Android UI之ImageView
前言
这篇博客聊一聊在Android下ImageView的使用,在此篇博客中,会讲解到ImageView的一些属性的使用,以及ImageView展示图片的放大、缩小、旋转等操作。最后再讲解一下Android4.0项目中最常用的一个功能,从网络获取图片的示例。本文所有讲解均会附上示例代码,并在最后提供源码下载。
ImageView
ImageView,图像视图,直接继承自View类,它的主要功能是用于显示图片,实际上它不仅仅可以用来显示图片,任何Drawable对象都可以使用ImageView来显示。ImageView可以适用于任何布局中,并且Android为其提供了缩放和着色的一些操作。
ImageView的一些常用属性,并且这些属性都有与之对应的getter、setter方法:
- android:adjustViewBounds:设置ImageView是否调整自己的边界来保持所显示图片的长宽比。
- android:maxHeight:设置ImageView的最大高度。
- android:maxWidth:设置ImageView的最大宽度。
- android:scaleType:设置所显示的图片如何缩放或移动以适应ImageView的大小。
- android:src:设置ImageView所显示的Drawable对象的ID。
对于android:scaleType属性,因为关于图像在ImageView中的显示效果,所以有如下属性值可以选择:
- matrix:使用matrix方式进行缩放。
- fitXY:横向、纵向独立缩放,以适应该ImageView。
- fitStart:保持纵横比缩放图片,并且将图片放在ImageView的左上角。
- fitCenter:保持纵横比缩放图片,缩放完成后将图片放在ImageView的中央。
- fitEnd:保持纵横比缩放图片,缩放完成后将图片放在ImageView的右下角。
- center:把图片放在ImageView的中央,但是不进行任何缩放。
- centerCrop:保持纵横比缩放图片,以使图片能完全覆盖ImageView。
- centerInside:保持纵横比缩放图片,以使得ImageView能完全显示该图片。
图片基本显示
下面通过一个示例效果,来说明一下ImageView是如何显示图片的,再此示例中,需要使用到一个green.png的图片,需要放到Drawable文件夹下,关于Android的资源文件,以后再进行详解。
布局代码:
1 <?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
2 <LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
3 android:layout_width="match_parent"
4 android:layout_height="match_parent"
5 android:orientation="vertical" >
6
7 <TextView 8 android:layout_width="match_parent"
9 android:layout_height="wrap_content"
10 android:text="scaleType:center,未缩放,在ImageView的中心" />
11
12 <ImageView 13 android:id="@+id/imageview1"
14 android:layout_width="200dp"
15 android:layout_height="100dp"
16 android:background="#F00"
17 android:scaleType="center"
18 android:src="@drawable/green" />
19
20 <TextView 21 android:layout_width="match_parent"
22 android:layout_height="wrap_content"
23 android:text="scaleType:fitCenter,按比例缩放" />
24
25 <ImageView 26 android:id="@+id/imageview2"
27 android:layout_width="300dp"
28 android:layout_height="200dp"
29 android:background="#FFF"
30 android:padding="10dp"
31 android:scaleType="fitCenter"
32 android:src="@drawable/green" />
33
34 </LinearLayout>
效果展示:
缩放与旋转图片
因为ImageView继承自View,所以在代码中设置其大小,可以使用View.setLayoutParams(new LinearLayout.LayoutParams(newWidth,newHeight))方法,这个方法可以直接设定View下的所有控件的外观大小,所以这里也适用于ImageView。
而对于ImageView的旋转,这里涉及到一个Matrix类的使用。它表示一个3x3的坐标变换矩阵,可以在这个矩阵内,对其进行变换、旋转操作,它需要通过构造函数显式的初始化之后才可以使用。
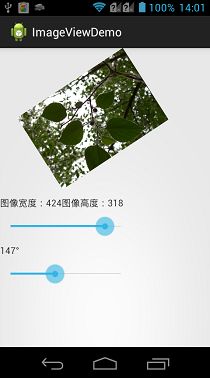
下面通过一个示例来说明一下图片的放大缩小与旋转的示例,在示例中会提供两个SeekBar,对于SeekBar如果不了解的话,可以参见我的另外一篇博客,Android—UI之Progress。这两个SeekBar一个设置ImageView显示图片的大小,另一个设置旋转的角度。对于图片大小,通过DisplayMetrics设置屏幕的宽度为图像的最大宽度,具体操作在注释中已经写明,这里不在累述。
布局代码:
1 <?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
2 <LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
3 android:layout_width="match_parent"
4 android:layout_height="match_parent"
5 android:orientation="vertical" >
6
7 <ImageView 8 android:id="@+id/imageview3"
9 android:layout_width="200dp"
10 android:layout_height="150dp"
11 android:scaleType="fitCenter"
12 android:src="@drawable/green" />
13
14 <TextView 15 android:id="@+id/tv1"
16 android:layout_width="match_parent"
