LLVM 源码分析 (一) pass 类
Pass interface - Implemented by all 'passes'. Subclass this if you are an interprocedural optimization or you do not fit into any of the more constrained passes described below.
#include "llvm/Support/Compiler.h"
#include <string>
namespace llvm {
class BasicBlock;
class Function;
class Module;
class AnalysisUsage;
class PassInfo;
class ImmutablePass;
class PMStack;
class AnalysisResolver;
class PMDataManager;
class raw_ostream;
class StringRef;
// AnalysisID - Use the PassInfo to identify a pass...
typedef const void* AnalysisID;
/// Different types of internal pass managers. External pass managers
/// (PassManager and FunctionPassManager) are not represented here.
/// Ordering of pass manager types is important here.
enum PassManagerType {
PMT_Unknown = 0,
PMT_ModulePassManager = 1, ///< MPPassManager
PMT_CallGraphPassManager, ///< CGPassManager
PMT_FunctionPassManager, ///< FPPassManager
PMT_LoopPassManager, ///< LPPassManager
PMT_RegionPassManager, ///< RGPassManager
PMT_BasicBlockPassManager, ///< BBPassManager
PMT_Last
};
// Different types of passes.
enum PassKind {
PT_BasicBlock,
PT_Region,
PT_Loop,
PT_Function,
PT_CallGraphSCC,
PT_Module,
PT_PassManager
};
//===----------------------------------------------------------------------===//
/// Pass interface - Implemented by all 'passes'. Subclass this if you are an
/// interprocedural optimization or you do not fit into any of the more
/// constrained passes described below.
///
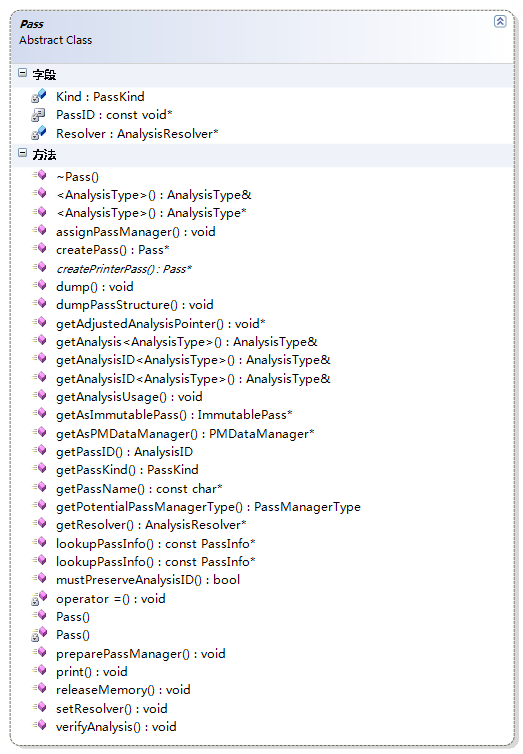
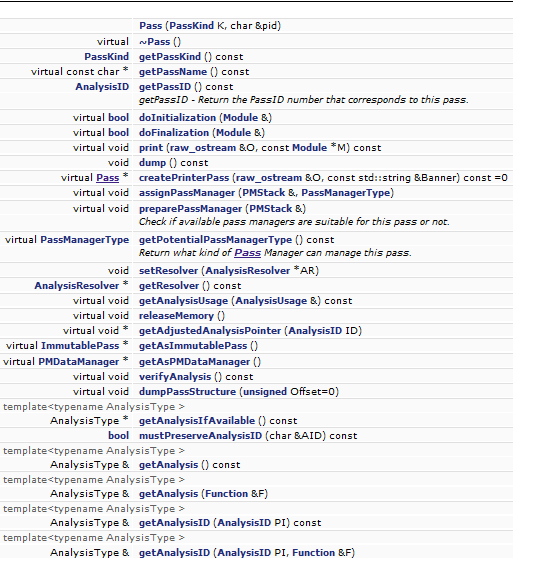
class Pass {
AnalysisResolver *Resolver; // Used to resolve analysis
const void *PassID;
PassKind Kind;
void operator=(const Pass&) LLVM_DELETED_FUNCTION;
Pass(const Pass &) LLVM_DELETED_FUNCTION;
public:
explicit Pass(PassKind K, char &pid) : Resolver(0), PassID(&pid), Kind(K) { }
virtual ~Pass();
PassKind getPassKind() const { return Kind; }
/// getPassName - Return a nice clean name for a pass. This usually
/// implemented in terms of the name that is registered by one of the
/// Registration templates, but can be overloaded directly.
