A Test in MASM and GCC 64-bits for instruction mov and lea
这篇文章被朋友指出了一个最大的问题,影响了文章中提到的最重要的结论。要说清问题需要比较大的篇幅,因此另外新写了一个文章描述,请大家同时参考两个文章。另外一个文章: MASM mov指令的进一步测试
When handling address in assemble code, behavior in Windows (using MASM) and Linux (using GCC) might be totally different for the similar code. Here is a test to verify the behavior for a line of code: "mov register, variable" or "mov %register, variable". In Windows, the code move address of variable into register but in Linux, the code move the content of variable into register. To make things more complex, MASM has keyword OFFSET to PIC code and GCC is using register RIP for PIC code. So I wrote a test to check the behavior in those cases.
The code for mov in MASM not using OFFSET:
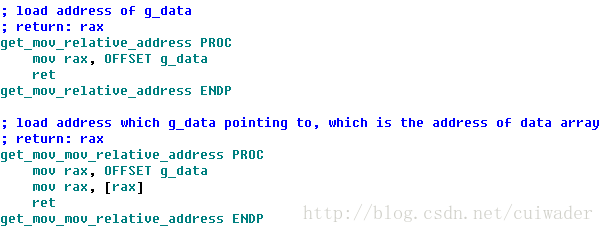
The code for mov in MASM using OFFSET:
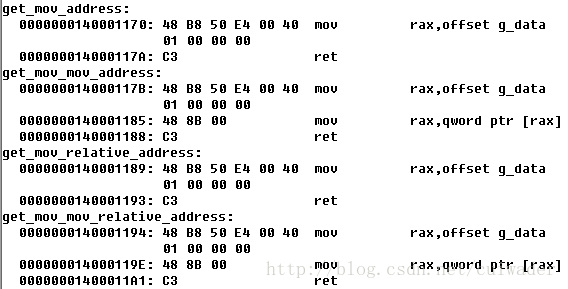
And the disassembled code for those function using dumpbin:
From the source code and disassembled code, it comes the first conclusion:
- There is no different between adding OFFSET before variable and not adding OFFSET before variable in MASM.
- There is no different between adding OFFSET before variable and not adding OFFSET before variable in MASM.
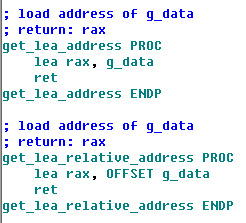
- lea will cost the capability of PIC in MASM.
To complete the code:
The output of those printf:
- "mov register, variable" will load the address of variable to register, which is the same as lea.
Now it's the time to show the code for Linux.
The code for mov in GCC not using %RIP:
The code for mov in GCC using %RIP:
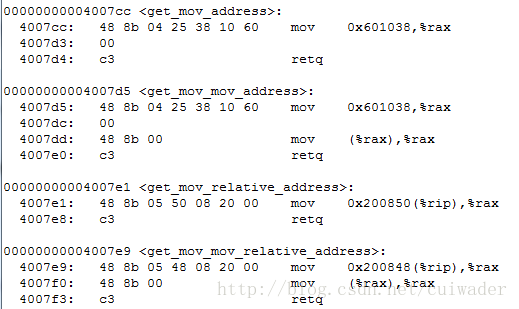
And disassembled code for those functions using objdump:
From the source code and disassembled code, it comes the first conclusion:
- "mov variable, %register" will cost the capability of PIC in GCC. Actually link will fail with option -pie.
- The opcode is different with MASM. It is 8B here and B8 in MASM (opcode 48 is to designate 64-bits operand). B8 is for moving immediate operand. So it means that OFFSET in MASM is actually a immediate number from compiler.
And its disassemble code:
From the source code and disassembled code, it comes the first conclusion:
- "lea variable, %register" will cost the capability of PIC in GCC.
The main code is the same as Windows and the output from those printf:
- "mov variable, %register" will load the content of variable to register, which is not the same as lea and not the same as MASM. So for GCC, if want to load the address of variable, use lea.
- "mov variable[%rip], %register" is the same.
- Is it the same for local variable instead of global?
- What if using RIP in MASM?
- What if using [g_data] or (g_data)?
- Is it the same for 32-bits?
- Is it the same for label and variable?
The source code for the test:
main.c
/**
* This is a test for address behavior in Windows and Linux 64bits for
* instruction mov and lea using OFFSET or RIP.
