强大的提示控件TextInputLayout使用以及源码分析
本篇博客带来一个具有强大提示的Material Design风格的控件TextInputLayout,使用这个控件可以非常方便的做出用户登录界面帐号密码输入框的效果,文章将会从以下TextInputLayout使用和TextInputLayout源码分析两个方面对这个强大的控件进行分析。
TextInputLayout的使用
这里使用TextInputLayout简单写一个登录的界面
布局代码
<LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
xmlns:app="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res-auto"
android:gravity="center_horizontal"
android:orientation="vertical"
tools:context="com.example.administrator.textinputdemo2.LoginActivity">
<ScrollView
android:id="@+id/login_form"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent">
<LinearLayout
android:id="@+id/email_login_form"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:orientation="vertical">
<android.support.design.widget.TextInputLayout
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
app:hintAnimationEnabled="true"
app:errorEnabled="true"
android:id="@+id/textInputLayout">
<AutoCompleteTextView
android:id="@+id/email"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:hint="@string/prompt_email"
android:inputType="textEmailAddress"
android:maxLines="1"
android:singleLine="true" />
</android.support.design.widget.TextInputLayout>
<android.support.design.widget.TextInputLayout
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content">
<EditText
android:id="@+id/password"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:hint="@string/prompt_password"
android:imeActionId="@+id/login"
android:imeActionLabel="@string/action_sign_in_short"
android:imeOptions="actionUnspecified"
android:inputType="textPassword"
android:maxLines="1"
android:singleLine="true" />
</android.support.design.widget.TextInputLayout>
<Button
android:id="@+id/email_sign_in_button"
style="?android:textAppearanceSmall"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_marginTop="16dp"
android:text="@string/action_sign_in"
android:textStyle="bold" />
</LinearLayout>
</ScrollView>
</LinearLayout>
LoginActivity代码
public class LoginActivity extends AppCompatActivity {
private TextInputLayout textInputLayout;
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_login);
textInputLayout = (TextInputLayout)findViewById(R.id.textInputLayout);
//检测长度应该低于6位数
textInputLayout.getEditText().addTextChangedListener(new MinLengthTextWatcher(textInputLayout, "长度应低于6位数!"));
//开启计数
textInputLayout.setCounterEnabled(true);
textInputLayout.setCounterMaxLength(10);//最大输入限制数
}
class MinLengthTextWatcher implements TextWatcher{
private String errorStr;
private TextInputLayout textInputLayout;
public MinLengthTextWatcher(TextInputLayout textInputLayout, String errorStr){
this.textInputLayout = textInputLayout;
this.errorStr = errorStr;
}
@Override
public void beforeTextChanged(CharSequence s, int start, int count, int after) {
}
@Override
public void onTextChanged(CharSequence s, int start, int before, int count) {
}
@Override
public void afterTextChanged(Editable s) {
// 文字改变后回调
if(textInputLayout.getEditText().getText().toString().length()<=6){
textInputLayout.setErrorEnabled(false);
}else{
textInputLayout.setErrorEnabled(true);
textInputLayout.setError(errorStr);
}
}
}
}
