JSP简明记录
JSP全名为Java Server Pages,中文名叫java服务器页面,其根本是一个简化的Servlet设计,它是由Sun公司倡导、许多公司参与一起建立的一种动态网页技术标准。
一、:Page指令
page指令用于设置一些页面的基本属性
language="java" 页面中使用的语言为java. import="java.util.*" 就是导包. 是所有属性中唯一一个可以在页面中出现多次的属性. pageEncoding="UTF-8" 页面保存到硬盘编码. contentType="text/html; charset=UTF-8" 发送给浏览器的编码 . 以上两个码表最好一致. 但是一般设置一个属性即可.另外一个属性自动设置. autoFlush="true" 如果缓冲区装满是否自动刷新到浏览器. 如果装满并没有选择自动刷新,那么会抛出异常. buffer="8kb" 决定jsp输出缓冲区大小为8kb errorPage="" 配置当前页面的错误页面 isErrorPage="false" 指定当前页面是否是一个错误页面
<%@ page language="java" import="java.util.*,java.io.*" pageEncoding="UTF-8" contentType="text/html; charset=UTF-8"
autoFlush="true" buffer="8kb" errorPage="/page/error.jsp" session="true"
%>
<%@ page import="java.util.*" %>
<%
String path = request.getContextPath();
String basePath = request.getScheme()+"://"+request.getServerName()+":"+request.getServerPort()+path+"/";
session.getAttribute("");
int i = 1/0;
%>
<!DOCTYPE HTML PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD HTML 4.01 Transitional//EN">
<html>
<head>
<base href="<%=basePath%>">
<title>My JSP 'index.jsp' starting page</title>
<meta http-equiv="pragma" content="no-cache">
<meta http-equiv="cache-control" content="no-cache">
<meta http-equiv="expires" content="0">
<meta http-equiv="keywords" content="keyword1,keyword2,keyword3">
<meta http-equiv="description" content="This is my page">
<!--
<link rel="stylesheet" type="text/css" href="styles.css">
-->
</head>
<body>
This is jsp page. <br>
</body>
</html>
下面是其对应的error.jsp,当我们访问index.jsp时,会跳转到本页面并打印对应的错误信息/by zero
<%@ page language="java" import="java.util.*" pageEncoding="ISO-8859-1"
isErrorPage="true"
%>
<%
String path = request.getContextPath();
String basePath = request.getScheme()+"://"+request.getServerName()+":"+request.getServerPort()+path+"/";
%>
<!DOCTYPE HTML PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD HTML 4.01 Transitional//EN">
<html>
<head>
<base href="<%=basePath%>">
<title>My JSP 'error.jsp' starting page</title>
<meta http-equiv="pragma" content="no-cache">
<meta http-equiv="cache-control" content="no-cache">
<meta http-equiv="expires" content="0">
<meta http-equiv="keywords" content="keyword1,keyword2,keyword3">
<meta http-equiv="description" content="This is my page">
<!--
<link rel="stylesheet" type="text/css" href="styles.css">
-->
</head>
<body>
This is my Error page. <br>
<%=exception.getMessage() %>
</body>
</html>
二、:JSP的9大内置对象
(1)对象列举
对象名称<span style="white-space:pre"> </span>对象类型 request<span style="white-space:pre"> </span>HttpServletRequest response<span style="white-space:pre"> </span>HttpServletResponse session<span style="white-space:pre"> </span>HttpSession exception<span style="white-space:pre"> </span>Throwable application<span style="white-space:pre"> </span>ServletContext config<span style="white-space:pre"> </span>ServletConfig page<span style="white-space:pre"> </span>Object 没用. out<span style="white-space:pre"> </span>JspWriter 用于向浏览器输出信息 pageContext<span style="white-space:pre"> </span>PageContext<span style="white-space:pre"> </span>9大内置对象的首领.
