mina学习笔记四:交互的核心IoSession
这一章讲的就是IoSession,session这个词做web应用的人应该都是耳熟能详,在mina中IoSession也是起着相同的作用。mina为每个客户端提供了会话session,session是服务器端和客户端的连接持有者,直到连接中断session才会被销毁。
IoSession不仅是connection的相关信息,同时,服务器端还能通过他存储其他可能需要的数据信息。好,让我们一步一步剖析IoSession那不平凡的一生吧。
1. IoSession在服务器端的创建第一步:accept(processor,handle)
接着上节说,我们已经知道,NioSocketAcceptor.bind()后,最终会生成一个在自身维护的executor线程池内提交的任务Acceptor(单一线程),该任务不断的轮询判断服务是否关闭、同时等待新的连接接入。当有新的连接接入时:
- Acceptor.run(){
- ...
- //selectedHandles()获取一个selector中注册的服务监听的serversocketchannel的迭代器
- processHandles(selectedHandles());
- ...
- }
- private void processHandles(Iterator<ServerSocketChannel> handles) throws Exception {
- while (handles.hasNext()) {
- H handle = handles.next();
- handles.remove();
- // 创建session并将本地的processor处理池当参数传递给session
- // 注意这里还未分配具体的processor
- S session = accept(processor, handle);
- if (session == null) {
- continue;
- }
- // 初始化Session
- initSession(session, null, null);
- // 将session分配给具体的processor
- session.getProcessor().add(session);
- }
- }
- public NioSocketSession(IoService service, IoProcessor<NioSession> processor, SocketChannel channel) {
- //AbstractIoSession(IoService service)
- this.service = service;
- this.handler = service.getHandler();
- //保存当前的处理时间信息
- long currentTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
- creationTime = currentTime;
- lastThroughputCalculationTime = currentTime;
- lastReadTime = currentTime;
- lastWriteTime = currentTime;
- lastIdleTimeForBoth = currentTime;
- lastIdleTimeForRead = currentTime;
- lastIdleTimeForWrite = currentTime;
- //在关闭时的动作,下面以此展开对IoFuture的探讨。
- closeFuture.addListener(SCHEDULED_COUNTER_RESETTER);
- //为session创建唯一的ID
- sessionId = idGenerator.incrementAndGet();
- //END AbstractIoSession(IoService service)
- //NioSession(IoProcessor<NioSession> processor, IoService service, Channel channel)
- //即当前session的SocketChannel
- this.channel = channel;
- //这是ioservice中的processor池哦
- this.processor = processor;
- //这步过滤器链厉害了,后面细说
- filterChain = new DefaultIoFilterChain(this);
- //END NioSession(IoProcessor<NioSession> processor, IoService service, Channel channel)
- //设置各种初始参数
- config = new SessionConfigImpl();
- this.config.setAll(service.getSessionConfig());
- }
我们细细的分析一下NioSocketSession在初始化时做了哪些工作,首先持有了sevice及其处理类引用,并设置了一些初始时间信息,然后他在关闭时注册了监听操作closeFuture.addListener(SCHEDULED_COUNTER_RESETTER)。
1.1 IoFuture
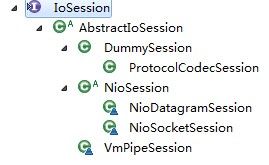
我们已经很多次看到IoFuture,有必要来详细了解一下IoFuture的作用。那用过Executor的同学都知道,submit()提交Callback的任务后将返回一个Future表示这个任务的操作结果,这里的IoFuture的作用是类似的,他代表一次相关于IoSession的操作的操作结果,同时,还可以在他完成时获取定义相关的操作。我们看下他的子类结构图
图4.1 IoFuture子类结构图
由图中可见,对session相关的操作例如关闭、连接、写、读等操作,IoFuture全都有子类去支持。session的操作可以很方便的通过IoFuture查看处理的结果。我们看下IoFuture接口的API清单:
- addListener(IoFutureListener<?>)
- await()
- await(long)
- await(long, TimeUnit)
- awaitUninterruptibly()
- awaitUninterruptibly(long)
- awaitUninterruptibly(long, TimeUnit)
- getSession()
- isDone()
- removeListener(IoFutureListener<?>)
- public interface IoFutureListener<F extends IoFuture> extends EventListener {
- void operationComplete(F future);
- }
在他的直接实现子类DefaultIoFuture里面,我们看一下该类很主要一个实现方法setValue(Object newValue),所有其他子类都会调用该方法以完成具体的操作:
- public void setValue(Object newValue) {
- synchronized (lock) {
- // 已经完成则直接返回
- if (ready) {
- return;
- }
- //设置结果
- result = newValue;
- //设置完成状态
- ready = true;
- //唤醒所有等待线程
- if (waiters > 0) {
- lock.notifyAll();
- }
- }
- 知监听器执行完成操作
- notifyListeners();
- }
- private void checkDeadLock() {
- // Only read / write / connect / write future can cause dead lock.
