RemoteViews完全解析
一、概述
什么是RemoteViews?从字面意思可以理解为远程View。需要注意的是,RemoteViews并不是View的子类,它是Object的子类。它的作用是可以跨进程更新界面,是不是功能很强大?它在实际应用中主要在通知栏和桌面小控件,下面就全部基于通知栏来分析。
二、演示
三、RemoteViews在通知栏上的应用
定义了两个按钮,分别用来发送不同的通知
<LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android" xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools" android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="match_parent" tools:context=".MainActivity" android:orientation="vertical" >
<Button android:id="@+id/btn_normal" android:layout_width="wrap_content" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:text="普通通知" />
<Button android:id="@+id/btn_zdy" android:layout_width="wrap_content" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:text="自定义通知" />
</LinearLayout>
java代码
case R.id.btn_normal:
//1.创建通知对象
Notification nf = new Notification() ;
//2.通知的一些常用设置
//图标
nf.icon = R.drawable.ic_launcher ;
//通知时间
nf.when = System.currentTimeMillis();
//消息来临时显示的提示信息
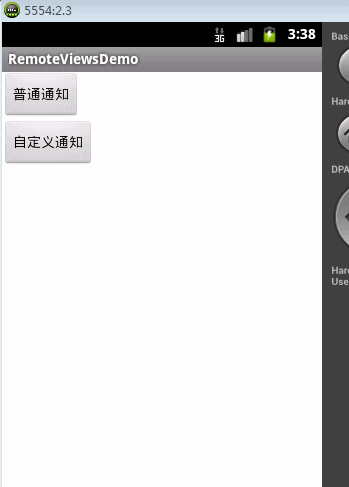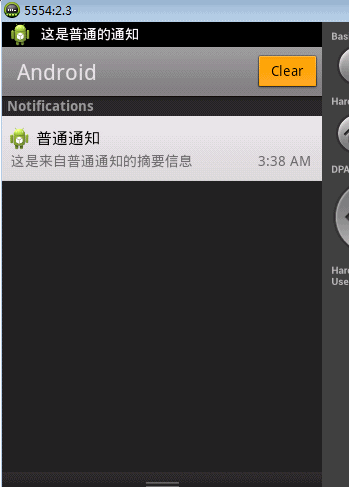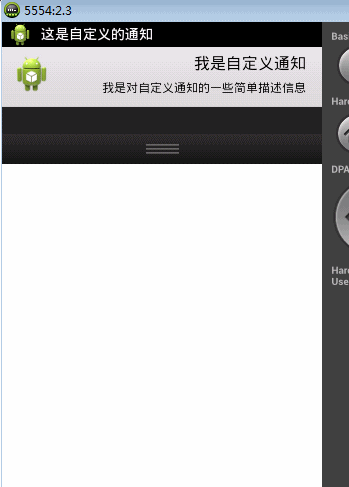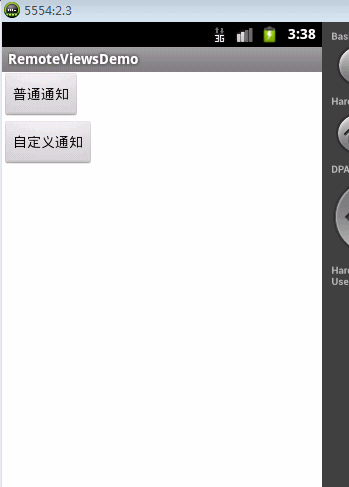
nf.tickerText = "这是普通的通知";
//设置通知自动取消
nf.flags = Notification.FLAG_AUTO_CANCEL;
//3.创建延时意图
Intent intent = new Intent(this,NormalNotificationActivity.class);
PendingIntent pi = PendingIntent.getActivity(this, 0, intent, PendingIntent.FLAG_UPDATE_CURRENT);
//
nf.setLatestEventInfo(this, "普通通知", "这是来自普通通知的摘要信息", pi);
//4.创建notificationmanager对象
NotificationManager nm = (NotificationManager) getSystemService(NOTIFICATION_SERVICE);
//这里的id最好保证每次都是不一样的,否则第二次发送无效
nm.notify(nId++ , nf);
break;
这只是一个简单的通知,并没有涉及RemoteViews,主要是知道普通的通知应该如何书写。
case R.id.btn_zdy:
//1.创建通知对象
Notification myNf = new Notification() ;
//2.通知的一些常用设置
//图标
myNf.icon = R.drawable.ic_launcher ;
//通知时间
myNf.when = System.currentTimeMillis();
myNf.tickerText = "这是自定义的通知";
myNf.flags = Notification.FLAG_AUTO_CANCEL;
//3.创建延时意图
Intent myIntent = new Intent(this,NormalNotificationActivity.class);
PendingIntent myPi = PendingIntent.getActivity(this, 0, myIntent, PendingIntent.FLAG_UPDATE_CURRENT);
/** * 注意:这个字段是要配合nf.contentView这个字段一起使用的,如果只是设置一个会报错 * nf.contentIntent = pi ; */
/****************** *没有设置contentIntent时:java.lang.IllegalArgumentException: contentIntent required: pkg=com.lw.remoteviewsdemo id=0 notification=Notification(vibrate=null,sound=null,defaults=0x0,flags=0x10) * ****************************/
//4.创建RemoteViews
RemoteViews rv = new RemoteViews(getPackageName(),R.layout.activity_mynotification);
//给remoteviews手动设置值
rv.setTextViewText(R.id.msg, "我是自定义通知");
rv.setTextViewText(R.id.des, "我是对自定义通知的一些简单描述信息");
myNf.contentView = rv ;
myNf.contentIntent = myPi ;
//5.创建notificationmanager对象
NotificationManager myNm= (NotificationManager) getSystemService(NOTIFICATION_SERVICE);
//这里的id最好保证每次都是不一样的,否则第二次发送无效
myNm.notify(nId++ , myNf);
break;
这是自定义通知,上面的都有注释,就几个注意的地方说下,使用自定义通知需要为通知的这两个属性赋值,否则就会报上面提到的异常,少一个都不行。
myNf.contentView = rv ;
myNf.contentIntent = myPi ;
还有一点就是在通知myNm.notify(nId++ , myNf)的第一个参数不要设置为一个常量,否则只能发送一个通知。
四、RemoteViews源码分析
在概述中提到,RemoteViews是跨进程更新UI的,也就是通过Binder,那么也就是说RemoteViews肯定实现了序列化接口,看源码:
public class RemoteViews implements Parcelable, Filter 再看上面的例子,RemoteViews是如何自定义一些文本内容的呢,大部分都是通过setTextViewText()等方法完成的,看源码
public void setTextViewText(int viewId, CharSequence text) {
setCharSequence(viewId, "setText", text);
}