17 android:layout_height="wrap_content"
18 android:layout_marginTop="10dp"
19 android:text="图像宽度:240 图像高度:150" />
20
21 <SeekBar 22 android:id="@+id/sbSize"
23 android:layout_width="200dp"
24 android:layout_height="wrap_content"
25 android:layout_marginTop="10dp"
26 android:max="240"
27 android:progress="120" />
28
29 <TextView 30 android:id="@+id/tv2"
31 android:layout_width="match_parent"
32 android:layout_height="wrap_content"
33 android:layout_marginTop="10dp"
34 android:text="0°" />
35
36 <SeekBar 37 android:id="@+id/sbRotate"
38 android:layout_width="200dp"
39 android:layout_height="wrap_content"
40 android:layout_marginTop="10dp"
41 android:max="360" />
42
43 </LinearLayout>
实现代码:
1 package com.bgxt.imageviewdemo; 2
3 import android.annotation.SuppressLint; 4 import android.app.Activity; 5 import android.graphics.Bitmap; 6 import android.graphics.BitmapFactory; 7 import android.graphics.Matrix; 8 import android.graphics.drawable.BitmapDrawable; 9 import android.os.Bundle; 10 import android.util.DisplayMetrics; 11
12 import android.widget.ImageView; 13 import android.widget.LinearLayout; 14 import android.widget.SeekBar; 15 import android.widget.SeekBar.OnSeekBarChangeListener; 16 import android.widget.TextView; 17
18 @SuppressLint("NewApi") 19 public class ChangeImageActivity extends Activity implements
20 OnSeekBarChangeListener { 21 private int minWidth = 80; 22 private ImageView imageView; 23 private TextView textview1, textview2; 24 Matrix matrix=new Matrix(); 25
26 @Override 27 protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) { 28 // TODO Auto-generated method stub
29 super.onCreate(savedInstanceState); 30 setContentView(R.layout.layout_changeimage); 31
32 imageView = (ImageView) findViewById(R.id.imageview3); 33 SeekBar seekbar1 = (SeekBar) findViewById(R.id.sbSize); 34 SeekBar seekbar2 = (SeekBar) findViewById(R.id.sbRotate); 35 textview1 = (TextView) findViewById(R.id.tv1); 36 textview2 = (TextView) findViewById(R.id.tv2); 37
38 //获取当前屏幕的尺寸,并设置图片放大的最大尺寸,不能超过屏幕尺寸
39 DisplayMetrics dm = new DisplayMetrics(); 40 getWindowManager().getDefaultDisplay().getMetrics(dm); 41 seekbar1.setMax(dm.widthPixels - minWidth); 42
43 seekbar1.setOnSeekBarChangeListener(this); 44 seekbar2.setOnSeekBarChangeListener(this); 45 } 46
47 @Override 48 public void onProgressChanged(SeekBar seekBar, int progress, 49 boolean fromUser) { 50 if (seekBar.getId() == R.id.sbSize) { 51 //设置图片的大小
52 int newWidth=progress+minWidth; 53 int newHeight=(int)(newWidth*3/4); 54 imageView.setLayoutParams(new LinearLayout.LayoutParams(newWidth, newHeight)); 55 textview1.setText("图像宽度:"+newWidth+"图像高度:"+newHeight); 56 } else if (seekBar.getId() == R.id.sbRotate){ 57 //获取当前待旋转的图片
58 Bitmap bitmap=BitmapFactory.decodeResource(getResources(), R.drawable.green); 59 //设置旋转角度
60 matrix.setRotate(progress,30,60); 61 //通过待旋转的图片和角度生成新的图片
62 bitmap=Bitmap.createBitmap(bitmap,0,0,bitmap.getWidth(),bitmap.getHeight(),matrix,true); 63 //绑定图片到控件上
64 imageView.setImageBitmap(bitmap); 65 textview2.setText(progress+"°"); 66 } 67 } 68
