如何实现iOS图书动画-第2部分(下)
- 原文链接 : How to Create an iOS Book Open Animation: Part 2
- 原文作者 : Vincent Ngo
- 译文出自 : 开发技术前线 www.devtf.cn
- 译者 : kmyhy
状态 2 - 打开书
现在,状态1的动画完成了,我们可以转移到状态2的处理中来。在这里我们将一本合起的书转换成一本打开的书。在setStartPositionForPush(_:toVC:)方法下添加如下方法:
func setEndPositionForPush(fromVC: BooksViewController, toVC: BookViewController) {
//1
for cell in fromVC.collectionView!.visibleCells() as! [BookCoverCell] {
cell.alpha = 0
}
//2
for cell in toVC.collectionView!.visibleCells() as! [BookPageCell] {
cell.layer.transform = transforms[cell]!
cell.updateShadowLayer(animated: true)
}
}上述代码解释如下:
- 隐藏所有书的封面,因为接下来我们要显示所选图书的内容。
- 在BookViewController中遍历书中每一页并读取先前保存在transform数组中的的Transform。
在从BooksViewController导航到BookViewController后,我们还需要进行一些清理工作。
在上面的方法之后加入如下方法:
func cleanupPush(fromVC: BooksViewController, toVC: BookViewController) {
// Add background back to pushed view controller
toVC.collectionView?.backgroundColor = toViewBackgroundColor
}在Push完成时,我们将BookViewController的Collection View的背景色设回原来保存的颜色,隐藏位于它下面的内容。
实现打开书的动画
现在我们已经实现了助手方法,接下来要实现Push动画了!
在空的animateTransition(_:)方法中加入以下代码:
//1
let container = transitionContext.containerView()
//2
if isPush {
//3
let fromVC = transitionContext.viewControllerForKey(UITransitionContextFromViewControllerKey) as! BooksViewController
let toVC = transitionContext.viewControllerForKey(UITransitionContextToViewControllerKey) as! BookViewController
//4
container.addSubview(toVC.view)
// Perform transition
//5
self.setStartPositionForPush(fromVC, toVC: toVC)
UIView.animateWithDuration(self.transitionDuration(transitionContext), delay: 0.0, usingSpringWithDamping: 0.7, initialSpringVelocity: 0.7, options: nil, animations: {
//6
self.setEndPositionForPush(fromVC, toVC: toVC)
}, completion: { finished in
//7
self.cleanupPush(fromVC, toVC: toVC)
//8
transitionContext.completeTransition(finished)
})
} else {
//POP
}以上代码解释如下:
- 获取Container View,Container View在两个View Controller发生转场时充当父视图的角色。
- 判断当前的转场动作是否是一个Push动作。
- 如果是,分别获取fromVC(BooksViewController)和toVC(BookViewController)。
- 将toVC(BookViewController)加到Container View。
- 设定Push动作的起止点,即toVC和fromVC。
- 开始动画。从起始点(书合起的状态)转变到终点(书打开状态)。
- 执行清理动作。
- 告诉系统,转换完成。
在Navigation Controller中应用Push动画
现在我们已经创建好Push动画,接下来就是将它应用到自定义的Navigation Controller中了。
打开BooksViewController.swift在类声明中增加属性:
var transition: BookOpeningTransition?transition属性用于保存Transition对象,通过它我们可以知道当前动画是Push动画还是Pop动画。
然后在文件末尾的大括号之后加入一个扩展:
extension BooksViewController {
func animationControllerForPresentController(vc: UIViewController) -> UIViewControllerAnimatedTransitioning? {
// 1
var transition = BookOpeningTransition()
// 2
transition.isPush = true
// 3
self.transition = transition
// 4
return transition
}
}通过扩展,我们将一部分代码分离出来。这里,我们将和转换动画有关的方法放到了一起。上面的这个方法创建并返回了一个Transition对象。
以上代码解释如下:
- 创建一个新的Transition。
- 因为我们是要弹出或者Push一个Controller,所以将isPush设置为true。
- 保存当前Transition对象。
- 返回Transition对象。
现在打开CustomNavigationController.swift并将Push的if语句替换为:
if operation == .Push {
if let vc = fromVC as? BooksViewController {
return vc.animationControllerForPresentController(toVC)
}
}上述语句判断当前Push的View Controller是不是一个BooksViewController,如果是,用我们创建的BookOpeningTransition呈现BookViewController。
编译运行,选择某本书,你将看到书缓缓由合起状态打开:

书直接从合起状态跳到了打开状态,原因在于我们没有加载cell(书页)!
