libjson 编译和使用 - 2. 配置使用lib文件
继续上一篇编译后我们这次来讲怎么配置使用刚生产的lib文件。
1. 在之前的libjson所在的解决方案里新建一个控制台应用程序,叫TestLibjson。
2. 右键TestLibjson项目,选择属性。按下图设置导入libjson的头文件。(虽然我们已经编译成lib库文件,但我们还是要在我们的项目里加入头文件。)
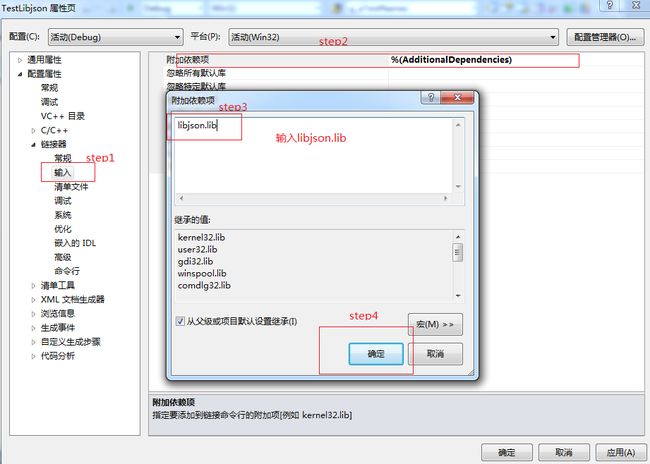
3. 在属性里加入刚刚生产的libjson.lib文件。如下图设置。
好了,配置设置好了,接下来我们写写测试代码
首先新建下列文.h和.cpp文件
在TestLibjson.h文件加入以下代码。
#include "libjson.h"
class TestLibjson
{
public:
TestLibjson();
void ParseJSON(JSONNODE *n);
};
在TestLibjson.cpp文件加入代码。
// TestLibjson.cpp : 定义控制台应用程序的入口点。
//
#include "stdafx.h"
#include <stdlib.h>
#include "TestLibjson.h"
#include "libjson.h"
TestLibjson::TestLibjson()//构造函数
{
}
void TestLibjson::ParseJSON(JSONNODE *n){//解析json文件
if (n == NULL){
printf("Invalid JSON Node\n");
return;
}
JSONNODE_ITERATOR i = json_begin(n);
while (i != json_end(n)){
if (*i == NULL){
printf("Invalid JSON Node\n");
return;
}
// recursively call ourselves to dig deeper into the tree
if (json_type(*i) == JSON_ARRAY || json_type(*i) == JSON_NODE){
ParseJSON(*i);
}
// get the node name and value as a string
json_char *node_name = json_name(*i);
// find out where to store the values
if (strcmp(node_name, "RootA") == 0){
json_char *node_value = json_as_string(*i);
printf("rootA: %s\n", node_value);
json_free(node_value);
}
else if (strcmp(node_name, "ChildA") == 0){
json_char *node_value = json_as_string(*i);
printf("ChildA: %s\n", node_value);
json_free(node_value);
}
else if (strcmp(node_name, "ChildB") == 0)
printf("childB: %d\n", json_as_int(*i));
// cleanup and increment the iterator
json_free(node_name);
++i;
}
system("pause");
}
int _tmain()//程序入口
{
char *json = "{\"RootA\":\"Value in parent node\",\"ChildNode\":{\"ChildA\":\"String Value\",\"ChildB\":42}}";
JSONNODE *n = json_parse(json);
TestLibjson tl = TestLibjson();
tl.ParseJSON(n);
json_delete(n);
return 0;
}
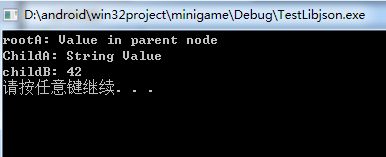
运行结果
注意,这里我们用的的libjson的Debug模式,如果你用的是release模式,那你还需要设置libOption.h文件,把它的#define JSON_DEBUG 注释掉。
下一篇:libjson 编译和使用 - 3. libjson的C接口 API