(2)pageContext可操作的四个域
可以设置键值,根据键获得值,删除和查找,最后是打印出设置的键值。
<%@ page language="java" import="java.util.*" pageEncoding="UTF-8"%>
<%
String path = request.getContextPath();
String basePath = request.getScheme()+"://"+request.getServerName()+":"+request.getServerPort()+path+"/";
%>
<!DOCTYPE HTML PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD HTML 4.01 Transitional//EN">
<html>
<head>
<base href="<%=basePath%>">
<title>My JSP 'pageContext01.jsp' starting page</title>
<meta http-equiv="pragma" content="no-cache">
<meta http-equiv="cache-control" content="no-cache">
<meta http-equiv="expires" content="0">
<meta http-equiv="keywords" content="keyword1,keyword2,keyword3">
<meta http-equiv="description" content="This is my page">
<!--
<link rel="stylesheet" type="text/css" href="styles.css">
-->
</head>
<body>
<%
// PageContext可以操作4个域
//增
pageContext.setAttribute("name","requestTom", PageContext.REQUEST_SCOPE);
pageContext.setAttribute("name","sessionTom", PageContext.SESSION_SCOPE);
pageContext.setAttribute("name","applicationTom", PageContext.APPLICATION_SCOPE);
//根据键获得值
pageContext.getAttribute("name", PageContext.REQUEST_SCOPE);
//删
pageContext.removeAttribute("name",PageContext.REQUEST_SCOPE);
//查所有键
pageContext.getAttributeNamesInScope(PageContext.REQUEST_SCOPE);
// find 从4个域中找 ,从小到大.一旦找到立刻停止,并返回找到的.
pageContext.findAttribute("name");
%>
request: <%=request.getAttribute("name") %><br>
session: <%=session.getAttribute("name") %><br>
application: <%=application.getAttribute("name") %><br>
findAttribute:<%= pageContext.findAttribute("name") %><br>
</body>
</html>
其打印结果如下:
request: null session: sessionTom application: applicationTom findAttribute:sessionTom
三、:JSP中的动作标签
下面是两种跳转方式,都可以跳转到指定页面,但是我们常用的是第二种的方式
(1)forward方式:
<body>
<%-- JSP动作标签
分担jsp页面的java代码
--%>
<jsp:forward page="/index.jsp"></jsp:forward>
<%-- //下面的代码相当于上面的标签
request.getRequestDispatcher("/index.jsp").forward(request, response);
--%>
</body>
(2)include方式:
<body>
<%-- JSP动作标签
<span style="white-space:pre"> </span>分担jsp页面的java代码
--%>
<jsp:include page="/index.jsp"></jsp:include>
<%--
<span style="white-space:pre"> </span>// jsp 动态包含
<span style="white-space:pre"> </span>request.getRequestDispatcher("/index.jsp").include(request, response);
--%>
</body>
四、:JSP中表单提交和转换
(1)首先定义一个demo.jsp页面
在该jsp页面中,我们定义了四个输入框,用户名、密码、年龄和入职日期,对应的action = day10-jsp/AServlet
method = "post";
<%@ page language="java" import="java.util.*" pageEncoding="UTF-8"%>
<%
String path = request.getContextPath();
String basePath = request.getScheme()+"://"+request.getServerName()+":"+request.getServerPort()+path+"/";
%>
<!DOCTYPE HTML PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD HTML 4.01 Transitional//EN">
<html>
<head>
<base href="<%=basePath%>">
<title>My JSP 'demo.jsp' starting page</title>
<meta http-equiv="pragma" content="no-cache">
<meta http-equiv="cache-control" content="no-cache">
<meta http-equiv="expires" content="0">
<meta http-equiv="keywords" content="keyword1,keyword2,keyword3">
<meta http-equiv="description" content="This is my page">
<!--
<link rel="stylesheet" type="text/css" href="styles.css">
-->
</head>
<body>
<form action="/day10-jsp/AServlet" method="post" >
用户名:<input type="text" name="name" /><br>
密码:<input type="password" name="password" /><br>
年龄:<input type="text" name="age" /><br>
入职日期:<input type="text" name="hiredate" /><br>
<input type="submit" value="登录" />
</form>
</body>
</html>
(2)AServlet接收处理表单信息
使用Servlet接收jsp传递过来的表单信息有两种方式,第一种使用的是我们注释掉的方式,也就是使用request的接收方式,第二种是使用BeanUtils工具类的方式。
import java.io.IOException;
import java.lang.reflect.InvocationTargetException;
import java.util.Date;
import javax.servlet.ServletException;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServlet;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletResponse;
import org.apache.commons.beanutils.BeanUtils;
import org.apache.commons.beanutils.ConvertUtils;
public class AServlet extends HttpServlet {
public void doGet(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response)
throws ServletException, IOException {
// 创建User对象
User u = new User();
// 将表单参数封装到User对象
//参数1: 填写User对象
//参数2: 填写需要封装到User对象的参数Map
try {
//如果我们需要BeanUtils支持非8大基本数据类型.我们只要给BeanUtils添加类型转换器即可
//注意:注册类型转换器,必须写在populate方法之前.
