Android bluetooth介绍(二): android 蓝牙代码架构及其uart 到rfcomm流程
关键词:蓝牙blueZ UART HCI_UART H4 HCI L2CAP RFCOMM
版本:基于android4.2之前版本 bluez
内核:linux/linux3.08
系统:android/android4.1.3.4
作者:xubin341719(欢迎转载,请注明作者,请尊重版权谢谢)
欢迎指正错误,共同学习、共同进步!!
Android bluetooth介绍(一):基本概念及硬件接口
Android bluetooth介绍(二): android 蓝牙代码架构及其uart 到rfcomm流程
Android bluetooth介绍(三): 蓝牙扫描(scan)设备分析
Android bluetooth介绍(四): a2dp connect流程分析
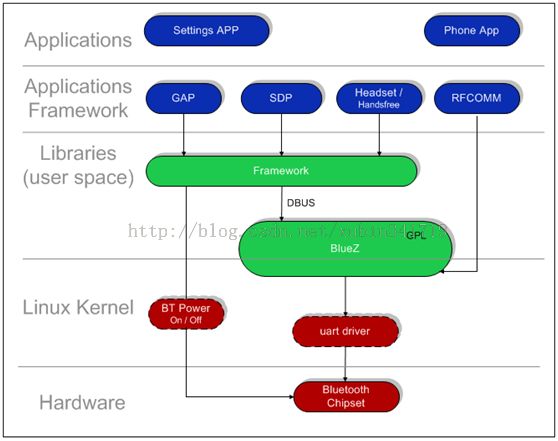
一、Android Bluetooth Architecture蓝牙代码架构部分(google 官方蓝牙框架)
Android的蓝牙系统,自下而上包括以下一些内容如上图所示:
1、串口驱动
Linux的内核的蓝牙驱动程、Linux的内核的蓝牙协议的层
2、BlueZ的适配器
BlueZ的(蓝牙在用户空间的函式库)
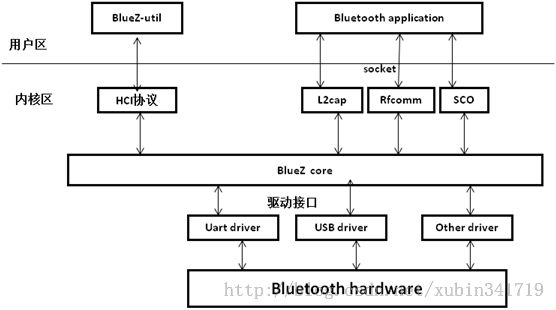
bluez代码结构
Bluetooth协议栈BlueZ分为两部分:内核代码和用户态程序及工具集。
(1)、内核代码:由BlueZ核心协议和驱动程序组成
Bluetooth协议实现在内核源代码 kernel/net/bluetooth中。包括hci,l2cap,hid,rfcomm,sco,SDP,BNEP等协议的实现。
(2)、驱动程序:kernel/driver/bluetooth中,包含Linuxkernel对各种接口的
Bluetooth device的驱动,如:USB接口,串口等。
(3)、用户态程序及工具集:
包括应用程序接口和BlueZ工具集。BlueZ提供函数库以及应用程序接口,便于程序员开发bluetooth应用程序。BlueZ utils是主要工具集,实现对bluetooth设备的初始化和控制。
3、蓝牙相关的应用程序接口
Android.buletooth包中的各个Class(蓝牙在框架层的内容-----java)
| 类名 |
作用 |
| BluetoothAdapter |
本地蓝牙设备的适配类,所有的蓝牙操作都要通过该类完成 |
| BluetoothClass |
用于描述远端设备的类型,特点等信息 |
| BluetoothDevice |
蓝牙设备类,代表了蓝牙通讯过程中的远端设备 |
| BluetoothServerSocket |
蓝牙设备服务端,类似ServerSocket |
| BluetoothSocket |
蓝牙设备客户端,类似Socket |
| BluetoothClass.Device |
蓝牙关于设备信息 |
| BluetoothClass.Device.Major |
蓝牙设备管理 |
| BluetoothClass.Service |
蓝牙相关服务 |
同样下图也是一张比较经典的蓝牙代码架构图(google官方提供)
二、蓝牙通过Hciattach启动串口流程:
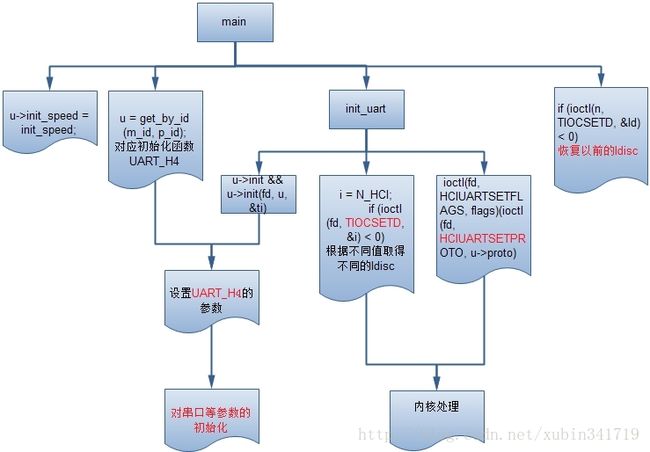
1、hciattach总体流程
三、具体代码分析
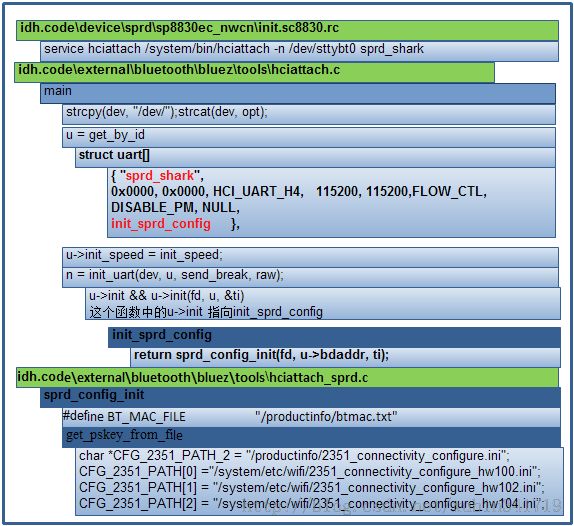
1、initrc中定义
idh.code\device\sprd\sp8830ec_nwcn\init.sc8830.rc
- service hciattach /system/bin/hciattach -n /dev/sttybt0 sprd_shark
- socket bluetooth stream 660 bluetooth bluetooth
- user bluetooth
- group wifi bluetooth net_bt_admin net_bt inet net_raw net_admin system
- disabled
- oneshot
2、/system/bin/hciattach 执行的Main函数
idh.code\external\bluetooth\bluez\tools\hciattach.c
service hciattach /system/bin/hciattach -n /dev/sttybt0 sprd_shark