///
virtual const char *getPassName() const;
/// getPassID - Return the PassID number that corresponds to this pass.
AnalysisID getPassID() const {
return PassID;
}
/// print - Print out the internal state of the pass. This is called by
/// Analyze to print out the contents of an analysis. Otherwise it is not
/// necessary to implement this method. Beware that the module pointer MAY be
/// null. This automatically forwards to a virtual function that does not
/// provide the Module* in case the analysis doesn't need it it can just be
/// ignored.
///
virtual void print(raw_ostream &O, const Module *M) const;
void dump() const; // dump - Print to stderr.
/// createPrinterPass - Get a Pass appropriate to print the IR this
/// pass operates on (Module, Function or MachineFunction).
virtual Pass *createPrinterPass(raw_ostream &O,
const std::string &Banner) const = 0;
/// Each pass is responsible for assigning a pass manager to itself.
/// PMS is the stack of available pass manager.
virtual void assignPassManager(PMStack &,
PassManagerType) {}
/// Check if available pass managers are suitable for this pass or not.
virtual void preparePassManager(PMStack &);
/// Return what kind of Pass Manager can manage this pass.
virtual PassManagerType getPotentialPassManagerType() const;
// Access AnalysisResolver
void setResolver(AnalysisResolver *AR);
AnalysisResolver *getResolver() const { return Resolver; }
/// getAnalysisUsage - This function should be overriden by passes that need
/// analysis information to do their job. If a pass specifies that it uses a
/// particular analysis result to this function, it can then use the
/// getAnalysis<AnalysisType>() function, below.
///
virtual void getAnalysisUsage(AnalysisUsage &) const;
/// releaseMemory() - This member can be implemented by a pass if it wants to
/// be able to release its memory when it is no longer needed. The default
/// behavior of passes is to hold onto memory for the entire duration of their
/// lifetime (which is the entire compile time). For pipelined passes, this
/// is not a big deal because that memory gets recycled every time the pass is
/// invoked on another program unit. For IP passes, it is more important to
/// free memory when it is unused.
///
/// Optionally implement this function to release pass memory when it is no
/// longer used.
///
virtual void releaseMemory();
/// getAdjustedAnalysisPointer - This method is used when a pass implements
/// an analysis interface through multiple inheritance. If needed, it should
/// override this to adjust the this pointer as needed for the specified pass
/// info.
virtual void *getAdjustedAnalysisPointer(AnalysisID ID);
virtual ImmutablePass *getAsImmutablePass();
virtual PMDataManager *getAsPMDataManager();
/// verifyAnalysis() - This member can be implemented by a analysis pass to
/// check state of analysis information.
virtual void verifyAnalysis() const;
// dumpPassStructure - Implement the -debug-passes=PassStructure option
virtual void dumpPassStructure(unsigned Offset = 0);
// lookupPassInfo - Return the pass info object for the specified pass class,
// or null if it is not known.
static const PassInfo *lookupPassInfo(const void *TI);
// lookupPassInfo - Return the pass info object for the pass with the given
// argument string, or null if it is not known.
static const PassInfo *lookupPassInfo(StringRef Arg);
// createPass - Create a object for the specified pass class,
// or null if it is not known.
static Pass *createPass(AnalysisID ID);
/// getAnalysisIfAvailable<AnalysisType>() - Subclasses use this function to
/// get analysis information that might be around, for example to update it.
/// This is different than getAnalysis in that it can fail (if the analysis
/// results haven't been computed), so should only be used if you can handle
/// the case when the analysis is not available. This method is often used by
/// transformation APIs to update analysis results for a pass automatically as
/// the transform is performed.