ConvertUtils.register(new MyDateConverter(), Date.class);
//BeanUtils在封装时可以完成类型转换. 自动转换的范围 只限于 8个基本数据类型
BeanUtils.populate(u,request.getParameterMap());
} catch (IllegalAccessException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (InvocationTargetException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println(u);
/* //1 获得参数
String name = request.getParameter("name");
String password = request.getParameter("password");
//2 封装参数 User
User u = new User();
u.setName(name);
u.setPassword(password);*/
//-------------------------------------------------------
//3 将User对象交给业务类处理
//4 根据处理结果
//成功=>在session加入成功标识,并重定向到成功页面
//失败=>回到登录页面.提示错误信息
}
public void doPost(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response)
throws ServletException, IOException {
doGet(request, response);
}
}
(3)表单传递的User对象
建立一个User对象,包括name、password、age、hiredate等
import java.util.Date;
//javaBean
//1.要求为属性提供get/set方法任意之一
//2.需要有空参构造
//3.实现串行化接口(可选)
public class User {
private String name;
private String password;
private int age;
private Date hiredate;
public Date getHiredate() {
return hiredate;
}
public void setHiredate(Date hiredate) {
this.hiredate = hiredate;
}
public int getAge() {
return age;
}
public void setAge(int age) {
this.age = age;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public String getPassword() {
return password;
}
public void setPassword(String password) {
this.password = password;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "User [name=" + name + ", password=" + password + ", age=" + age
+ ", hiredate=" + hiredate + "]";
}
}
(4)定义一个MyDateConverter转换器
因为BeanUtils工具类中没用对应的date转换器,所以我们要自己定义一个date转换器,并在AServlet中注册这个转换器,来实现转换date的目的。
import java.text.ParseException;
import java.text.SimpleDateFormat;
import java.util.Date;
import org.apache.commons.beanutils.Converter;
public class MyDateConverter implements Converter {
//我们填写转换代码
//参数1: 没用, 告诉实现者,需要转换成什么类型
//参数2: 待转换表单参数
//返回值: 转换结果
public Object convert(Class arg0, Object arg1) {
//1 创建sdf
SimpleDateFormat sdf = new SimpleDateFormat("yyyy/MM/dd");
//2 转换参数2
String dateStr = arg1.toString();
try {
Date date = sdf.parse(dateStr);
//3 将转换结果返回
return date;
} catch (ParseException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
return null;
}
}
}
最终的结果是,我们成功在console中打印表单锁提交的信息。
如:User [name=tom, password=123, age=22, hiredate=Wed Jun 15 00:00:00 CST 2016]
五、:JSTL标签库
JSTL全名为JavaServer Pages Standard Tag Library,JSTL是由JCP(Java Community Process)所制定的标准规范,它主要提供给Java Web开发人员一个标准通用的标签函数库。
(1)if 判断标签
<html>
<head>
<base href="<%=basePath%>">
<title>My JSP 'demo1.jsp' starting page</title>
<meta http-equiv="pragma" content="no-cache">
<meta http-equiv="cache-control" content="no-cache">
<meta http-equiv="expires" content="0">
<meta http-equiv="keywords" content="keyword1,keyword2,keyword3">
<meta http-equiv="description" content="This is my page">
<!--
<link rel="stylesheet" type="text/css" href="styles.css">
-->
</head>
<body>
<!-- core库
c:if 判断 标签
-->
<%
request.setAttribute("num1",10);
request.setAttribute("num2", 100);
%>
<c:if test="${num1 > num2}">
num1 比较大!!
</c:if>
<c:if test="${num1 < num2}">
num2 比较大!!
</c:if>
</body>
</html>
输出结果:num2 比较大!!
<html>
<head>
<base href="<%=basePath%>">
<title>My JSP 'demo1.jsp' starting page</title>
<meta http-equiv="pragma" content="no-cache">
<meta http-equiv="cache-control" content="no-cache">
<meta http-equiv="expires" content="0">
<meta http-equiv="keywords" content="keyword1,keyword2,keyword3">
<meta http-equiv="description" content="This is my page">
<!--
<link rel="stylesheet" type="text/css" href="styles.css">
-->
</head>
<body>
<!-- core库
ifelse 标签
choose
when(可以出现多次)
otherwise
根据num1 num2 的大小,在页面提示值大的那个
-->
<%
request.setAttribute("num1",1000);
request.setAttribute("num2", 100);
%>
<c:choose>
<c:when test="${num1>num2}">
num1 比较大!