传进两个参数,/dev/sttybt0 和 sprd_shark
- nt main(int argc, char *argv[])
- {
- ………………
- for (n = 0; optind < argc; n++, optind++) {
- char *opt;
- opt = argv[optind];
- switch(n) {
- case 0://(1)、解析驱动的位置;
- dev[0] = 0;
- if (!strchr(opt, '/'))
- strcpy(dev, "/dev/");
- strcat(dev, opt);
- break;
- case 1://(2)、解析串口的配置相关参数;
- if (strchr(argv[optind], ',')) {
- int m_id, p_id;
- sscanf(argv[optind], "%x,%x", &m_id, &p_id);
- u = get_by_id(m_id, p_id);
- } else {
- u = get_by_type(opt);
- }
- if (!u) {
- fprintf(stderr, "Unknown device type or id\n");
- exit(1);
- }
- break;
- case 2://(3)、通过对前面参数的解析,把uart[i]中的数值初始化;
- u->speed = atoi(argv[optind]);
- break;
- case 3:
- if (!strcmp("flow", argv[optind]))
- u->flags |= FLOW_CTL;
- else
- u->flags &= ~FLOW_CTL;
- break;
- case 4:
- if (!strcmp("sleep", argv[optind]))
- u->pm = ENABLE_PM;
- else
- u->pm = DISABLE_PM;
- break;
- case 5:
- u->bdaddr = argv[optind];
- break;
- }
- }
- ………………
- if (init_speed)//初始化串口速率;
- u->init_speed = init_speed;
- ………………
- n = init_uart(dev, u, send_break, raw);//(4)、初始化串口;
- ………………
- return 0;
- }
(1)、解析驱动的位置;
- if (!strchr(opt, '/'))
- strcpy(dev, "/dev/");
- service hciattach /system/bin/hciattach -n /dev/sttybt0 sprd_shark
- dev = /dev/ttyb0
(2)、解析串口的配置相关参数;获取参数对应的结构体;
- u = get_by_id(m_id, p_id);
- static struct uart_t * get_by_id(int m_id, int p_id)
- {
- int i;
- for (i = 0; uart[i].type; i++) {
- if (uart[i].m_id == m_id && uart[i].p_id == p_id)
- return &uart[i];
- }
- return NULL;
- }
这个函数比较简单,通过循环对比,如传进了的参数sprd_shark和uart结构体中的对比,找到对应的数组。如果是其他蓝牙芯片,如博通、RDA、BEKN等着到其相对应的初始化配置函数。
- struct uart_t uart[] = {
- { "any", 0x0000, 0x0000, HCI_UART_H4, 115200, 115200,
- FLOW_CTL, DISABLE_PM, NULL, NULL },
- { "sprd_shark", 0x0000, 0x0000, HCI_UART_H4, 115200, 115200,
- FLOW_CTL, DISABLE_PM, NULL, init_sprd_config },
- { "ericsson", 0x0000, 0x0000, HCI_UART_H4, 57600, 115200,
- FLOW_CTL, DISABLE_PM, NULL, ericsson },
- ………………
