
一般情况下,button_bar是隐藏的,当其显示时占用wrap_content,剩余空间全部给headers+prefs_frame。headers和prefs_frame的显示比例为4:6
参考:http://mobile.51cto.com/abased-375428.htm