</c:when>
<c:when test="${num1==num2}">
num1 与num2 相等!
</c:when>
<c:otherwise>
num2 比较大!
</c:otherwise>
</c:choose>
</body>
</html>
输出结果:num1 比较大!
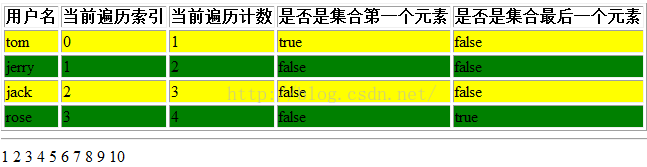
第一个是使用forEach来画一个表格,第二个是遍历数字
<!DOCTYPE HTML PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD HTML 4.01 Transitional//EN">
<html>
<head>
<base href="<%=basePath%>">
<title>My JSP 'demo1.jsp' starting page</title>
<meta http-equiv="pragma" content="no-cache">
<meta http-equiv="cache-control" content="no-cache">
<meta http-equiv="expires" content="0">
<meta http-equiv="keywords" content="keyword1,keyword2,keyword3">
<meta http-equiv="description" content="This is my page">
<!--
<link rel="stylesheet" type="text/css" href="styles.css">
-->
<style type="text/css">
.one{
background-color: yellow;
}
.two{
background-color: green;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<!-- core库
foreach 遍历标签
-->
<%
List list = new ArrayList();
list.add("tom");
list.add("jerry");
list.add("jack");
list.add("rose");
request.setAttribute("list", list);
%>
<table border="1">
<tr>
<th>用户名</th>
<th>当前遍历索引</th>
<th>当前遍历计数</th>
<th>是否是集合第一个元素</th>
<th>是否是集合最后一个元素</th>
</tr>
<c:forEach items="${list}" var="name" varStatus="st" >
<tr class="${st.index%2==0?"one":"two"}" >
<td>${name}</td>
<td>${st.index}</td>
<td>${st.count}</td>
<td>${st.first}</td>
<td>${st.last}</td>
</tr>
</c:forEach>
</table>
<hr>
<!-- 数数的功能-->
<c:forEach begin="1" end="10" step="1" var="num" >
${num}
</c:forEach>
</body>
</html>
输出结果:一个表格和一串数字,并且使用CSS来改变了颜色
(4)fmt格式化日期
<!DOCTYPE HTML PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD HTML 4.01 Transitional//EN">
<html>
<head>
<base href="<%=basePath%>">
<title>My JSP 'ftm1.jsp' starting page</title>
<meta http-equiv="pragma" content="no-cache">
<meta http-equiv="cache-control" content="no-cache">
<meta http-equiv="expires" content="0">
<meta http-equiv="keywords" content="keyword1,keyword2,keyword3">
<meta http-equiv="description" content="This is my page">
<!--
<link rel="stylesheet" type="text/css" href="styles.css">
-->
</head>
<body>
<!--
格式化日期
fmt:formatDate
-->
<fmt:formatDate value="<%=new Date() %>"
pattern="yyyy/MM/dd hh:mm:ss" var="date" scope="request" />
${requestScope.date}
</body>
</html>
输出结果为:2016/06/15 02:41:09
(5)fmt格式化数字
<!DOCTYPE HTML PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD HTML 4.01 Transitional//EN">
<html>
<head>
<base href="<%=basePath%>">
<title>My JSP 'ftm1.jsp' starting page</title>
<meta http-equiv="pragma" content="no-cache">
<meta http-equiv="cache-control" content="no-cache">
<meta http-equiv="expires" content="0">
<meta http-equiv="keywords" content="keyword1,keyword2,keyword3">
<meta http-equiv="description" content="This is my page">
<!--
<link rel="stylesheet" type="text/css" href="styles.css">
-->
</head>
<body>
<!--
格式化数字
fmt:formatNumber
-->
<fmt:formatNumber value="3.1415926" pattern="0000.00000000000" var="num1" scope="request" ></fmt:formatNumber>
<fmt:formatNumber value="3.1415926" pattern="####.###########" var="num2" scope="request" ></fmt:formatNumber>
${requestScope.num1}<br>
${requestScope.num2}<br>
</body>
</html>
输出结果为:0003.141592600003.1415926
以上是对传智老师视频讲课内容的总结,方便自己以后当做笔记来查看