调用了setCharSequence方法,注意:这里的第二个参数是setText,是不是和TextView的setText很像呢,点进去
public void setCharSequence(int viewId, String methodName, CharSequence value) {
addAction(new ReflectionAction(viewId, methodName, ReflectionAction.CHAR_SEQUENCE, value));
}
那么ReflectionAction又是什么东西呢?从字面可以理解为反射动作。
/** * Base class for the reflection actions. */
private class ReflectionAction extends Action {
static final int TAG = 2;
static final int BOOLEAN = 1;
static final int BYTE = 2;
static final int SHORT = 3;
static final int INT = 4;
static final int LONG = 5;
static final int FLOAT = 6;
static final int DOUBLE = 7;
static final int CHAR = 8;
static final int STRING = 9;
static final int CHAR_SEQUENCE = 10;
static final int URI = 11;
// BITMAP actions are never stored in the list of actions. They are only used locally
// to implement BitmapReflectionAction, which eliminates duplicates using BitmapCache.
static final int BITMAP = 12;
static final int BUNDLE = 13;
static final int INTENT = 14;
从源码可以看出,它是Action的子类,从注释可以看出它是反射类的基类,通过之前传递过来的setText来进行反射获取信息,这个类需要配合一会分析的RemoteViews的apply()方法配合看。再回到前面的addAction方法
/** * Add an action to be executed on the remote side when apply is called. * * @param a The action to add */
private void addAction(Action a) {
if (hasLandscapeAndPortraitLayouts()) {
throw new RuntimeException("RemoteViews specifying separate landscape and portrait" +
" layouts cannot be modified. Instead, fully configure the landscape and" +
" portrait layouts individually before constructing the combined layout.");
}
if (mActions == null) {
mActions = new ArrayList<Action>();
}
mActions.add(a);
// update the memory usage stats
a.updateMemoryUsageEstimate(mMemoryUsageCounter);
}
可以看出,系统首先判断mActions是否为null,如果为null,则创建一个存放Action的List集合,然后就将传递过来的Action添加到mActions中。再来看一些Action源码
/** * Base class for all actions that can be performed on an * inflated view. * * SUBCLASSES MUST BE IMMUTABLE SO CLONE WORKS!!!!! */
private abstract static class Action implements Parcelable {
public abstract void apply(View root, ViewGroup rootParent,
OnClickHandler handler) throws ActionException;
public static final int MERGE_REPLACE = 0;
public static final int MERGE_APPEND = 1;
public static final int MERGE_IGNORE = 2;
public int describeContents() {
return 0;
}
/** * Overridden by each class to report on it's own memory usage */
public void updateMemoryUsageEstimate(MemoryUsageCounter counter) {
// We currently only calculate Bitmap memory usage, so by default, don't do anything
// here
return;
}
public void setBitmapCache(BitmapCache bitmapCache) {
// Do nothing
}
public int mergeBehavior() {
return MERGE_REPLACE;
}
public abstract String getActionName();
public String getUniqueKey() {
return (getActionName() + viewId);
}
int viewId;
}
从注释可以看出它是一个在被填充的展现出来的所有Action的基类,实现Parcelable接口。
简单来说setTextViewText(int viewId, CharSequence text) 方法首先将其封装成一个动作Action类,然后添加到一个actions集合中去。
接着,再来看看RemoteViews的apply方法
public View apply(Context context, ViewGroup parent) {
return apply(context, parent, null);
}
再点进去
public View apply(Context context, ViewGroup parent, OnClickHandler handler) {
RemoteViews rvToApply = getRemoteViewsToApply(context);
View result;
Context c = prepareContext(context);
LayoutInflater inflater = (LayoutInflater)
c.getSystemService(Context.LAYOUT_INFLATER_SERVICE);
inflater = inflater.cloneInContext(c);
inflater.setFilter(this);