- { "bk3211", 0x0000, 0x0000, HCI_UART_BCSP, 115200, 921600, 0, DISABLE_PM, NULL, beken_init, NULL},
- { NULL, 0 }
- };
注意:init_sprd_config这个函数在uart_init中用到,这个函数其实对我们具体芯片的初始化配置。
注释:HCI_UART_H4和HCI_UART_BCSP的区别如下图。

(3)、通过对前面参数的解析,把uart[i]中的数值初始化;
- u->speed = atoi(argv[optind]);
- break;
(4)、初始化串口;
- n = init_uart(dev, u, send_break, raw);
- idh.code\external\bluetooth\bluez\tools\hciattach.c
- /* Initialize UART driver */
- int init_uart(char *dev, struct uart_t *u, int send_break)
- {
- struct termios ti;
- int fd, i;
- fd = open(dev, O_RDWR | O_NOCTTY);//打开串口设备,其中标志
- //O_RDWR,可以对此设备进行读写操作;
- //O_NOCTTY:告诉Unix这个程序不想成为“控制终端”控制的程序,不说明这个标志的话,任何输入都会影响你的程序。
- //O_NDELAY:告诉Unix这个程序不关心DCD信号线状态,即其他端口是否运行,不说明这个标志的话,该程序就会在DCD信号线为低电平时停止。
- //但是不要以控制 tty 的模式,因为我们并不希望在发送 Ctrl-C
- 后结束此进程
- if (fd < 0) {
- perror(“Can’t open serial port”);
- return -1;
- }
- //drop fd’s data;
- tcflush(fd, TCIOFLUSH);//清空数据线
- if (tcgetattr(fd, &ti) < 0) {
- perror(“Can’t get port settings”);
- return -1;
- }
- cfmakeraw(&ti);
- cfmakeraw sets the terminal attributes as follows://此函数设置串口终端的以下这些属性,
- termios_p->c_iflag &= ~(IGNBRK|BRKINT|PARMRK|ISTRIP
- |INLCR|IGNCR|ICRNL|IXON);
- termios_p->c_oflag &= ~OPOST;
- termios_p->c_lflag &= ~(ECHO|ECHONL|ICANON|ISIG|IEXTEN);
- termios_p->c_cflag &= ~(CSIZE|PARENB) ;
- termios_p->c_cflag |=CS8;
- ti.c_cflag |= CLOCAL;//本地连接,无调制解调器控制
- if (u->flags & FLOW_CTL)
- ti.c_cflag |= CRTSCTS;//输出硬件流控
- else
- ti.c_cflag &= ~CRTSCTS;
- if (tcsetattr(fd, TCSANOW, &ti) < 0) {//启动新的串口设置
- perror(“Can’t set port settings”);
- return -1;
- }
- /* Set initial baudrate */
- if (set_speed(fd, &ti, u->init_speed) < 0) {//设置串口的传输速率bps, 也可以使
- //用 cfsetispeed 和 cfsetospeed 来设置
- perror(“Can’t set initial baud rate”);
- return -1;
- }
- tcflush(fd, TCIOFLUSH);//清空数据线
- if (send_break)
- tcsendbreak(fd, 0);
- //int tcsendbreak ( int fd, int duration );Sends a break for
- //the given time.在串口线上发送0值,至少维持0.25秒。
- //If duration is 0, it transmits zero-valued bits for at least 0.25 seconds, and
- //not more than 0.5seconds.