导航控制器从BooksViewController切换到BookViewController,这二者都是UICollecitonViewController。UICollectionViewCell没有在主线程中加载,因此代码一开始的时候以为cell的个数为0——这样当然不会有动画产生。
我们需要让Collection View有足够的时间去加载所有的Cell。
打开BooksViewController.swift将openBook(_:)方法替换为:
func openBook(book: Book?) {
let vc = storyboard?.instantiateViewControllerWithIdentifier("BookViewController") as! BookViewController
vc.book = selectedCell()?.book
//1
vc.view.snapshotViewAfterScreenUpdates(true)
//2
dispatch_async(dispatch_get_main_queue(), { () -> Void in self.navigationController?.pushViewController(vc, animated: true) return }) }以上代码解释如下:
- 告诉BookViewController在动画一开始之前截屏。
- 将Push BookViewController的动作放到主线程中进行,这样就有时间去加载cell了。
编译、运行,这次你将看到正确的Push动画了:
这样看起来是不是好多啦?
现在,关于Push动画的内容就到此结束,接下来,我们开始实现Pop动画。
实现Pop动画的助手方法
一个View Controller的Pop动作刚好和Push相反。状态1是图书打开的状态,而状态2则变成了书合起的状态:

Open up BookOpeningTransition.swift and add the following code:
打开BookOpeningTransition.swift,加入以下方法:
// MARK: Pop methods
func setStartPositionForPop(fromVC: BookViewController, toVC: BooksViewController) {
// Remove background from the pushed view controller
toViewBackgroundColor = fromVC.collectionView?.backgroundColor
fromVC.collectionView?.backgroundColor = nil
}setStartPositionForPop(_:toVC)方法仅仅是保存BookViewController的背景色并将BooksViewController的Collection View的背景色删除。注意,你不需要创建任何cell动画,因为书在这个时候是打开状态。
接着,在上面的方法后面加入这个方法:
func setEndPositionForPop(fromVC: BookViewController, toVC: BooksViewController) {
//1
let coverCell = toVC.selectedCell()
//2
for cell in toVC.collectionView!.visibleCells() as! [BookCoverCell] {
if cell != coverCell {
cell.alpha = 1
}
}
//3
for cell in fromVC.collectionView!.visibleCells() as! [BookPageCell] {
closePageCell(cell)
}
}这个方法创建Pop动画的起止点,即从打开变成合起:
- 获取选择的书的封面。
- 在合起状态,在BooksViewController中遍历私有书的封面,然后对所有对象进行一个渐入效果。
- 在BookViewController中遍历当前图书的所有页,将所有cell转变成合起状态。
现在新建如下方法:
func cleanupPop(fromVC: BookViewController, toVC: BooksViewController) {
// Add background back to pushed view controller
fromVC.collectionView?.backgroundColor = self.toViewBackgroundColor
// Unhide the original book cover
toVC.selectedCell()?.alpha = 1
}这个方法在Pop动画完成时执行清理动作:将BooksViewController的Collection View的背景色设回它开始的值并显示封面。
在animateTransition(_:)方法里面,找到注释有“//POP”的else语句块,添加如下代码:
//1
let fromVC = transitionContext.viewControllerForKey(UITransitionContextFromViewControllerKey) as! BookViewController
let toVC = transitionContext.viewControllerForKey(UITransitionContextToViewControllerKey) as! BooksViewController
//2
container.insertSubview(toVC.view, belowSubview: fromVC.view)
//3
setStartPositionForPop(fromVC, toVC: toVC)
UIView.animateWithDuration(self.transitionDuration(transitionContext), animations: {
//4
self.setEndPositionForPop(fromVC, toVC: toVC)
}, completion: { finished in
//5
self.cleanupPop(fromVC, toVC: toVC)
//6
transitionContext.completeTransition(finished)
})以上代码解释如下:
- 获取动画中涉及的两个ViewController。现在,fromVC 是BookViewController (打开状态),toVC是BooksViewController(合起状态)。
- 向Container View中加入BooksViewController(在BookViewContorller的下方)。
- setStartPositionForPop(_:toVC) 方法先保存背景色,再将背景色设为nil。
- 执行动画,即从打开状态切换到合起状态。
- 动画完成,执行清理动作。将背景色设回原来值,显示封面。
- 通知动画完成。
在Navigation Controller中应用Pop动画
现在需要创建Pop动画,就如同我们在Push动画所做一样。
打开BooksViewController.swift,在animationControllerForPresentController(_:)方法后增加如下方法:
func animationControllerForDismissController(vc: UIViewController) -> UIViewControllerAnimatedTransitioning? {
var transition = BookOpeningTransition()
transition.isPush = false
self.transition = transition
return transition
}这里,我们创建了一个新的BookOpeningTransition对象,但不同的是isPush设置为false。
打开CustomNavigationController.swift,然后替换Pop部分的if语句为:
if operation == .Pop {
if let vc = toVC as? BooksViewController {
return vc.animationControllerForDismissController(vc)
}
}上述代码返回一个Transition对象,并执行Pop动画,合起书本。
编译,运行程序,选择一本书,查看它的打开和合起。如下图所示:
创建互动式的Navigation Controller
打开和合起动画搞定了——但我们还能更进一步!我们为什么不用一个更直观的捏放手势来打开和合起书本呢?