使用TextInputLayout非常简单,它是一个ViewGroup,里面可以包裹EditText或者AutoCompleteTextView,以下几个属性和方法需要声明一下:
app:hintAnimationEnabled="true"可以开启动画,这个为true时,获得焦点的时候hint提示问题会动画地移动上去。
app:errorEnabled="true"时,开启错误提示
textInputLayout.setCounterEnabled(true);用于 开启计数
textInputLayout.setCounterMaxLength(10);设置最大输入限制数
textInputLayout.setError(errorStr);设置错误提示的信息
textInputLayout.getEditText().addTextChangedListener()用于给textInputLayout包裹的EditText设置内容变化监听,我们可以自己重写一个监听实现里面的方法进行相关逻辑的处理
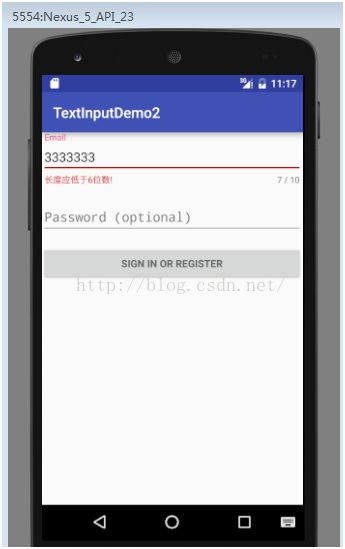
效果如下:
TextInputLayout源码分析
TextInputLayout继承自LinearLayout,说明它是一个ViewGroup
public class TextInputLayout extendsLinearLayout
先从构造函数开始看起
public TextInputLayout(Context context, AttributeSet attrs, int defStyleAttr) {
// Can't call through to super(Context, AttributeSet, int) since it doesn't exist on API 10
super(context, attrs);
setOrientation(VERTICAL);
setWillNotDraw(false);
setAddStatesFromChildren(true);
这里它自动设置了VERTICAL的Orientation,说明这个TextInputLayout是一个竖直的排列,那字数超过部分的提示,在哪里添加的呢?说明在源码中必定有添加这个提示的逻辑,这里我们后面在讨论,先继续往下看
mCollapsingTextHelper.setTextSizeInterpolator(AnimationUtils.FAST_OUT_SLOW_IN_INTERPOLATOR);
mCollapsingTextHelper.setPositionInterpolator(new AccelerateInterpolator());
mCollapsingTextHelper.setCollapsedTextGravity(Gravity.TOP | GravityCompat.START);
final TypedArray a = context.obtainStyledAttributes(attrs,
R.styleable.TextInputLayout, defStyleAttr, R.style.Widget_Design_TextInputLayout);
mHint = a.getText(R.styleable.TextInputLayout_android_hint);
mHintAnimationEnabled = a.getBoolean(
R.styleable.TextInputLayout_hintAnimationEnabled, true);
这里出现了一个mCollapsingTextHelper,通过它可以设置文字大小的加速动画,FAST_OUT_SLOW_IN_INTERPOLATOR,快出慢进的效果,还有设置位置的加速器setPositionInterpolator,setCollapsedTextGravity设置折叠文字的Gravity,看来这个mCollapsingTextHelper的作用还是很强大的,我们后面再看它的源码,先继续往下看
final TypedArray a = context.obtainStyledAttributes(attrs,
R.styleable.TextInputLayout, defStyleAttr, R.style.Widget_Design_TextInputLayout);
mHint = a.getText(R.styleable.TextInputLayout_android_hint);
mHintAnimationEnabled = a.getBoolean(
R.styleable.TextInputLayout_hintAnimationEnabled, true);
if (a.hasValue(R.styleable.TextInputLayout_android_textColorHint)) {
mDefaultTextColor = mFocusedTextColor =
a.getColorStateList(R.styleable.TextInputLayout_android_textColorHint);
}
final int hintAppearance = a.getResourceId(
R.styleable.TextInputLayout_hintTextAppearance, -1);
if (hintAppearance != -1) {
setHintTextAppearance(
a.getResourceId(R.styleable.TextInputLayout_hintTextAppearance, 0));
}
mErrorTextAppearance = a.getResourceId(R.styleable.TextInputLayout_errorTextAppearance, 0);
final boolean errorEnabled = a.getBoolean(R.styleable.TextInputLayout_errorEnabled, false);
a.recycle();
从TypedArray中取出一些用户给TextInputLayout设置的属性,比如给hint设置的文字,mHintAnimationEnabled,hint内文字的动画是否可用,还有hintAppearance的值,mErrorTextAppearance是错误提示文字的样式,errorEnabled是否开启错误提示
setErrorEnabled(errorEnabled);
并通过setErrorEnabled把errorEnabled的值设置给TextInputLayout,TextInputLayout是一个ViewGroup,所以addView方法是必须的
public void addView(View child, int index, ViewGroup.LayoutParams params) {
if (child instanceof EditText) {
setEditText((EditText) child);
super.addView(child, 0, updateEditTextMargin(params));
} else {
// Carry on adding the View...