- //where place register u’s init function;
- if (u->init && u->init(fd, u, &ti) < 0)
- //所有bluez支持的蓝牙串口设备类型构成了一个uart结构数组,通过
- //查找对应的uart类型,这个uart的init成员显示了它的init调用方法;
- struct uart_t uart[] = {
- { "any", 0x0000, 0x0000, HCI_UART_H4, 115200, 115200,FLOW_CTL, DISABLE_PM, NULL, NULL },
- { "sprd_shark", 0x0000, 0x0000, HCI_UART_H4, 115200, 115200,FLOW_CTL, DISABLE_PM, NULL, init_sprd_config },
- { "ericsson", 0x0000, 0x0000, HCI_UART_H4, 57600, 115200,FLOW_CTL, DISABLE_PM, NULL, ericsson },
- ………………
- { "bk3211", 0x0000, 0x0000, HCI_UART_BCSP, 115200, 921600, 0, DISABLE_PM, NULL, beken_init, NULL},
- { NULL, 0的init函数名为bcsp,定义在本文件中**;
- return -1;
- tcflush(fd, TCIOFLUSH);//清空数据线
- /* Set actual baudrate */
- if (set_speed(fd, &ti, u->speed) < 0) {
- perror(“Can’t set baud rate”);
- return -1;
- }
- /* Set TTY to N_HCI line discipline */
- i = N_HCI;
- if (ioctl(fd, TIOCSETD, &i) < 0) {//
- TIOCSETD int *ldisc//改变到 i 行规,即hci行规
- Change to the new line discipline pointed to by ldisc. The available line disciplines are listed in
- /* ioctl (fd, TIOCSERGETLSR, &result) where result may be as below */
- /* line disciplines */
- #define N_TTY 0
- ……
- #define N_HCI 15 /* Bluetooth HCI UART */
- perror(“Can’t set line discipline”);
- return -1;
- }
- if (ioctl(fd, HCIUARTSETPROTO, u->proto) < 0) {
- //设置hci设备的proto操作函数集为hci_uart操作集;
- perror(“Can’t set device”);
- return -1;
- }
- return fd;
- }
这里一个重要的部分是:u->init指向init_sprd_config
4、uart具体到芯片的初始化init_sprd_config(这部分根据不同的芯片,对应进入其相应初始化部分)
idh.code\external\bluetooth\bluez\tools\hciattach_sprd.c
- int sprd_config_init(int fd, char *bdaddr, struct termios *ti)
- {
- int i,psk_fd,fd_btaddr,ret = 0,r,size=0,read_btmac=0;
- unsigned char resp[30];
- BT_PSKEY_CONFIG_T bt_para_tmp;
- char bt_mac[30] = {0};
- char bt_mac_tmp[20] = {0};
- uint8 bt_mac_bin[32] = {0};
- fprintf(stderr,"init_sprd_config in \n");
- //(1)、这部分检查bt_mac,如果存在,从文件中读取,如果不存在,随机生成,并写入相应文件;
- if(access(BT_MAC_FILE, F_OK) == 0) {//这部分检查bt_mac
