GXPT(二)——初识集合
集合是什么??集合就是容器,主要用于存储和管理对象。
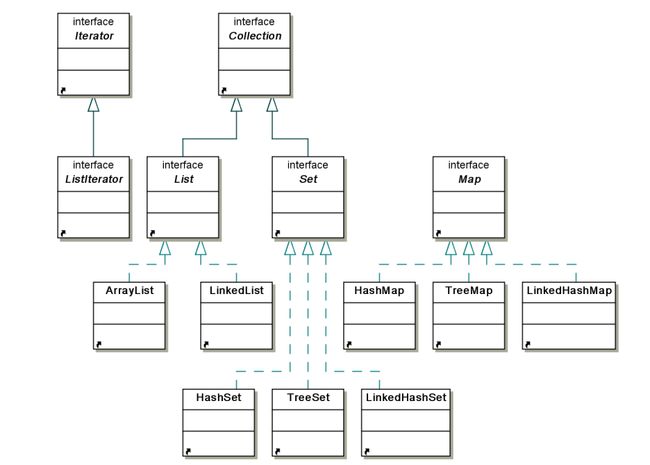
*******基本集合:
Collecion:是构造类集框架的基础。它声明所有类集都将拥有的核心方法。所有的类集实现Collection。
List:有序的Collection,使用此接口能精确的控制每个元素插入的位置。用户能够使用索引(元素在List中的位置,类似于数组下标)来访问List中的元素。List允许有相同的元素。
Set:一种不包含重复的元素的Collection。
Map:没有继承Collection接口,在数组中我们是通过数组下标来对其内容索引的,而在Map中我们通过对象来对对象进行索引,用来索引的对象叫做key,其对应的对象叫做value。这就是我们平时说的键值对Map提供key到value的映射。一个Map中不能包含相同的key,每个key只能映射一个value。
*******自定义实体集合:
方式一:复用性差的实体集合类
实体类:
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using 集合.集合.灵活性差的ORMapping;
namespace TableToCollection.实体
{
public class Person
{
public string strID { get; set; }
public string strName { get; set; }
public int intAge { get; set; }
}
}
实体集合类:
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Collections;
using TableToCollection.实体;
namespace TableToCollection.集合.灵活性差的集合
{
public class PersonCollection_bad:IEnumerable
{
private ArrayList list;
public int Count
{
get { return list.Count; }
}
#region 构造函数
public PersonCollection_bad()
{
list = new ArrayList();
}
#endregion
#region 添加
public void Add(Person p)
{
this.list.Add(p);
}
public void AddAr(Person[] ps)
{
this.list.AddRange(ps);
}
#endregion
#region 删除
public void Remove(Person p)
{
this.list.Remove(p);
}
public void RemoveAt(int index)
{
this.list.RemoveAt(index);
}
public void RemoveRange(int index, int count)
{
this.list.RemoveRange(index, count);
}
public void Clear() {
this.list.Clear();
}
#endregion
#region 自定义索引器
public Object this[int index]
{
get
{
return list[index];
}
set
{
list[index] = value;
}
}
#endregion
#region 支持foreach语句遍历
public IEnumerator GetEnumerator()
{
return list.GetEnumerator();
}
#endregion
}
}
方式二:复用性好的实体集合类
基础实体集合类:
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
namespace 集合.集合.灵活性好的集合
{
public class BaseCollection<T>:IEnumerable<T>,IEnumerator<T>,IList<T>
{
private List<T> list;
//定义索引
private int position;
public int Count
{
get {
if (list != null)
{
return list.Count;
}
return -1;
}
}
/// <summary>
/// 确定集合中特定对象的索引
/// </summary>
/// <param name="TObject">特定的对象</param>
/// <returns>如果在列表中找到,则为item 的索引;否则为 -1</returns>
public int IndexOf(T TObject)
{
return this.list.IndexOf(TObject);
}
#region 构造方法
public BaseCollection(){
this.list = new List<T>();
this.position = -1;
}
#endregion
#region 添加
/// <summary>
/// 将对象添加到集合的尾部
/// </summary>
/// <param name="TObject">要添加到集合尾部的对象</param>
public void Add(T TObject)
{
this.list.Add(TObject);
}
/// <summary>
/// 将指定集合里的元素添加到集合尾部
/// </summary>
/// <param name="TCollection">要添加到集合尾部的集合对象</param>
public void AddRange(ICollection<T> TCollection)
{
this.list.AddRange(TCollection);
}
#endregion
#region 删除
/// <summary>
/// 从集合中移除特定对象的第一个匹配项
/// </summary>
/// <param name="TObject">TObject</param>
/// <returns>true:移除成功;false:移除失败</returns>
public bool Remove(T TObject) {
return this.list.Remove(TObject);
}
/// <summary>