打开BookOpeningTransition.swift,增加如下属性定义:
// MARK: Interaction Controller
var interactionController: UIPercentDrivenInteractiveTransition?然后打开CustomNavigationController.swift,加入下列代码:
func navigationController(navigationController: UINavigationController, interactionControllerForAnimationController animationController: UIViewControllerAnimatedTransitioning) -> UIViewControllerInteractiveTransitioning? {
if let animationController = animationController as? BookOpeningTransition {
return animationController.interactionController
}
return nil
}在这个方法中,我们从BookOpeningTransition对象获得了一个interactionController。这样导航控制器能够跟踪动画进程以便用户可以用捏放手势打开和合起书。
打开BooksViewController.swift,在trnasitoin变量下增加如下属性:
//1
var interactionController: UIPercentDrivenInteractiveTransition?
//2
var recognizer: UIGestureRecognizer? {
didSet {
if let recognizer = recognizer {
collectionView?.addGestureRecognizer(recognizer)
}
}
}这两个属性的作用分别是:
- interactionController 是一个UIPercentDrivenInteractiveTransition类,它负责管理View Contorller之间转场的自定义动画。interactionController由一个Transition Animator生成,后者是一个实现了UIViewControllerAnimatorTransitioning协议的对象。而我们已经拥有了BookOpeningTransition——这就是一个实现了UIViewControllerAnimatorTransitioning的对象。interactionController能够控制Push动画和Pop动画之间的进度。关于这个类的更多内容,请参考Apple官方文档。
- recognizer 是一个UIGestureRecognizer。我们用这个手势识别器实现以捏放手势开合书本。
在BooksViewController扩展的animationControllerForPresentController(_:)方法中,transition.isPush=true一行下面,加入代码:
transition.interactionController = interactionController这句代码让CustomNavigationController知道要用哪个interaction controller。
在animationControllerForDismissController(_:)方法中transition.isPush=false一行下面加入同样的代码:
transition.interactionController = interactionController在viewDidLoad()方法中增加代码:
recognizer = UIPinchGestureRecognizer(target: self, action: "handlePinch:")这里我们初始化了一个UIPinchGestureRecognizer,允许用户在做出捏放手势时调用handlePinch(_:)方法。
在viewDidLoad()方法下面实现这个方法:
// MARK: Gesture recognizer action
func handlePinch(recognizer: UIPinchGestureRecognizer) {
switch recognizer.state {
case .Began:
//1
interactionController = UIPercentDrivenInteractiveTransition()
//2
if recognizer.scale >= 1 {
//3
if recognizer.view == collectionView {
//4
var book = self.selectedCell()?.book
//5
self.openBook(book)
}
//6
} else {
//7
navigationController?.popViewControllerAnimated(true)
}
case .Changed:
//8
if transition!.isPush {
//9
var progress = min(max(abs((recognizer.scale - 1)) / 5, 0), 1)