- LOGD("%s: %s exists",__FUNCTION__, BT_MAC_FILE);
- fd_btaddr = open(BT_MAC_FILE, O_RDWR);// #define BT_MAC_FILE "/productinfo/btmac.txt"
- if(fd_btaddr>=0) {
- size = read(fd_btaddr, bt_mac, sizeof(bt_mac));//读取BT_MAC_FILE中的地址;
- LOGD("%s: read %s %s, size=%d",__FUNCTION__, BT_MAC_FILE, bt_mac, size);
- if(size == BT_RAND_MAC_LENGTH){
- LOGD("bt mac already exists, no need to random it");
- fprintf(stderr, "read btmac ok \n");
- read_btmac=1;
- }
- …………
- }else{//如果不存在,就随机生成一个bt_mac地址,写入/productinfo/btmac.txt
- fprintf(stderr, "btmac.txt not exsit!\n");
- read_btmac=0;
- mac_rand(bt_mac);
- LOGD("bt random mac=%s",bt_mac);
- printf("bt_mac=%s\n",bt_mac);
- write_btmac2file(bt_mac);
- fd_btaddr = open(BT_MAC_FILE, O_RDWR);
- if(fd_btaddr>=0) {
- size = read(fd_btaddr, bt_mac, sizeof(bt_mac));
- LOGD("%s: read %s %s, size=%d",__FUNCTION__, BT_MAC_FILE, bt_mac, size);
- if(size == BT_RAND_MAC_LENGTH){
- LOGD("bt mac already exists, no need to random it");
- fprintf(stderr, "read btmac ok \n");
- read_btmac=1;
- }
- close(fd_btaddr);
- …………
- }
- /* Reset the BT Chip */
- memset(resp, 0, sizeof(resp));
- memset(&bt_para_tmp, 0, sizeof(BT_PSKEY_CONFIG_T) );
- ret = getPskeyFromFile( (void *)(&bt_para_tmp) );//ret = get_pskey_from_file(&bt_para_tmp);//(2)、PSKey参数、射频参数的设定;
- if(ret != 0){//参数失败处理
- fprintf(stderr, "get_pskey_from_file faill \n");
- /* Send command from hciattach*/
- if(read_btmac == 1){
- memcpy(bt_para_setting.device_addr, bt_mac_bin, sizeof(bt_para_setting.device_addr));// (3)、读取失败,把bt_para_setting中defaut参数写入;
- }
- if (write(fd, (char *)&bt_para_setting, sizeof(BT_PSKEY_CONFIG_T)) != sizeof(BT_PSKEY_CONFIG_T)) {
- fprintf(stderr, "Failed to write reset command\n");
- return -1;
- }
- }else{//getpskey成功处理
- /* Send command from pskey_bt.txt*/
- if(read_btmac == 1){
- memcpy(bt_para_tmp.device_addr, bt_mac_bin, sizeof(bt_para_tmp.device_addr));
- }
- …………
- return 0;
- }