super.addView(child, index, params);
}
}
只有当child 是 EditText的时候,会调用自身的setEditText方法,然后调用父类LinearLayout的addView方法,如果不是EditText,也调用父类的addView方法,查看setEditText方法 内部
private void setEditText(EditText editText) {
// If we already have an EditText, throw an exception
if (mEditText != null) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("We already have an EditText, can only have one");
}
mEditText = editText;
// Use the EditText's typeface, and it's text size for our expanded text
mCollapsingTextHelper.setTypeface(mEditText.getTypeface());
mCollapsingTextHelper.setExpandedTextSize(mEditText.getTextSize());
mCollapsingTextHelper.setExpandedTextGravity(mEditText.getGravity());
如果TextInputLayout内已经有了一个EditText,再添加就会报错,使用CollapsingTextHelper把传进来的editText的相关属性取出进行设置
mEditText.addTextChangedListener(new TextWatcher() {
@Override
public void afterTextChanged(Editable s) {
updateLabelVisibility(true)<pre name="code" class="java">
然后给EditText设置文本变化的监听,在文本改变之前,正在改变的时候都可以做相应的逻辑处理,往下看有更改EditText的Margin的方法
private LayoutParams updateEditTextMargin(ViewGroup.LayoutParams lp) {
// Create/update the LayoutParams so that we can add enough top margin
// to the EditText so make room for the label
LayoutParams llp = lp instanceof LayoutParams ? (LayoutParams) lp : new LayoutParams(lp);
if (mTmpPaint == null) {
mTmpPaint = new Paint();
}
mTmpPaint.setTypeface(mCollapsingTextHelper.getTypeface());
mTmpPaint.setTextSize(mCollapsingTextHelper.getCollapsedTextSize());
llp.topMargin = (int) -mTmpPaint.ascent();
return llp;
}
设置提示文字的样式
public void setHintTextAppearance(@StyleRes int resId) {
mCollapsingTextHelper.setCollapsedTextAppearance(resId);
mFocusedTextColor = ColorStateList.valueOf(mCollapsingTextHelper.getCollapsedTextColor());
if (mEditText != null) {
updateLabelVisibility(false);
// Text size might have changed so update the top margin
LayoutParams lp = updateEditTextMargin(mEditText.getLayoutParams());
mEditText.setLayoutParams(lp);
mEditText.requestLayout();
}
}
设置错误提示开启和关闭的方法
public void setErrorEnabled(boolean enabled) {
if (mErrorEnabled != enabled) {
if (mErrorView != null) {
ViewCompat.animate(mErrorView).cancel();
}
if (enabled) {
mErrorView = new TextView(getContext());
mErrorView.setTextAppearance(getContext(), mErrorTextAppearance);
mErrorView.setVisibility(INVISIBLE);
addView(mErrorView);
if (mEditText != null) {
// Add some start/end padding to the error so that it matches the EditText
ViewCompat.setPaddingRelative(mErrorView, ViewCompat.getPaddingStart(mEditText),
0, ViewCompat.getPaddingEnd(mEditText), mEditText.getPaddingBottom());
}
} else {
removeView(mErrorView);
mErrorView = null;
}
mErrorEnabled = enabled;
}
}
如果enabled为true的时候,这里会new一个TextView,给TextView设置文本信息和设为可见,然后使用addView(mErrorView)方法,将其添加到TextInputLayout之中,还记得前面我们提过TextInputLayout之中肯定应该会有一个添加错误提示信息的方法,在这里我们找到了,同时这里的代码也是值得我们进行学习的,只有当用户设置错误提示为真的时候,才会new一个TextView,这样是比较省性能的,接下来是setError方法,设置错误提示的文本信息,里面是一些判断和动画的设置
public void setError(@Nullable CharSequence error) {
if (!mErrorEnabled) {
if (TextUtils.isEmpty(error)) {
// If error isn't enabled, and the error is empty, just return
return;
}
// Else, we'll assume that they want to enable the error functionality
setErrorEnabled(true);
}
if (!TextUtils.isEmpty(error)) {
ViewCompat.setAlpha(mErrorView, 0f);
mErrorView.setText(error);
ViewCompat.animate(mErrorView)
.alpha(1f)
.setDuration(ANIMATION_DURATION)
.setInterpolator(AnimationUtils.FAST_OUT_SLOW_IN_INTERPOLATOR)