- if (!(this instanceof CloseFuture || this instanceof WriteFuture || this instanceof ReadFuture || this instanceof ConnectFuture)) {
- return;
- }
- // Get the current thread stackTrace.
- // Using Thread.currentThread().getStackTrace() is the best solution,
- // even if slightly less efficient than doing a new Exception().getStackTrace(),
- // as internally, it does exactly the same thing. The advantage of using
- // this solution is that we may benefit some improvement with some
- // future versions of Java.
- StackTraceElement[] stackTrace = Thread.currentThread().getStackTrace();
- // Simple and quick check.
- for (StackTraceElement s : stackTrace) {
- if (AbstractPollingIoProcessor.class.getName().equals(s.getClassName())) {
- IllegalStateException e = new IllegalStateException("t");
- e.getStackTrace();
- throw new IllegalStateException("DEAD LOCK: " + IoFuture.class.getSimpleName()
- + ".await() was invoked from an I/O processor thread. " + "Please use "
- + IoFutureListener.class.getSimpleName() + " or configure a proper thread model alternatively.");
- }
- }
- // And then more precisely.
- for (StackTraceElement s : stackTrace) {
- try {
- Class<?> cls = DefaultIoFuture.class.getClassLoader().loadClass(s.getClassName());
- if (IoProcessor.class.isAssignableFrom(cls)) {
- throw new IllegalStateException("DEAD LOCK: " + IoFuture.class.getSimpleName()
- + ".await() was invoked from an I/O processor thread. " + "Please use "
- + IoFutureListener.class.getSimpleName()
- + " or configure a proper thread model alternatively.");
- }
- } catch (Exception cnfe) {
- // Ignore
- }
- }
- }
1.2 IoSession的过滤器链
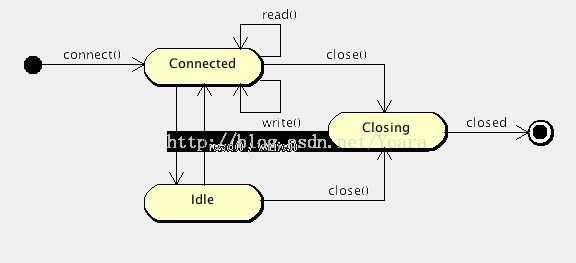
IoSession是有状态的,它包括:- Connected :IoSession已被创建且生效。
- Idle :会话在一定时间内没有处理任何请求,它包括下面三个子状态:
- Idle for read : 一段时间内没有接受数据。
- Idle for write : 一段时间内没有发送数据。
- Idle for both : 一段时间内没有产生接受或发送数据的操作。
- Closing : IoSession正在关闭中。
- Closed : session已经被关闭。
图4.2 IoSession状态变化图
- filterChain = new DefaultIoFilterChain(this);
IoSession会先继承IoService的过滤器链,过滤器链将放在下一节统一分析。
2. IoSession在服务器端的创建第二步:initSession(session, null, null)
这一步initSession(session, null, null);主要的有两段可配置的属性,一个就是存储attribute属性键值对的Map,默认是ConcurrentHashMap;另一个就是发送队列,默认是ConcurrentLinkedQueue。若要实现自己的数据结构,需要重写接口IoSessionDataStructureFactory或继承DefaultIoSessionDataStructureFactory。- try {
- ((AbstractIoSession) session).setAttributeMap(session.getService().getSessionDataStructureFactory()
- .getAttributeMap(session));
- } catch (IoSessionInitializationException e) {
- throw e;
- } catch (Exception e) {
- throw new IoSessionInitializationException("Failed to initialize an attributeMap.", e);
- }
- try {
- ((AbstractIoSession) session).setWriteRequestQueue(session.getService().getSessionDataStructureFactory()
- .getWriteRequestQueue(session));
- } catch (IoSessionInitializationException e) {
- throw e;
- } catch (Exception e) {
- throw new IoSessionInitializationException("Failed to initialize a writeRequestQueue.", e);
- }
3. IoSession在服务器端的创建第三步:session.getProcessor().add(session);
这一步就是为我们新生成的IoSession在IoService的Processor池中指定一个Processor处理。分配的方式就是取模分配,完成后在分配Processor中增加该IoSession的引用。SimpleIoProcessorPool中的代码如下:- public final void add(S session) {
