Linux 内存检测工具 memwatch的使用
1. 官网下载memwatch的源码
推荐使用地址http://www.linkdata.se/sourcecode/memwatch/
2. linux环境下压缩包解压
使用命令:tar -xzvf memwatch-2.71.tar.gz
查看memwatch目录结构:
结构说明:
makefile 编译使用不再多说
USING 说明memwatch如何使用,包括使用memwatch.c 监测内存时需要定义#define new wmNew #define delete wmDelete,需要包含头文件memwatch.h等等
readme 如何编译,链接自己的代码,生成可执行程序 ( 默认生成a.out ) 监测内存
memwatch.c MW系列接口定义
memwatch.h MW系列接口声明
test.c 自带的测试程序,可以换成自己的代码
3. 如何得到memwatch.log
解包之后,进入目录memwatch-2.71,直接make即可生成 a.out ,执行a.out,最后当前目录下会生成memwatch.log.
4. 注意事项
(1)手动编译时,添加宏定义$(CC) -DMEMWATCH -DMW_STDIO test.c memwatch.c
(2)测试程序,添加头文件memwatch.h
(3)定义宏
#define new wmNew
#define delete wmDelete
5. 监测日志查看,分析
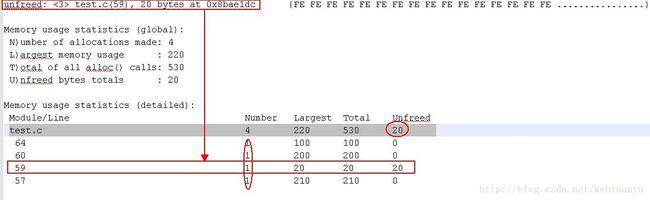
上图显示了,在test.c 文件申请了但没有释放的内存的地方line 59 .
参照代码比对
/*
** NOTE: Running this program in a Win32 or Unix environment
** will probably result in a segmentation fault or protection
** error. These errors may be caused by MEMWATCH when it is
** looking at memory to see if it owns it, or may be caused by
** the test program writing to memory it does not own.
**
** MEMWATCH has two functions called 'mwIsReadAddr()' and
** 'mwIsSafeAddr()', which are system-specific.
** If they are implemented for your system, and works
** correctly, MEMWATCH will identify garbage pointers and
** avoid causing segmentation faults, GP's etc.
**
** If they are NOT implemented, count on getting the core
** dumped when running this test program! As of this writing,
** the safe-address checking has been implemented for Win32
** and ANSI-C compliant systems. The ANSI-C checking traps
** SIGSEGV and uses setjmp/longjmp to resume processing.
**
** Note for Win95 users: The Win32 IsBadReadPtr() and its
** similar functions can return incorrect values. This has
** not happened under WinNT, though, just Win95.
**
** 991009 Johan Lindh
**
*/
#include <stdio.h>
#include <signal.h>
#include "memwatch.h"
#ifndef SIGSEGV
#error "SIGNAL.H does not define SIGSEGV; running this program WILL cause a core dump/crash!"
#endif
#ifndef MEMWATCH
#error "You really, really don't want to run this without memwatch. Trust me."
#endif
#if !defined(MW_STDIO) && !defined(MEMWATCH_STDIO)
#error "Define MW_STDIO and try again, please."
#endif
int main()
{
char *p;
/* Collect stats on a line number basis */
mwStatistics( 2 );
/* Slows things down, but OK for this test prg */
/* mwAutoCheck( 1 ); */
TRACE("Hello world!\n");
p = malloc(210);
free(p);
p = malloc(20);
p = malloc(200); /* causes unfreed error */
p[-1] = 0; /* causes underflow error */
free(p);
p = malloc(100);
p[ -(int)(sizeof(long)*8) ] = -1; /* try to damage MW's heap chain */
free( p ); /* should cause relink */
mwSetAriFunc( mwAriHandler );
ASSERT(1==2);
mwLimit(1000000);
mwNoMansLand( MW_NML_ALL );
......
return 0;
}
发现在line 57,59,60,64四个地方分别申请了内存,只有第59行申请的内存没有释放!刚好和log unfreed对应的行数一样。
6. memwatch 扩展用法
详细用法可参见memwatch.h,也有一篇不错的 文章。
更多内存泄露工具,后续研究!