result = inflater.inflate(rvToApply.getLayoutId(), parent, false);
rvToApply.performApply(result, parent, handler);
return result;
}
首先,通过上下文获取RemoteViews,然后调用performApply()方法,再看下performApply()源码
private void performApply(View v, ViewGroup parent, OnClickHandler handler) {
if (mActions != null) {
handler = handler == null ? DEFAULT_ON_CLICK_HANDLER : handler;
final int count = mActions.size();
for (int i = 0; i < count; i++) {
Action a = mActions.get(i);
a.apply(v, parent, handler);
}
}
}
这里就可以看出来了,首先判断mActions集合是否为null,不为null,依次遍历actions,然后将处理交给action的apply方法,由于之前我调用的是setTextViewText方法,在那里添加的action的是ReflectionAction,所以这里查看的是ReflectionAction的apply方法,
@Override
public void apply(View root, ViewGroup rootParent, OnClickHandler handler) {
final View view = root.findViewById(viewId);
if (view == null) return;
Class param = getParameterType();
if (param == null) {
throw new ActionException("bad type: " + this.type);
}
Class klass = view.getClass();
Method method;
try {
method = klass.getMethod(this.methodName, getParameterType());
}
catch (NoSuchMethodException ex) {
throw new ActionException("view: " + klass.getName() + " doesn't have method: "
+ this.methodName + "(" + param.getName() + ")");
}
if (!method.isAnnotationPresent(RemotableViewMethod.class)) {
throw new ActionException("view: " + klass.getName()
+ " can't use method with RemoteViews: "
+ this.methodName + "(" + param.getName() + ")");
}
try {
//noinspection ConstantIfStatement
if (false) {
Log.d(LOG_TAG, "view: " + klass.getName() + " calling method: "
+ this.methodName + "(" + param.getName() + ") with "
+ (this.value == null ? "null" : this.value.getClass().getName()));
}
method.invoke(view, this.value);
}
catch (Exception ex) {
throw new ActionException(ex);
}
}
从上面的代码可以看出,主要是通过反射来执行代码,而方法名之前也已经有了,只需要调用invoke即可。OK,这就是RemoteViews的大致流程了。下面就这种思想使用RemoteViews来实现一个跨进程更新UI的例子
五、使用RemoteViews跨进程更新UI的Demo
1.思路
创建两个应用,一个作为本地,一个作为远程,当然如果想要在一个应用使用两个Activity实现也是可以的,只需要在其中一个你想要的Activity作为远程Activity中的配置文件中指定以下代码即可,我这里就是使用两个应用,效果观看更加明显。
android:process=":remote"通知栏的跨进程是通过Binder实现的,我这里就通过广播接受者来实现。OK,上代码
2.代码
本地布局文件
<LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android" xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools" android:orientation="vertical" android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="match_parent" tools:context=".MainActivity" >
<TextView android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:text="我是应用RemoteViewsTest1" />
<LinearLayout android:id="@+id/ll_layout" android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="match_parent" ></LinearLayout>
</LinearLayout>
子LinearLayout是用来存放从远程传递过来的布局的。
本地java代码
public class MainActivity extends Activity {
private IntentFilter filter;
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_main);
ll_layout = (LinearLayout) findViewById(R.id.ll_layout);
filter = new IntentFilter("com.lw.remoteviewstest1");
registerReceiver(mRemoteViewsReceiver, filter);
}
private BroadcastReceiver mRemoteViewsReceiver = new BroadcastReceiver() {
@Override
public void onReceive(Context context, Intent intent) {
RemoteViews remoteViews = intent
.getParcelableExtra("remoteViews");
if (remoteViews != null) {
updateLayout(remoteViews);
}
}
};
private LinearLayout ll_layout;
@Override
protected void onDestroy() {
super.onDestroy();
//反注册广播接受者
if(mRemoteViewsReceiver != null ){
unregisterReceiver(mRemoteViewsReceiver);