/// 从集合中移除指定索引处的对象
/// </summary>
/// <param name="index">索引值,从0开始</param>
public void RemoveAt(int index)
{
this.list.RemoveAt(index);
}
/// <summary>
/// 集合删除所有对象
/// </summary>
public void Clear() {
this.list.Clear();
}
#endregion
#region 插入
/// <summary>
/// 在集合的特定位置插入对象
/// </summary>
/// <param name="index">索引,从0开始</param>
/// <param name="TObject">被插入的对象</param>
public void Insert(int index, T TObject)
{
this.list.Insert(index, TObject);
}
#endregion
#region 取值
/// <summary>
/// 获取或设置指定索引处的元素
/// </summary>
/// <param name="index">索引值从0开始</param>
/// <returns>TObject</returns>
public T this[int index]
{
get
{
return this.list[index];
}
set
{
this.list[index] = value;
}
}
#endregion
#region 实现ICollection<T>,因为IList<T>继承ICollection<T>
//获取一个值,该值指示 System.Collections.Generic.ICollection<T> 是否为只读。
public bool IsReadOnly
{
get
{
return true;
}
}
//确定 System.Collections.Generic.ICollection<T> 是否包含特定值。
public bool Contains(T item)
{
return this.list.Contains(item);
}
//从特定的 System.Array 索引处开始,将 System.Collections.Generic.ICollection<T> 的元素复制到一个
public void CopyTo(T[] array, int arrayIndex)
{
this.list.CopyTo(array, arrayIndex);
}
#endregion
#region 支持foreach语句遍历
#region 实现IEnumerable<T>接口
System.Collections.Generic.IEnumerator<T> System.Collections.Generic.IEnumerable<T>.GetEnumerator()
{
return (System.Collections.Generic.IEnumerator<T>)this;
}
#region 实现IEnumerable接口,因为IEnumerable<T>继承IEnumerable
System.Collections.IEnumerator System.Collections.IEnumerable.GetEnumerator()
{
return (System.Collections.IEnumerator)this;
}
#endregion
#endregion
#region 实现IEnumerator<T>接口
//获取集合中的当前元素。
T System.Collections.Generic.IEnumerator<T>.Current
{
get {
try
{
return this.list[position];
}
catch (IndexOutOfRangeException)
{
throw new InvalidOperationException();
}
}
}
#region 实现IEnumerator接口,因为IEnumerator<T>继承IEnumerator
//获取集合中的当前元素。
object System.Collections.IEnumerator.Current
{
get
{
try
{
return this.list[position];
}
catch (IndexOutOfRangeException)
{
throw new InvalidOperationException();
}
}
}
//将枚举数推进到集合的下一个元素。
bool System.Collections.IEnumerator.MoveNext()
{
this.position++;
return (this.position < this.list.Count);
}
//将枚举数设置为其初始位置,该位置位于集合中第一个元素之前。
void System.Collections.IEnumerator.Reset()
{
this.position = -1;
}
#endregion
#region 实现IDisposable接口,因为IEnumerator<T>继承IDisposable
public void Dispose()
{
this.position = -1;
}
#endregion
#endregion
#endregion
}
}
具体实体集合类:
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using TableToCollection.实体;
namespace 集合.集合.灵活性好的集合
{
public class PersonBaseCollection:BaseCollection<Person>
{
}
}
*******比较:
为什么说方式二的灵活性好,复用性高呢?原因是它采用了泛型,解决了方式一种服务类型固定的问题。方式二将95%重复的代码抽象出来,将需要扩展的,或者是属于某个实体集合类本身的代码,写到自己的实体集合类中。
*******总结:
问题一:
从上面我们知道了实体的样子,也知道了实体集合的样子和作用,那么有一个问题就来了:是否可以用实体集合类代替实体呢?难道只是为了解耦合(实体:属性 ,便于参数传递; 实体集合:提供操作,管理实体对象),才有实体和实体集合这两种东西出现吗?
问题二:
老师说过,集合其实就是容器,可是我怎么没有体会出来呢??