*/
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <malloc.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
#include "types.h"
#define COUNT 2
extern ADDRESS get_mov_address();
extern ADDRESS get_mov_mov_address();
extern ADDRESS get_mov_relative_address();
extern ADDRESS get_mov_mov_relative_address();
extern ADDRESS get_lea_address();
extern ADDRESS get_lea_relative_address();
DATA** g_data = NULL;
int main()
{
int i = 0;
ADDRESS address;
DATA* data;
g_data = malloc(sizeof(DATA*) * COUNT);
memset(g_data, 0, sizeof(DATA*) * COUNT);
printf("address of g_data:\t\t %#016x\n", &g_data);
printf("g_data point to:\t\t %#016x\n", g_data);
for (i=0; i<COUNT; ++i) {
data = malloc(sizeof(DATA));
printf("address of #%d data:\t\t %#016x\n", i, &data);
printf("#%d data point to:\t\t %#016x\n", i, data);
g_data[i] = data;
}
address = get_mov_address();
printf("get_mov_address:\t\t %#016x\n", address);
address = get_mov_mov_address();
printf("get_mov_mov_address:\t\t %#016x\n", address);
address = get_mov_relative_address();
printf("get_mov_relative_address:\t %#016x\n", address);
address = get_mov_mov_relative_address();
printf("get_mov_mov_relative_address:\t %#016x\n", address);
address = get_lea_address();
printf("get_lea_address:\t\t %#016x\n", address);
address = get_lea_relative_address();
printf("get_lea_relative_address:\t %#016x\n", address);
/* don't care memory leak */
return 0;
}
types.h
/**
* This is a test for address behavior in Windows and Linux 64bits for
* instruction mov and lea using OFFSET or RIP.
*/
#include <stdint.h> // it should be avaliable after VS2010
#if _WIN32 || _WIN64
#if _WIN64
typedef uint64_t ADDRESS;
#else
#error Only 64bits mode is supported
#endif
#endif
#if __GNUC__
#if __x86_64__ || __ppc64__
typedef uint64_t ADDRESS;
#else
#error Only 64bits mode is supported
#endif
#endif
typedef struct {
int32_t donnot_care;
} DATA;
address.asm ;** ;* This is a test for address behavior in Windows and Linux 64bits for ;* instruction mov and lea using OFFSET or RIP. ;** .CODE ; g_data is a pointer array for data ; using NEAR and using QWORD is totally different for MASM ; NEAR is treated as a label so in mov instruction, MASM will adding OFFSET ; but QWORD is treated as a variable so in mov, MASM will load its value extrn g_data:NEAR ;extrn g_data:QWORD ; load address of g_data ; return: rax get_mov_address PROC mov rax, g_data ret get_mov_address ENDP ; load address which g_data pointing to, which is the address of data array ; return: rax get_mov_mov_address PROC mov rax, g_data mov rax, [rax] ret get_mov_mov_address ENDP ; load address of g_data ; return: rax get_mov_relative_address PROC mov rax, OFFSET g_data ret get_mov_relative_address ENDP ; load address which g_data pointing to, which is the address of data array ; return: rax get_mov_mov_relative_address PROC mov rax, OFFSET g_data mov rax, [rax] ret get_mov_mov_relative_address ENDP ; load address of g_data ; return: rax get_lea_address PROC lea rax, g_data ret get_lea_address ENDP ; load address of g_data ; return: rax get_lea_relative_address PROC lea rax, OFFSET g_data ret get_lea_relative_address ENDP END
address.S #** #* This is a test for address behavior in Windows and Linux 64bits for #* instruction mov and lea using OFFSET or RIP. #** .text .extern g_data # load address of g_data # return: rax .global get_mov_address get_mov_address: # this will cause link fail if linked with -pie option. # remove this line if link with -pie option mov g_data, %rax ret # load address which g_data pointing to, which is the address of data array # return: rax .global get_mov_mov_address get_mov_mov_address: # this will cause link fail if linked with -pie option. # remove this line if link with -pie option mov g_data, %rax mov (%rax), %rax ret # load address of g_data # return: rax .global get_mov_relative_address get_mov_relative_address: mov g_data(%rip), %rax ret # load address which g_data pointing to, which is the address of data arrry # return: rax .global get_mov_mov_relative_address get_mov_mov_relative_address: mov g_data(%rip), %rax mov (%rax), %rax ret # load address of g_data # return: rax .global get_lea_address get_lea_address: # this will cause link fail if linked with -pie option. # remove this line if link with -pie option lea g_data, %rax ret # load address of g_data .global get_lea_relative_address get_lea_relative_address: lea g_data(%rip), %rax ret
makefile for Linux #** #* This is a test for address behavior in Windows and Linux 64bits for #* instruction mov and lea using OFFSET or RIP. #** CC = gcc AS = gcc LD = gcc OUTDIR = ./ CFLAGS = -c -m64 -fPIC AFLAGS = -c # -pie option can only be used if the code of address.S is PIC # see the comments in address.S for more detail #LDFLAGS = -pie LDFLAGS = CSOURCES = $(wildcard *.c) ASOURCES = $(wildcard *.S) COBJS = $(addprefix $(OUTDIR), $(notdir $(patsubst %.c, %.o, $(CSOURCES)))) AOBJS = $(addprefix $(OUTDIR), $(notdir $(patsubst %.S, %.o, $(ASOURCES)))) TARGET = address .PHONY: all clean all: $(TARGET) $(TARGET): $(COBJS) $(AOBJS) $(LD) $(LDFLAGS) -o $(OUTDIR)$@ $(COBJS) $(AOBJS) $(COBJS): $(CSOURCES) $(CC) $(CFLAGS) -o $@ $(filter $(*F).c, $(CSOURCES)) $(AOBJS): $(ASOURCES) $(AS) $(AFLAGS) -o $@ $(filter $(*F).S, $(ASOURCES)) clean: rm -r *.o