(1)、这部分检查bt_mac,如果存在,从文件中读取,如果不存在,随机生成,并写入相应文件/productinfo/btmac.txt;
(2)、PSKey参数、射频参数的设定;
get_pskey_from_file(&bt_para_tmp);这个函数后面分析;
(3)、读取失败,把bt_para_setting中defaut参数写入;频率、主从设备设定等……
- // pskey file structure default value
- BT_PSKEY_CONFIG_T bt_para_setting={
- 5,
- 0,
- 0,
- 0,
- 0,
- 0x18cba80,
- 0x001f00,
- 0x1e,
- {0x7a00,0x7600,0x7200,0x5200,0x2300,0x0300},
- …………
- };
5、get_pskey_from_file 解析相关射频参数
idh.code\external\bluetooth\bluez\tools\pskey_get.c
- int getPskeyFromFile(void *pData)
- {
- …………
- char *BOARD_TYPE_PATH = "/dev/board_type";//(1)、判断PCB的版本;
- int fd_board_type;
- char board_type_str[MAX_BOARD_TYPE_LEN] = {0};
- int board_type;
- char *CFG_2351_PATH_2 = "/productinfo/2351_connectivity_configure.ini";//(2)、最终生成ini文件存储的位置;
- char *CFG_2351_PATH[MAX_BOARD_TYPE];
- (3)、针对不同PCB版本,不同的ini配置文件;
- CFG_2351_PATH[0] = "/system/etc/wifi/2351_connectivity_configure_hw100.ini";
- CFG_2351_PATH[1] = "/system/etc/wifi/2351_connectivity_configure_hw102.ini";
- CFG_2351_PATH[2] = "/system/etc/wifi/2351_connectivity_configure_hw104.ini";
(4)、下面函数就不做具体分析,大致意识是,根据/dev/board_type中,读取的PCB类型,设置不同的ini文件。
- ………………
- ret = chmod(CFG_2351_PATH_2, 0644);
- ALOGE("chmod 0664 %s ret:%d\n", CFG_2351_PATH_2, ret);
- if(pBuf == pBuf2)
- free(pBuf1);
- ………………
- }
(1)、判断PCB的版本;
char *BOARD_TYPE_PATH = "/dev/board_type";
(2)、最终生成ini文件存储的位置,就是系统运行时读取ini文件的地方;
char *CFG_2351_PATH_2 ="/productinfo/2351_connectivity_configure.ini";
(3)、针对不同PCB版本,不同的ini配置文件;
- CFG_2351_PATH[0] = "/system/etc/wifi/2351_connectivity_configure_hw100.ini";
- CFG_2351_PATH[1] = "/system/etc/wifi/2351_connectivity_configure_hw102.ini";
- CFG_2351_PATH[2] = "/system/etc/wifi/2351_connectivity_configure_hw104.ini";
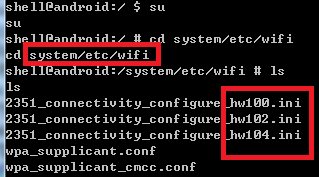
(4)、下面函数就不做具体分析,大致意识是,根据/dev/board_type中,读取的PCB类型,设置不同的ini文件。 覆盖到(2)中的文件。
四、HCI_UART_H4和H4层的加入
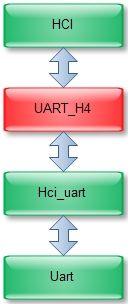
uart->hci_uart->Uart-H4->hci:从uart开始分析,介绍整个驱动层数据流(涉及tty_uart中断, 线路层ldisc_bcsp、tasklet、work queue、skb_buffer的等)