///
template<typename AnalysisType> AnalysisType *
getAnalysisIfAvailable() const; // Defined in PassAnalysisSupport.h
/// mustPreserveAnalysisID - This method serves the same function as
/// getAnalysisIfAvailable, but works if you just have an AnalysisID. This
/// obviously cannot give you a properly typed instance of the class if you
/// don't have the class name available (use getAnalysisIfAvailable if you
/// do), but it can tell you if you need to preserve the pass at least.
///
bool mustPreserveAnalysisID(char &AID) const;
/// getAnalysis<AnalysisType>() - This function is used by subclasses to get
/// to the analysis information that they claim to use by overriding the
/// getAnalysisUsage function.
///
template<typename AnalysisType>
AnalysisType &getAnalysis() const; // Defined in PassAnalysisSupport.h
template<typename AnalysisType>
AnalysisType &getAnalysis(Function &F); // Defined in PassAnalysisSupport.h
template<typename AnalysisType>
AnalysisType &getAnalysisID(AnalysisID PI) const;
template<typename AnalysisType>
AnalysisType &getAnalysisID(AnalysisID PI, Function &F);
};
1.assignPassManager
/// Each pass is responsible for assigning a pass manager to itself.
/// PMS is the stack of available pass manager.
virtual void assignPassManager(PMStack &,
PassManagerType) {}
Reimplemented in llvm::BasicBlockPass, llvm::FunctionPass, llvm::ModulePass, llvm::RegionPass, llvm::CallGraphSCCPass, and llvm::LoopPass.
eg.
// Add the requested pass to the best available pass manager. P->assignPassManager(activeStack, getTopLevelPassManagerType());
2.preparePassManager
/// Check if available pass managers are suitable for this pass or not. virtual void preparePassManager(PMStack &);
eg.
// Give pass a chance to prepare the stage. P->preparePassManager(activeStack);
3.getPotentialPassManagerType
/// Return what kind of Pass Manager can manage this pass. virtual PassManagerType getPotentialPassManagerType() const;
4.getPassManagerType
virtual PassManagerType getPassManagerType() const {
return PMT_CallGraphPassManager;
}
enum PassManagerType {
PMT_Unknown = 0,
PMT_ModulePassManager = 1, ///< MPPassManager
PMT_CallGraphPassManager, ///< CGPassManager
PMT_FunctionPassManager, ///< FPPassManager
PMT_LoopPassManager, ///< LPPassManager
PMT_RegionPassManager, ///< RGPassManager
PMT_BasicBlockPassManager, ///< BBPassManager
PMT_Last
};
5.createPass
// createPass - Create a object for the specified pass class, // or null if it is not known. static Pass *createPass(AnalysisID ID);
eg.
AnalysisID FinalID = overridePass(PassID, TargetID);
if (FinalID == 0)
return FinalID;
Pass *P = Pass::createPass(FinalID);
6.createPrinterPass
/// createPrinterPass - Get a Pass appropriate to print the IR this
/// pass operates on (Module, Function or MachineFunction).
virtual Pass *createPrinterPass(raw_ostream &O,
const std::string &Banner) const = 0;
Implemented in llvm::PassManagerImpl, llvm::BasicBlockPass, llvm::MPPassManager, llvm::FunctionPass, llvm::ModulePass, llvm::FunctionPassManagerImpl, llvm::RegionPass, llvm::CallGraphSCCPass, and llvm::LoopPass.
eg.
Pass *PP = P->createPrinterPass(
dbgs(), std::string("*** IR Dump Before ") + P->getPassName() + " ***");
7.print
/// print - Print out the internal state of the pass. This is called by /// Analyze to print out the contents of an analysis. Otherwise it is not /// necessary to implement this method. Beware that the module pointer MAY be /// null. This automatically forwards to a virtual function that does not /// provide the Module* in case the analysis doesn't need it it can just be /// ignored. /// virtual void print(raw_ostream &O, const Module *M) const;
8.dump
/// dump - print descriptor to dbgs() with a newline.
void dump() const;
9 getPassName
/// getPassName - Return a nice clean name for a pass. This usually
/// implemented in terms of the name that is registered by one of the
/// Registration templates, but can be overloaded directly.