- //请注意这里是两步,第一步getProcessor(session)在下面段代码,创建(若没有)并返回Processor
- //第二步在该Processor中add(session),这里就是调用AbstractPollingIoProcessor.add(),后面有更多描述
- getProcessor(session).add(session);
- }
- private IoProcessor<S> getProcessor(S session) {
- IoProcessor<S> processor = (IoProcessor<S>) session.getAttribute(PROCESSOR);
- if (processor == null) {
- if (disposed || disposing) {
- throw new IllegalStateException("A disposed processor cannot be accessed.");
- }
- processor = pool[Math.abs((int) session.getId()) % pool.length];
- if (processor == null) {
- throw new IllegalStateException("A disposed processor cannot be accessed.");
- }
- session.setAttributeIfAbsent(PROCESSOR, processor);
- }
- return processor;
- }
4. SimpleIoProcessorPool、IoProcess和NioSocketAcceptor之间的关系
上节我们留了个悬念,SimpleIoProcessorPool、IoProcess和IoServices之间的到底是关系呢?我们从SimpleIoProcessorPool初始化池说起:
这段代码将生成的线程池当做构造传参传递给所有的NioProcess,即数组池中所有NioProcess都是共享一个Executro线程池的(newCashedThreadPool)。AbstractPollingIoProcessor.add()方法做了这些工作:
- for (int i = 1; i < pool.length; i++) {
- ...
- pool[i] = processorConstructor.newInstance(this.executor);
- ...
- }
- public final void add(S session) {
- if (disposed || disposing) {
- throw new IllegalStateException("Already disposed.");
- }
- // 将session添加到ConcurrentLinkedQueue的队列中,并启动Processor 的worker线程
- newSessions.add(session);
- //启动Processor线程
- tartupProcessor();
- }
我们很有必要具体看一下Processor线程做了什么:
- private class Processor implements Runnable {
- public void run() {
- ...
- for (;;) {
- try {
- // 监控空闲时间
- long t0 = System.currentTimeMillis();
- int selected = select(1000);
- long t1 = System.currentTimeMillis();
- long delta = (t1 - t0);
- ...
- // 注册新的session连接,并初始化session信息,如过滤器链,
- // 通知service的监听器
- nSessions += handleNewSessions();
- ...
- // 处理新的请求
- if (selected > 0) {
- process();
- }
- ...
- // 移除
- nSessions -= removeSessions();
- // 通知空闲监听器
- notifyIdleSessions(currentTime);
- ...
- //关闭
- if (isDisposing()) {
- for (Iterator<S> i = allSessions(); i.hasNext();) {
- scheduleRemove(i.next());
- }
- wakeup();
- }
- } catch ...
- }
- ...
- }
- }
- //在selector上注册感兴趣的相应集合读操作
- SelectableChannel ch = (SelectableChannel) session.getChannel();
- ch.configureBlocking(false);
- session.setSelectionKey(ch.register(selector, SelectionKey.OP_READ, session));
- //将service的过滤器链设置在session上
- IoFilterChainBuilder chainBuilder = session.getService().getFilterChainBuilder();
- chainBuilder.buildFilterChain(session.getFilterChain());
- //回调监听器
- IoServiceListenerSupport listeners = ((AbstractIoService) session.getService()).getListeners();
- listeners.fireSessionCreated(session);
- SimpleIoProcessorPool维护一组IoProcess[] ,每个IoProcess都在线程池中绑定了工作线程,该工作线程开启一个selector并监听session交互OP_READ。
- public NioProcessor(Executor executor) {
- super(executor);
- try {
- selector = Selector.open();
- } catch (IOException e) {
- throw new RuntimeIoException("Failed to open a selector.", e);
- }
- }
- NioSocketAcceptor持有一个pool的引用
- NioSocketAcceptor自身也有个单线程的executor,用于监听新的session的链接OP_ACCEPT。
- NioSocketAcceptor.init() throws Exception {
- selector = Selector.open();
- }