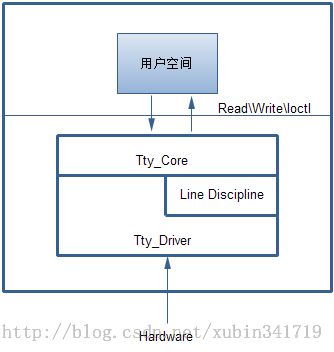
这是数据的流动过程,最底层的也就是和硬件打交道的是uart层了,它的存在和起作用是通过串口驱动来保证的,这个请参阅附录,但是其它的层我们都不知道什么时候work的,下面来看。
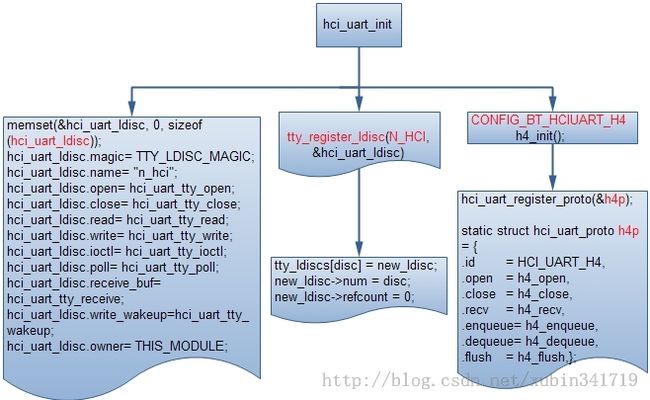
1、idh.code\kernel\drivers\bluetooth\hci_ldisc.c
- static int __init hci_uart_init(void)
- {
- static struct tty_ldisc_ops hci_uart_ldisc;
- int err;
- /* Register the tty discipline */
- memset(&hci_uart_ldisc, 0, sizeof (hci_uart_ldisc));
- hci_uart_ldisc.magic = TTY_LDISC_MAGIC;
- hci_uart_ldisc.name = "n_hci";
- hci_uart_ldisc.open = hci_uart_tty_open;
- hci_uart_ldisc.close = hci_uart_tty_close;
- hci_uart_ldisc.read = hci_uart_tty_read;
- hci_uart_ldisc.write = hci_uart_tty_write;
- hci_uart_ldisc.ioctl = hci_uart_tty_ioctl;
- hci_uart_ldisc.poll = hci_uart_tty_poll;
- hci_uart_ldisc.receive_buf = hci_uart_tty_receive;
- hci_uart_ldisc.write_wakeup = hci_uart_tty_wakeup;
- hci_uart_ldisc.owner = THIS_MODULE;
- if ((err = tty_register_ldisc(N_HCI, &hci_uart_ldisc))) {//(1)、这部分完成ldisc的注册;
- BT_ERR("HCI line discipline registration failed. (%d)", err);
- return err;
- }
- #ifdef CONFIG_BT_HCIUART_H4
- h4_init();//(2)、我们蓝牙芯片用的是H4,这部分完成H4的注册;
- #endif
- #ifdef CONFIG_BT_HCIUART_BCSP
- bcsp_init();
- #endif
- ………………
- return 0;
- }
(1)、这部分完成ldisc的注册;
tty_register_ldisc(N_HCI,&hci_uart_ldisc)
注册了一个ldisc,这是通过把新的ldisc放在一个ldisc的数组里面实现的,tty_ldiscs是一个全局的ldisc数组里面会根据序号对应一个ldisc,这个序号就是上层通过ioctl来指定的,比如我们在前面已经看到的:
i = N_HCI;
ioctl(fd, TIOCSETD, &i) < 0
可以看到这里指定的N_HCI刚好就是这里注册的这个号码15;
(2)、蓝牙芯片用的是H4,这部分完成H4的注册;
h4_init();
hci_uart_proto结构体的初始化:
idh.code\kernel\drivers\bluetooth\hci_h4.c
- static struct hci_uart_proto h4p = {
- .id = HCI_UART_H4,
- .open = h4_open,
- .close = h4_close,
- .recv = h4_recv,
- .enqueue = h4_enqueue,
- .dequeue = h4_dequeue,
- .flush = h4_flush,
- };
H4的注册:
idh.code\kernel\drivers\bluetooth\hci_h4.c
- int __init h4_init(void)
- {
- int err = hci_uart_register_proto(&h4p);
- if (!err)
- BT_INFO("HCI H4 protocol initialized");
- else