///
const char *Pass::getPassName() const {
AnalysisID AID = getPassID();
const PassInfo *PI = PassRegistry::getPassRegistry()->getPassInfo(AID);
if (PI)
return PI->getPassName();
return "Unnamed pass: implement Pass::getPassName()";
}
10.getPassID
/// getPassID - Return the PassID number that corresponds to this pass.
AnalysisID getPassID() const {
return PassID;
}
11. getPassKind
PassKind getPassKind() const { return Kind; }
12.setResolver
void Pass::setResolver(AnalysisResolver *AR) {
assert(!Resolver && "Resolver is already set");
Resolver = AR;
}
13.getResolver
AnalysisResolver *getResolver() const { return Resolver; }
14.
/// getAnalysisUsage - This function should be overriden by passes that need /// analysis information to do their job. If a pass specifies that it uses a /// particular analysis result to this function, it can then use the /// getAnalysis<AnalysisType>() function, below. /// virtual void getAnalysisUsage(AnalysisUsage &) const;
eg
virtual void getAnalysisUsage(AnalysisUsage &AU) const;
15.getAnalysis
/// getAnalysis<AnalysisType>() - This function is used by subclasses to get /// to the analysis information that they claim to use by overriding the /// getAnalysisUsage function. /// template<typename AnalysisType> AnalysisType &getAnalysis() const; // Defined in PassAnalysisSupport.h template<typename AnalysisType> AnalysisType &getAnalysis(Function &F); // Defined in PassAnalysisSupport.h
16 mustPreserveAnalysisID
/// mustPreserveAnalysisID - This method serves the same function as
/// getAnalysisIfAvailable, but works if you just have an AnalysisID. This
/// obviously cannot give you a properly typed instance of the class if you
/// don't have the class name available (use getAnalysisIfAvailable if you
/// do), but it can tell you if you need to preserve the pass at least.
bool Pass::mustPreserveAnalysisID(char &AID) const {
return Resolver->getAnalysisIfAvailable(&AID, true) != 0;
}
17.getAnalysisIfAvailable<AnalysisType>()
/// getAnalysisIfAvailable<AnalysisType>() - Subclasses use this function to
/// get analysis information that might be around, for example to update it.
/// This is different than getAnalysis in that it can fail (if the analysis
/// results haven't been computed), so should only be used if you can handle
/// the case when the analysis is not available. This method is often used by
/// transformation APIs to update analysis results for a pass automatically as
/// the transform is performed.
///
template<typename AnalysisType> AnalysisType *
getAnalysisIfAvailable() const; // Defined in PassAnalysisSupport.h
eg
MachineDominatorTree *MDT = P->getAnalysisIfAvailable<MachineDominatorTree>()
18. lookupPassInfo 用处很小 整个源码都没有用到
// lookupPassInfo - Return the pass info object for the pass with the given // argument string, or null if it is not known. static const PassInfo *lookupPassInfo(StringRef Arg);
19,getAdjustedAnalysisPointer
/// getAdjustedAnalysisPointer - This method is used when a pass implements /// an analysis interface through multiple inheritance. If needed, it should /// override this to adjust the this pointer as needed for the specified pass /// info. virtual void *getAdjustedAnalysisPointer(AnalysisID ID);
20.releaseMemory
/// releaseMemory() - This member can be implemented by a pass if it wants to /// be able to release its memory when it is no longer needed. The default /// behavior of passes is to hold onto memory for the entire duration of their /// lifetime (which is the entire compile time). For pipelined passes, this /// is not a big deal because that memory gets recycled every time the pass is /// invoked on another program unit. For IP passes, it is more important to /// free memory when it is unused. /// /// Optionally implement this function to release pass memory when it is no /// longer used. /// virtual void releaseMemory();