}
}
/** * 根据remoteViews更新ui * @param remoteViews */
protected void updateLayout(RemoteViews remoteViews) {
View view = remoteViews.apply(this, ll_layout);
ll_layout.addView(view);
};
}
主要在onCreate动态创建一个广播接收者,然后再onDestory中反注册,当从远程获取到remoteViews的时候调用updateLayout的方法,通过remoteViews的apply方法,这个方法前面已经详细分析了,就不在谈了。
远程布局文件
<RelativeLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:paddingBottom="@dimen/activity_vertical_margin"
android:paddingLeft="@dimen/activity_horizontal_margin"
android:paddingRight="@dimen/activity_horizontal_margin"
android:paddingTop="@dimen/activity_vertical_margin"
tools:context=".MainActivity" >
<Button
android:onClick="send"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="通过RemoteViews向另一个应用远程发送消息" />
</RelativeLayout> 远程java代码
public void send(View view){
//创建remoteviews
RemoteViews rv = new RemoteViews(getPackageName(),R.layout.activity_notification);
//创建intent,设置当点击按钮时要跳转的Activity
Intent sendIntent = new Intent(this,SecondActivity.class);
//创建延时意图
PendingIntent pendingIntent = PendingIntent.getActivity(this, 0, sendIntent, PendingIntent.FLAG_UPDATE_CURRENT);
//为延时意图中的按钮设置点击事件
rv.setOnClickPendingIntent(R.id.btn_toast, pendingIntent) ;
//创建隐式跳转
Intent intent = new Intent("com.lw.remoteviewstest1");
//将RemoteViews带到应用一中去
intent.putExtra("remoteViews", rv);
//发送广播
sendBroadcast(intent);
}
这里提下,如果想要为remoteviews添加点击事件,则必须使用PendingIntent,其实最后还是通过添加action,不过这里的action不是前面提到的反射action,而是SetOnClickPendingIntent,我们可以看下这个类的apply方法,这里只需要看最后一个代码,最后调用了setOnclickListener方法,其它的注释都比较详细,就不说了。
@Override
public void apply(View root, ViewGroup rootParent, final OnClickHandler handler) {
final View target = root.findViewById(viewId);
if (target == null) return;
// If the view is an AdapterView, setting a PendingIntent on click doesn't make much
// sense, do they mean to set a PendingIntent template for the AdapterView's children?
if (mIsWidgetCollectionChild) {
Log.w(LOG_TAG, "Cannot setOnClickPendingIntent for collection item " +
"(id: " + viewId + ")");
ApplicationInfo appInfo = root.getContext().getApplicationInfo();
// We let this slide for HC and ICS so as to not break compatibility. It should have
// been disabled from the outset, but was left open by accident.
if (appInfo != null &&
appInfo.targetSdkVersion >= Build.VERSION_CODES.JELLY_BEAN) {
return;
}
}
if (target != null) {
// If the pendingIntent is null, we clear the onClickListener
OnClickListener listener = null;
if (pendingIntent != null) {
listener = new OnClickListener() {
public void onClick(View v) {
// Find target view location in screen coordinates and
// fill into PendingIntent before sending.
final float appScale = v.getContext().getResources()
.getCompatibilityInfo().applicationScale;
final int[] pos = new int[2];
v.getLocationOnScreen(pos);
final Rect rect = new Rect();
rect.left = (int) (pos[0] * appScale + 0.5f);
rect.top = (int) (pos[1] * appScale + 0.5f);
rect.right = (int) ((pos[0] + v.getWidth()) * appScale + 0.5f);
rect.bottom = (int) ((pos[1] + v.getHeight()) * appScale + 0.5f);
final Intent intent = new Intent();
intent.setSourceBounds(rect);
handler.onClickHandler(v, pendingIntent, intent);
}
};
}
target.setOnClickListener(listener);
}
}
Demo整体思路:远程主要通过Intent携带RemoteViews传递到本地连接,本地连接获取到RemoteViews之后,调用apply方法返回个View对象,这个view对象就是远程RotateViews携带的布局,然后添加到本地对应的布局中去。
OK,这篇关于RemoteViews的学习总结就到这了。