.setListener(new ViewPropertyAnimatorListenerAdapter() {
@Override
public void onAnimationStart(View view) {
view.setVisibility(VISIBLE);
}
})
.start();
// Set the EditText's background tint to the error color
ViewCompat.setBackgroundTintList(mEditText,
ColorStateList.valueOf(mErrorView.getCurrentTextColor()));
} else {
if (mErrorView.getVisibility() == VISIBLE) {
ViewCompat.animate(mErrorView)
.alpha(0f)
.setDuration(ANIMATION_DURATION)
.setInterpolator(AnimationUtils.FAST_OUT_SLOW_IN_INTERPOLATOR)
.setListener(new ViewPropertyAnimatorListenerAdapter() {
@Override
public void onAnimationEnd(View view) {
view.setVisibility(INVISIBLE);
}
}).start();
// Restore the 'original' tint, using colorControlNormal and colorControlActivated
final TintManager tintManager = TintManager.get(getContext());
ViewCompat.setBackgroundTintList(mEditText,
tintManager.getTintList(R.drawable.abc_edit_text_material));
}
}
sendAccessibilityEvent(AccessibilityEvent.TYPE_WINDOW_CONTENT_CHANGED);
}
接下来是draw方法,调用了mCollapsingTextHelper的draw方法,说明这个TextInputLayout是画出来
<pre name="code" class="java">public void draw(Canvas canvas) {
super.draw(canvas);
mCollapsingTextHelper.draw(canvas);
}
onLayout方法,会拿到EditText的Left,Right等属性,然后使用mCollapsingTextHelper 来setExpandedBounds,设置一个Bound区域
protected void onLayout(boolean changed, int left, int top, int right, int bottom) {
super.onLayout(changed, left, top, right, bottom);
if (mEditText != null) {
final int l = mEditText.getLeft() + mEditText.getCompoundPaddingLeft();
final int r = mEditText.getRight() - mEditText.getCompoundPaddingRight();
mCollapsingTextHelper.setExpandedBounds(l,
mEditText.getTop() + mEditText.getCompoundPaddingTop(),
r, mEditText.getBottom() - mEditText.getCompoundPaddingBottom());
// Set the collapsed bounds to be the the full height (minus padding) to match the
// EditText's editable area
mCollapsingTextHelper.setCollapsedBounds(l, getPaddingTop(),
r, bottom - top - getPaddingBottom());
mCollapsingTextHelper.recalculate();
}
}
上面的有一句注释还是很重要的:设置折叠的bounds去匹配EditText可编辑区域的高,接下来我们查看CollapsingTextHelper这个非常重要的类的代码
public CollapsingTextHelper(View view) {
mView = view;
mTextPaint = new TextPaint();
mTextPaint.setAntiAlias(true);
mCollapsedBounds = new Rect();
mExpandedBounds = new Rect();
mCurrentBounds = new RectF();
}
构造函数中会把view传进来,而这个view就是TextInputLayout,同时new了一个TextPaint来进行文本的绘制,然后是new出来3个矩形区域,mCollapsedBounds:输入框处于折叠状态下的矩形区域,mExpandedBounds:提示框获得焦点,提示文字向上展开的矩形区域,mCurrentBounds:当前状态下的矩形区域;往下是一大堆set方法,然后有一个setExpandedBounds方法
void setExpandedBounds(int left, int top, int right, int bottom) {
if (!rectEquals(mExpandedBounds, left, top, right, bottom)) {
mExpandedBounds.set(left, top, right, bottom);
mBoundsChanged = true;
onBoundsChanged();
}
}
setCollapsedBounds方法
void setCollapsedBounds(int left, int top, int right, int bottom) {
if (!rectEquals(mCollapsedBounds, left, top, right, bottom)) {
mCollapsedBounds.set(left, top, right, bottom);
mBoundsChanged = true;
onBoundsChanged();
}
}
其实也没有什么,就是设置left,top, right, bottom,然后调用onBoundsChanged方法进行更新,接下来有setCollapsedTextAppearance方法,设置折叠时候文字的样式
void setCollapsedTextAppearance(int resId) {
TypedArray a = mView.getContext().obtainStyledAttributes(resId, R.styleable.TextAppearance);
if (a.hasValue(R.styleable.TextAppearance_android_textColor)) {
mCollapsedTextColor = a.getColor(
R.styleable.TextAppearance_android_textColor, mCollapsedTextColor);
}
if (a.hasValue(R.styleable.TextAppearance_android_textSize)) {
mCollapsedTextSize = a.getDimensionPixelSize(