//10
interactionController?.updateInteractiveTransition(progress)
//11
} else {
//12
var progress = min(max(abs((1 - recognizer.scale)), 0), 1)
//13
interactionController?.updateInteractiveTransition(progress)
}
case .Ended:
//14
interactionController?.finishInteractiveTransition()
//15
interactionController = nil
default:
break
}
}对于UIPinchGestureRecognizer,我们要关注这3个状态:开始状态,这让你知道捏放手势何时开始;改变状态,检测捏放手势的变化;结束状态,让你知道捏放手势何时结束。
handlePinch(_:)方法代码解释如下:
开始状态
1. 创建一个UIPercentDrivenInteractiveTransition 对象。
2. scale取决于捏合点之间的距离,判断scale值是否大于或者等于1。
3. 如果是,判断相关的View是否是一个Collection View。
4. 获取正在被捏合的书。
5. 执行Push BookViewController的动画,显示书本中的书页。
6. 如果 scale 小于 1…
7. …执行Pop BookViewController的动画,显示封面
改变状态 – 捏合过程中
8. 判断当前是否是Push动画。
9. 如果正在Push一个BookViewConroller,计算捏放手势的进度。该进度必然是0-1之间的数字。我们将原始值除以5以让用户拥有更好的控制感。否则用双指打开的手势打开一本书时,会突然跳到打开状态。
10. 基于我们计算的进度,更新动画进度。
11. 如果当前不是Push动画,则它应该是Pop动画。
12. 当双指捏合合起一本书时,scale值必然是从1慢慢变到0。
13. 最后, 更新动画进度。
结束状态 – 手势终止
14. 告诉系统,用户交互式动画完成。
15.将interaction controller 设置为 nil。
最后,我们需要实现“捏合以合起书本”的状态。当然,我们必须将手势识别器传递给BookViewController以便它会Pop。
打开BookViewController.swift,在book变量声明下增加一个属性:
var recognizer: UIGestureRecognizer? {
didSet {
if let recognizer = recognizer {
collectionView?.addGestureRecognizer(recognizer)
}
}
}当我们将手势识别器传递给BookViewController时,它会被添加到Collection View,因此我们可以跟踪到用户的“关书”手势。
然后需要在BooksViewController和BookViewController之间传递手势识别器。
打开BookOpeningTransition.swift。在cleanUpPush(_:toVC)方法中,在设置背景色之后添加如下代码:
// Pass the gesture recognizer
toVC.recognizer = fromVC.recognizer当我们从BooksViewController Push到BookViewController时,将捏放手势传递给BookViewController。这会导致捏放手势自动添加到Collection View中。
当我们从BookViewController Pop回BooksViewController时,我们必须将捏放手势又传递回去。
在cleanUpPop(_:toVC)方法中,在我设置背景色之后添加如下代码:
// Pass the gesture recognizer
toVC.recognizer = fromVC.recognizer编译、运行程序,选择一本书,用捏放手势打开和合起书:
捏放手势是一种天然就适合用于对书本进行“开关”的手势;它让我们的界面显得更加简单。我们不再需要导航栏的Back按钮——因此我们决定去掉它。
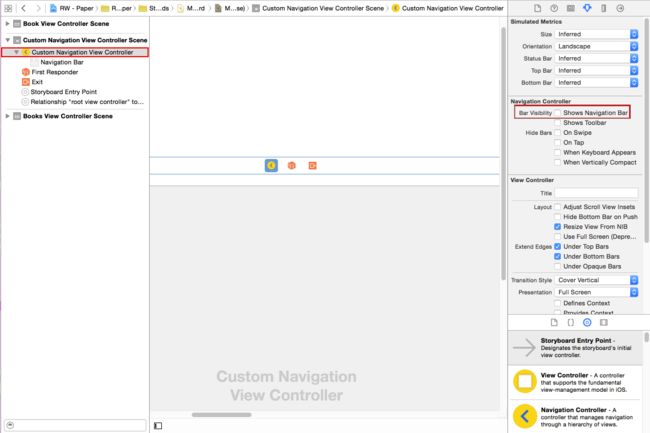
打开Main.storyboard,选择Custom Navigation View Controller,打开属性面板,在Navigation Controller一栏下面,取消Bar Visibility选项,如下所示:
接下来做什么
你可以在这里下载到上面所有步骤完成后的最终项目。
在本教程中,我们学习如何对Collection View进行自定义布局,让App的用户体验更加自然、也更加有趣。我们还创建了自定义动画,使用智能交互让用户以捏放手势开合一本书。这个App在实现了所有基本功能的同时,让程序显得更加的人性化和与众不同。
相比较之下,是默认的“淡入/淡出”动画更简单一些。它能节省你一部分开发时间。但是杰出的应用程序都应当有一些自己特有的地方,从而使它们能够脱颖而出。
要知道,每个人都喜欢记住那些用起来非常有趣的App,在UI上能让人感到兴奋而同时又没有牺牲功能的App。
希望你能喜欢本教程,再次感谢Attila Hegedüs提供了这个教程的示例项目。
如果对本教程有任何问题,请加入到下面的讨论中来!