- BT_ERR("HCI H4 protocol registration failed");
- return err;
- }
这是通过hci_uart_register_proto(&bcsp)来完成的,这个函数非常简单,本质如下:
hup[p->id]= p;其中static struct hci_uart_proto*hup[HCI_UART_MAX_PROTO];也就是说把对应于协议p的id和协议p连接起来,这样设计的好处是hci uart层本身可以支持不同的协议,包括h4、bcsp等,通过这个数组连接这些协议,等以后有数据的时候调用对应的协议来处理,这里比较关键的是h4里面的这些函数。
五、HCI层的加入
hci的加入是通过hci_register_dev函数来做的,这时候用户通过hciconfig就可以看到有一个接口了,通过这个接口用户可以访问底层的信息了,hci0已经生成;至于它在何时被加入的,我们再看看hciattach在内核里面的处理过程;
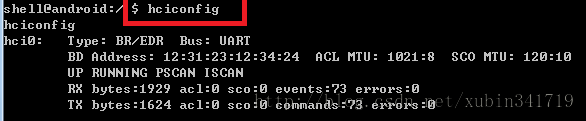
Ioctl的作用是设置一个新的ldisc;
2、HCIUARTSETPROTO的处理流程:

这部分比较重要,注册生成hci0, 初始化3个工作队列,hci_rx_work、hci_tx_work、hci_cmd_work;完成hci部分数据、命令的接收、发送。
六、数据在驱动的传递流程
1、uart数据接收
这部分流程比较简单,其实就是注册一个tty驱动程序和相对应的函数,注册相应的open\close\ioctl等方法,通过应用open /dev/ttyS*操作,注册中断接收函数,接收处理蓝牙模块触发中断的数据。
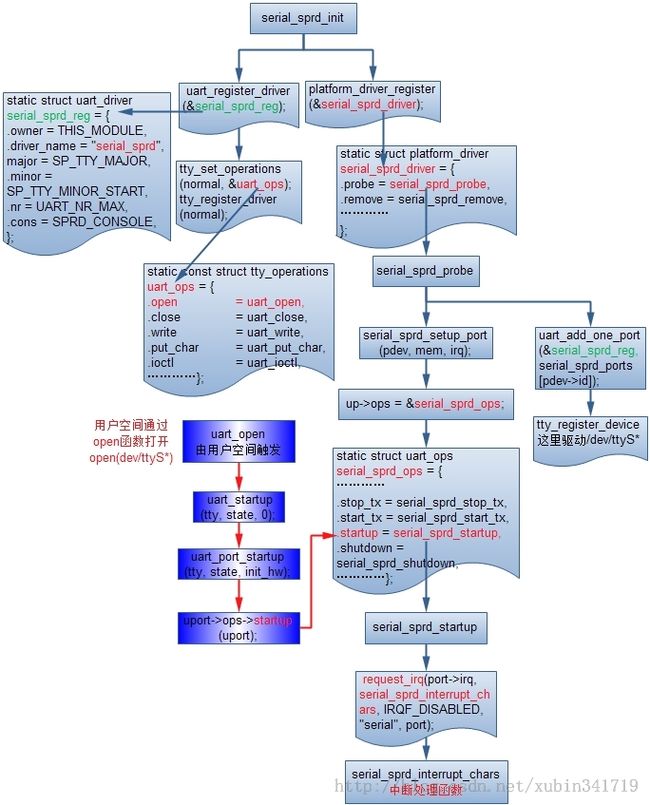
在这个中断函数里面会接受到来自于蓝牙模块的数据;在中断函数里面会先读取串口的状态寄存器判断是否是data准备好,如果准备好就调用serial_sprd_rx_chars函数来接收数据,下面看看这个函数是如何处理的:
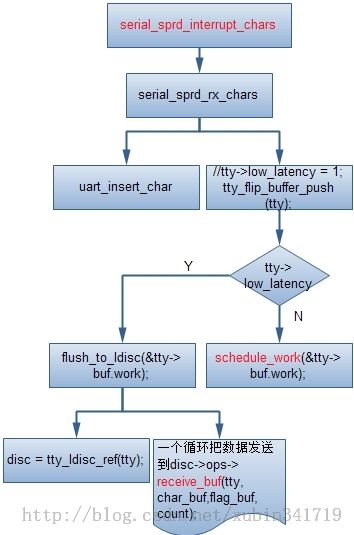
那就是把数据一个个的加入到uart层的缓冲区,直到底层不处于dataready状态,或者读了maxcount个数,当读完后就调用tty层的接口把数据传递给tty层,tty层则把数据交给了ldisc,于是控制权也就交给了hci_uart层;
七、Hci_uart的数据接收
它基本上就是要个二传手,通过:
- spin_lock(&hu->rx_lock);
- hu->proto->recv(hu,(void *) data, count);
- hu->hdev->stat.byte_rx+= count;
- spin_unlock(&hu->rx_lock);
八、H4层处理
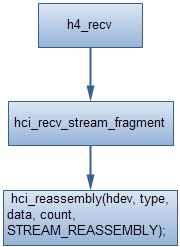
这层主要是通过函数h4_recv来处理的,根据协议处理包头、CRC等,然后调用更上层的hci_recv_frame来处理已经剥去h4包头的数据;
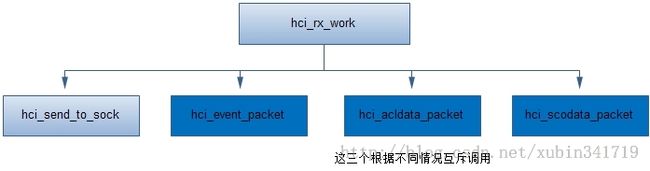
这里的hci_rx_work前面已经看到它了,它是一个工作队列用来处理hci层的数据接收的;先看是否有进程打开hci的socket用来监听数据,如果有的话,就把数据的一个copy发送给它,然后根据包的类型调用不同的处理函数,分别对应于event、acl、sco处理;
hci_event_packet是对于事件的处理,里面包含有包括扫描,信号,授权,pin码,总之基本上上层所能收到的事件,基本都是在这里处理的,它的很多信息都是先存起来,等待上层的查询然后才告诉上层;
hci_acldata_packet是一个经常的情况,也就是说上层通常都是使用的是l2cap层的接口,而l2cap就是基于这个的,如下图所示:
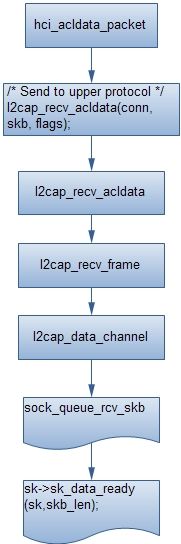
到这里如果有基于BTPROTO_L2CAP的socket,那么这个socket就可以收到数据了;再看看BTPROTO_RFCOMM的流程:
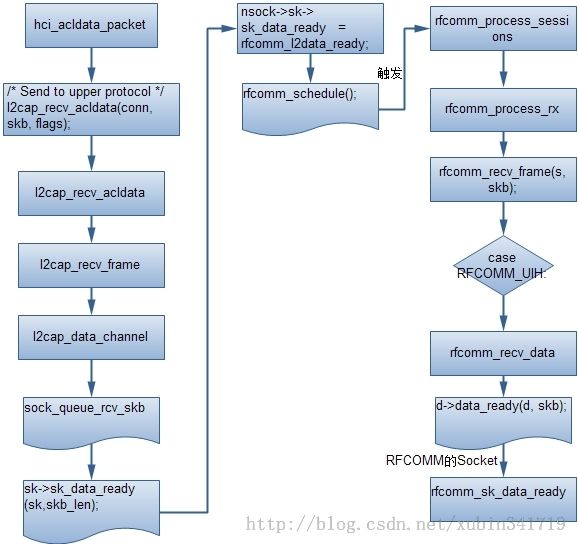
十、 数据流程的总结
简单总结一下,数据的流程,
|基本上是:
1, uart口取得蓝牙模块的数据;
2, uart口通过ldisc传给hci_uart;
3, hci_uart传给在其上的h4;
4, h4传给hci层;
5, hci层传给l2cap层
6, l2cap层再传给rfcomm;