R.styleable.TextAppearance_android_textSize, (int) mCollapsedTextSize);
}
a.recycle();
recalculate();
}
setExpandedTextAppearance:设置展开状态时文字的样式
void setExpandedTextAppearance(int resId) {
TypedArray a = mView.getContext().obtainStyledAttributes(resId, R.styleable.TextAppearance);
if (a.hasValue(R.styleable.TextAppearance_android_textColor)) {
mExpandedTextColor = a.getColor(
R.styleable.TextAppearance_android_textColor, mExpandedTextColor);
}
if (a.hasValue(R.styleable.TextAppearance_android_textSize)) {
mExpandedTextSize = a.getDimensionPixelSize(
R.styleable.TextAppearance_android_textSize, (int) mExpandedTextSize);
}
a.recycle();
recalculate();
}
都是取出mView(传进来的TextInputLayout)的属性取出来进行设置,我们会发现各个方法里都调用了recalculate()方法,也就是重新计算,我们查看一下这个方法
public void recalculate() {
if (mView.getHeight() > 0 && mView.getWidth() > 0) {
// If we've already been laid out, calculate everything now otherwise we'll wait
// until a layout
calculateBaseOffsets();
calculateCurrentOffsets();
}
}
判断条件是当TextInputLayout的Height与Width都大于0的时候会调用calculateBaseOffsets()与calculateCurrentOffsets()方法,注释的内容:如果TextInputLayout已经被laid out的时候,会去重新计算现在布局的一切,否则就等待。calculateBaseOffsets()方法,用于计算基本的偏移量,注意注释的内容:在计算折叠状态下的文字大小,也使用同样的逻辑
final int collapsedAbsGravity = GravityCompat.getAbsoluteGravity(mCollapsedTextGravity,
mIsRtl ? ViewCompat.LAYOUT_DIRECTION_RTL : ViewCompat.LAYOUT_DIRECTION_LTR);
switch (collapsedAbsGravity & Gravity.VERTICAL_GRAVITY_MASK) {
case Gravity.BOTTOM:
mCollapsedDrawY = mCollapsedBounds.bottom;
break;
case Gravity.TOP:
mCollapsedDrawY = mCollapsedBounds.top - mTextPaint.ascent();
break;
case Gravity.CENTER_VERTICAL:
default:
float textHeight = mTextPaint.descent() - mTextPaint.ascent();
float textOffset = (textHeight / 2) - mTextPaint.descent();
mCollapsedDrawY = mCollapsedBounds.centerY() + textOffset;
break;
}
switch (collapsedAbsGravity & Gravity.HORIZONTAL_GRAVITY_MASK) {
case Gravity.CENTER_HORIZONTAL:
mCollapsedDrawX = mCollapsedBounds.centerX() - (width / 2);
break;
case Gravity.RIGHT:
mCollapsedDrawX = mCollapsedBounds.right - width;
break;
case Gravity.LEFT:
default:
mCollapsedDrawX = mCollapsedBounds.left;
break;
}
取出collapsedAbsGravity的值,然后和各种Gravity进行比较,然后确定mCollapsedDrawY 和mCollapsedDrawX的值
mTextPaint.setTextSize(mExpandedTextSize);
width = mTextToDraw != null
? mTextPaint.measureText(mTextToDraw, 0, mTextToDraw.length()) : 0;
final int expandedAbsGravity = GravityCompat.getAbsoluteGravity(mExpandedTextGravity,
mIsRtl ? ViewCompat.LAYOUT_DIRECTION_RTL : ViewCompat.LAYOUT_DIRECTION_LTR);
switch (expandedAbsGravity & Gravity.VERTICAL_GRAVITY_MASK) {
case Gravity.BOTTOM:
mExpandedDrawY = mExpandedBounds.bottom;
break;
case Gravity.TOP:
mExpandedDrawY = mExpandedBounds.top - mTextPaint.ascent();
break;
case Gravity.CENTER_VERTICAL:
default:
float textHeight = mTextPaint.descent() - mTextPaint.ascent();
float textOffset = (textHeight / 2) - mTextPaint.descent();
mExpandedDrawY = mExpandedBounds.centerY() + textOffset;
break;
}
switch (expandedAbsGravity & Gravity.HORIZONTAL_GRAVITY_MASK) {
case Gravity.CENTER_HORIZONTAL:
mExpandedDrawX = mExpandedBounds.centerX() - (width / 2);
break;
case Gravity.RIGHT:
mExpandedDrawX = mExpandedBounds.right - width;
break;
case Gravity.LEFT:
default:
mExpandedDrawX = mExpandedBounds.left;
break;
}
取出expandedAbsGravity的值然后和各种Gravity进行比较,然后确定mCollapsedDrawY 和mCollapsedDrawX的值,最后调用clearTexture()方法清空texture(纹理的意思)
clearTexture();