69 @Override 70 public void onStartTrackingTouch(SeekBar seekBar) { 71 // TODO Auto-generated method stub
72
73 } 74
75 @Override 76 public void onStopTrackingTouch(SeekBar seekBar) { 77 // TODO Auto-generated method stub
78
79 } 80
81 }
效果展示:
从互联网获取图片
一个移动的平台开发,很多资源是不可能一直保存在本地的,更多实时性的东西,是需要直接通过网络及时获取的。这里通过一个从网上获取图片展示到ImageView的例子,来讲解一下这个功能的实现。
在Android4.0之后,增加了一些新特性,也增加了一些限制。其中有一个限制就是不能在主线程中访问网络,必须另开一条线程访问。但是这里又存在另外一个问题,在子线程中,无法直接操作UI控件的属性。如果你们使用的开发平台是Android4.0之下,就不存在这个问题,直接在主线程中访问网络操作UI控件即可。
我的解决方案就是,通过Thread类,进行多线程访问网络,再通过Handler类,进行消息传递。对于Thread类,是Java的知识,不再详细讲解,对于Handler类,这里简要说明一下。
在Android平台下,不允许Activity新启动的线程访问该Activity里的界面UI控件,这样就会导致新启动的线程无法动态改变界面UI控件的属性值。所以就需要借助Handler的消息传递机制来实现。Handler类的主要作用有两个:
- 在新启动的线程中发送消息。
- 在主线程中获取、处理消息。
上面描述的两个作用,发送消息好说,在需要的时候发送,那怎么确定什么时候接收消息呢?为了让主线程能接受并处理新启动的线程发送的消息,Android通过回调的方式来实现,开发人员只需要重写Handler类中处理消息的方法,handleMessage(Message)即可,其中Message封装了发送过来的消息。
Handler包含如下方法,用于实现发送和处理消息:
- void handleMessage(Message msg):处理消息的方法,用于被重写。
- final boolean hasMessage(int what):检查消息队列中是否包含what属性为指定值的消息。
- sendEmptyMessage(int what):立即发送空消息。
- final boolean sendEmptyMessageDelayed(int what,long delayMillis):指定delayMillis毫秒之后发送空消息。
- final boolean sendMessage(Message msg):立即发送消息。
- final boolean sendMessageDelayed(Message msg,long delayMillis):指定delayMillis毫秒之后发送消息。
Message封装了线程中传递的消息,如果对于一般的数据,Message提供了getData()和setData()方法来获取与设置数据,其中操作的数据是一个Bundle对象,这个Bundle对象提供一系列的getXxx()和setXxx()方法用于传递基本数据类型,对于基本数据类型,使用起来很简单,这里不再详细讲解。而对于复杂的数据类型,如一个对象的传递就要相对复杂一些。在Bundle中提供了两个方法,专门用来传递对象的,但是这两个方法也有相应的限制,需要实现特定的接口,当然,一些Android自带的类,其实已经实现了这两个接口中的某一个,可以直接使用。方法如下:
- putParcelable(String key,Parcelable value):需要传递的对象类实现Parcelable接口。
- pubSerializable(String key,Serializable value):需要传递的对象类实现Serializable接口。
还有另外一种方式在Message中传递对象,那就是使用Message自带的obj属性传值,它是一个Object类型,所以可以传递任意类型的对象,Message自带的有如下几个属性:
- int arg1:参数一,用于传递不复杂的数据,复杂数据使用setData()传递。
- int arg2:参数二,用于传递不复杂的数据,复杂数据使用setData()传递。
- Object obj:传递一个任意的对象。
- int what:定义的消息码,一般用于确定消息的来源。
下面这个示例,使用了两种方式获取传递消息,以一个随机数确定。在这个示例中,访问网络的代码会附上但是不会详解,如果对于Android中访问网络不熟悉的朋友,可以参见我另外一篇博客,Android--Http协议。
布局代码:
1 <?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
2 <LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
3 android:layout_width="match_parent"
4 android:layout_height="match_parent"
5 android:orientation="vertical" >
6
7
8 <Button android:id="@+id/btnInternet" android:layout_width="wrap_content"
9 android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:text="下载网络图片"/>
10 <TextView android:id="@+id/tbMsgType" android:layout_width="match_parent"
11 android:layout_height="wrap_content"/>
12 <ImageView android:id="@+id/ivInternet" android:layout_width="wrap_content"
13 android:layout_height="wrap_content"/>
14 </LinearLayout>
实现代码:
1 package com.bgxt.imageviewdemo; 2
3 import java.io.InputStream; 4 import java.net.HttpURLConnection; 5 import java.util.Random; 6
7 import com.bgxt.httputils.HttpUtils; 8