calculateCurrentOffsets方法,通过lerp方法获取mCurrentDrawX与mCurrentDrawY的值,如果mCollapsedTextColor != mExpandedTextColor,给mTextPaint设置颜色,而这个颜色会通过blendColors方法将mCollapsedTextColor与mExpandedTextColor进行混合,然后采用ViewCompat.postInvalidateOnAnimation方法进行刷新
private void calculateCurrentOffsets() {
final float fraction = mExpandedFraction;
interpolateBounds(fraction);
mCurrentDrawX = lerp(mExpandedDrawX, mCollapsedDrawX, fraction,
mPositionInterpolator);
mCurrentDrawY = lerp(mExpandedDrawY, mCollapsedDrawY, fraction,
mPositionInterpolator);
setInterpolatedTextSize(lerp(mExpandedTextSize, mCollapsedTextSize,
fraction, mTextSizeInterpolator));
if (mCollapsedTextColor != mExpandedTextColor) {
// If the collapsed and expanded text colors are different, blend them based on the
// fraction
mTextPaint.setColor(blendColors(mExpandedTextColor, mCollapsedTextColor, fraction));
} else {
mTextPaint.setColor(mCollapsedTextColor);
}
ViewCompat.postInvalidateOnAnimation(mView);
}
再看一下blendColors内部,也就是通过一个ratio对颜色进行计算,分别计算出ARGB
private static int blendColors(int color1, int color2, float ratio) {
final float inverseRatio = 1f - ratio;
float a = (Color.alpha(color1) * inverseRatio) + (Color.alpha(color2) * ratio);
float r = (Color.red(color1) * inverseRatio) + (Color.red(color2) * ratio);
float g = (Color.green(color1) * inverseRatio) + (Color.green(color2) * ratio);
float b = (Color.blue(color1) * inverseRatio) + (Color.blue(color2) * ratio);
return Color.argb((int) a, (int) r, (int) g, (int) b);
}
再看一下draw方法
public void draw(Canvas canvas) {
final int saveCount = canvas.save();
if (mTextToDraw != null && mDrawTitle) {
float x = mCurrentDrawX;
float y = mCurrentDrawY;
final boolean drawTexture = mUseTexture && mExpandedTitleTexture != null;
final float ascent;
final float descent;
// Update the TextPaint to the current text size
mTextPaint.setTextSize(mCurrentTextSize);
if (drawTexture) {
ascent = mTextureAscent * mScale;
descent = mTextureDescent * mScale;
} else {
ascent = mTextPaint.ascent() * mScale;
descent = mTextPaint.descent() * mScale;
}
if (DEBUG_DRAW) {
// Just a debug tool, which drawn a Magneta rect in the text bounds
canvas.drawRect(mCurrentBounds.left, y + ascent, mCurrentBounds.right, y + descent,
DEBUG_DRAW_PAINT);
}
if (drawTexture) {
y += ascent;
}
if (mScale != 1f) {
canvas.scale(mScale, mScale, x, y);
}
if (drawTexture) {
// If we should use a texture, draw it instead of text
canvas.drawBitmap(mExpandedTitleTexture, x, y, mTexturePaint);
} else {
canvas.drawText(mTextToDraw, 0, mTextToDraw.length(), x, y, mTextPaint);
}
}
canvas.restoreToCount(saveCount);
}
给TextPaint设置当前文字的大小,并给X,Y赋值
float x = mCurrentDrawX;
float y = mCurrentDrawY;
final boolean drawTexture = mUseTexture && mExpandedTitleTexture != null;
final float ascent;
final float descent;
// Update the TextPaint to the current text size
mTextPaint.setTextSize(mCurrentTextSize);
如果需要绘制纹理,则调用canvas的drawBitmap方法,否则canvas 的drawText方法,绘制文字
if (drawTexture) {
// If we should use a texture, draw it instead of text
canvas.drawBitmap(mExpandedTitleTexture, x, y, mTexturePaint);
} else {
canvas.drawText(mTextToDraw, 0, mTextToDraw.length(), x, y, mTextPaint);
}
还有一个calculateIsRtl方法,从右向左计算,是专门给左撇子设计的
private boolean calculateIsRtl(CharSequence text) {
final boolean defaultIsRtl = ViewCompat.getLayoutDirection(mView)
== ViewCompat.LAYOUT_DIRECTION_RTL;
return (defaultIsRtl
? TextDirectionHeuristicsCompat.FIRSTSTRONG_RTL
: TextDirectionHeuristicsCompat.FIRSTSTRONG_LTR).isRtl(text, 0, text.length());
}
到此,源码就基本分析完毕了。