9 import android.app.Activity; 10 import android.graphics.Bitmap; 11 import android.graphics.BitmapFactory; 12 import android.os.Bundle; 13 import android.os.Handler; 14 import android.os.Message; 15 import android.view.View; 16 import android.widget.Button; 17 import android.widget.ImageView; 18 import android.widget.TextView; 19 import android.widget.Toast; 20
21 public class InternetImageActivity extends Activity { 22 private Button btnInternet; 23 private ImageView ivInternet; 24 private TextView tvMsgType; 25 private Handler handler; 26
27 @Override 28 protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) { 29 // TODO Auto-generated method stub
30 super.onCreate(savedInstanceState); 31 setContentView(R.layout.activity_internetimage); 32
33 btnInternet = (Button) findViewById(R.id.btnInternet); 34 ivInternet = (ImageView) findViewById(R.id.ivInternet); 35 tvMsgType = (TextView) findViewById(R.id.tbMsgType); 36
37 // 定义一个handler,用于接收消息
38 handler = new Handler() { 39 @Override 40 public void handleMessage(Message msg) { 41 Bitmap bmp = null; 42 // 通过消息码确定使用什么方式传递图片信息
43 if (msg.what == 0) { 44 bmp = (Bitmap) msg.obj; 45 tvMsgType.setText("使用obj传递数据"); 46 } else { 47 Bundle ble = msg.getData(); 48 bmp = (Bitmap) ble.get("bmp"); 49 tvMsgType.setText("使用Bundle传递数据"); 50 } 51 // 设置图片到ImageView中
52 ivInternet.setImageBitmap(bmp); 53 } 54 }; 55
56 btnInternet.setOnClickListener(new View.OnClickListener() { 57 @Override 58 public void onClick(View v) { 59 //清空之前获取的数据
60 tvMsgType.setText(""); 61 ivInternet.setImageBitmap(null); 62 //定义一个线程类
63 new Thread() { 64 @Override 65 public void run() { 66 try { 67 //获取网络图片
68 InputStream inputStream = HttpUtils 69 .getImageViewInputStream(); 70 Bitmap bitmap = BitmapFactory 71 .decodeStream(inputStream); 72 Message msg = new Message(); 73 Random rd = new Random(); 74 int ird = rd.nextInt(10); 75 //通过一个随机数,随机选择通过什么方式传递图片信息到消息中
76 if (ird / 2 == 0) { 77 msg.what = 0; 78 msg.obj = bitmap; 79 } else { 80 Bundle bun = new Bundle(); 81 bun.putParcelable("bmp", bitmap); 82 msg.what = 1; 83 msg.setData(bun); 84 } 85 //发送消息
86 handler.sendMessage(msg); 87 } catch (Exception e) { 88
89 } 90 } 91 }.start(); 92 } 93 }); 94 } 95 }
访问网络类,代码:
1 package com.bgxt.httputils; 2
3 import java.io.IOException; 4 import java.io.InputStream; 5 import java.net.HttpURLConnection; 6 import java.net.URL; 7
8 public class HttpUtils { 9 private final static String URL_PATH = "http://ww4.sinaimg.cn/bmiddle/9e58dccejw1e6xow22oc6j20c80gyaav.jpg"; 10
11 public HttpUtils() { 12 } 13
14 public static InputStream getImageViewInputStream() throws IOException { 15 InputStream inputStream = null; 16 URL url = new URL(URL_PATH); 17 if (url != null) { 18 HttpURLConnection httpURLConnection = (HttpURLConnection) url 19 .openConnection(); 20 httpURLConnection.setConnectTimeout(3000); 21 httpURLConnection.setRequestMethod("GET"); 22 httpURLConnection.setDoInput(true); 23 int response_code = httpURLConnection.getResponseCode(); 24 if (response_code == 200) { 25 inputStream = httpURLConnection.getInputStream(); 26 } 27 } 28 return inputStream; 29 } 30 }
效果展示:
示例代码下载
总结
以上就讲解了ImageView的一些基本使用,对于Android项目而言,一般的用到更多的就是从网络获取图片的功能,所以这里着重讲解了一下。
转自:http://www.cnblogs.com/plokmju/p/android__ImageView.html