iOS quartz2D 的从零到一学习使用
什么是Quartz2D?二维的绘图引擎
什么是二维?平面
什么是引擎?经包装的函数库,方便开发者使用。也就是说苹果帮我们封装了一套绘图的函数库
同时支持iOS和Mac系统什么意思?用Quartz2D写的同一份代码,既可以运行在iphone上又可以运行在mac上,可以跨平台开发。
开发中比较常用的是截屏/裁剪/自定义UI控件。
Quartz2D在iOS开发中的价值就是自定义UI控件。
使用图形上下文画图,要遵循一下四个步骤
1.获取图像上下文
2.创建路径
3.将路径添加到图形上下文(add)
4.渲染图像上下文(fill,stroke)
以下方法请在UIView的drawRect方法中调用~
一.绘制一条直线的方法
#pragma mark - 直接使用图形上下文画图
- (void)oneMethod
{
//1.获取图形上下文,目前我们现在使用的都是UIGraphics开头,CoreGraphics,项目简称CG
CGContextRef ctx = UIGraphicsGetCurrentContext();
//2.描述路径
//2.1 创建路径
CGContextMoveToPoint(ctx, 10, 50);
//2.2 添加线到一个点
CGContextAddLineToPoint(ctx, 10,100);
//3.完成路线
CGContextStrokePath(ctx);
}
#pragma mark - 图形上下文 + CGPathRef画线
- (void)twoMethod
{
//1.获取图形上下文
CGContextRef ctx = UIGraphicsGetCurrentContext();
//2.使用path画线
CGMutablePathRef path = CGPathCreateMutable();
//3.添加点
CGPathMoveToPoint(path, NULL, 20, 50);
CGPathAddLineToPoint(path, NULL, 20, 100);
//4.将path添加到图形上下文
CGContextAddPath(ctx, path);
//5.渲染上下文
CGContextStrokePath(ctx);
}
#pragma mark - 贝塞尔曲线
- (void)threeMethod
{
//1.创建路径
UIBezierPath *path = [UIBezierPath bezierPath];
//2.画线
[path moveToPoint:CGPointMake(30, 50)];
[path addLineToPoint:CGPointMake(30, 100)];
//3.渲染
[path stroke];
}
#pragma mark - 图形上下文 + 贝塞尔曲线
- (void)fourMethod
{
//1.获得图形上下文
CGContextRef ctx = UIGraphicsGetCurrentContext();
//2.创建路径
UIBezierPath *path = [UIBezierPath bezierPath];
//3.画线
[path moveToPoint:CGPointMake(40, 50)];
[path addLineToPoint:CGPointMake(40, 100)];
//4.将path添加到上下文
CGContextAddPath(ctx, path.CGPath);
//5.渲染
CGContextStrokePath(ctx);
}
二.画两个相交的线,并且设置属性
#pragma mark - 画两个相交的线,并设置属性
- (void)drawTwoLineCrossSetAttribute
{
//1.获取图形上下文
CGContextRef ctx = UIGraphicsGetCurrentContext();
//2.将绘制路径,并且将其添加到图形上下文
CGContextMoveToPoint(ctx, 123, 45);
CGContextAddLineToPoint(ctx, 45, 80);
//3.添加另一条线
CGContextAddLineToPoint(ctx, 223, 159);
//设置颜色
[[UIColor greenColor] set];
//设置线的宽度
CGContextSetLineWidth(ctx, 10);
//设置链接外的链接类型
CGContextSetLineJoin(ctx, kCGLineJoinRound);
//设置线的头部方式
CGContextSetLineCap(ctx, kCGLineCapRound);
//4.渲染
CGContextStrokePath(ctx);
}

[[UIColor greenColor] set]
就不用考虑实线还是填充图形了。还有,
CGContextSetLineJoin
是设置连接处的样式,是枚举,
CGContextSetLineCap
是设置线的顶部的样式,也是枚举。
注意:设置各种属性的时候,一定要记住在渲染之前,否则无效
三.绘制两条不相交的线,并且设置各自属性
#pragma mark - 画两个不相交的线,并且设置各自属性
- (void)drawTwoLineNoCrossSetAttribute
{
//1.创建贝塞尔曲线路径
UIBezierPath *path = [UIBezierPath bezierPath];
//2.绘制路径
[path moveToPoint:CGPointMake(12, 49)];
[path addLineToPoint:CGPointMake(68, 34)];
[[UIColor redColor] set];
[path setLineWidth:5];
//3.渲染
[path stroke];
//绘制第二条路径
UIBezierPath *path2 = [UIBezierPath bezierPath];
[path2 moveToPoint:CGPointMake(145, 167)];
[path2 addLineToPoint:CGPointMake(98, 34)];
[[UIColor greenColor] set];
[path2 setLineWidth:10];
[path2 setLineCapStyle:kCGLineCapRound];
[path2 stroke];
}
使用贝塞尔曲线画图的好处在于,1.每一个贝塞尔底层都有一个图形上线文,如果是用CGContextMoveToPoint画图,实际上就是一个图形上下文,不好去控制,所以建议没多条线可以使用贝塞尔曲线或者说使用底层的CGMutablePathRef画线,比较靠谱。
四.绘制曲线
#pragma mark - 绘制曲线
- (void)drawQuadCurve
{
//1.获得图形上下文
CGContextRef ctx = UIGraphicsGetCurrentContext();
//2.设置起点
CGContextMoveToPoint(ctx, 10, 50);
/**
* 添加曲线的五个参数
*
* @param c#> 图形上下文
* @param cpx#> 将来要突出的x值
* @param cpy#> 要突出的y值
* @param x#> 曲线结束时的x
* @param y#> 曲线结束时的y
*/
CGContextAddQuadCurveToPoint(ctx, 160, 300, 310, 50);
//设置颜色
[[UIColor redColor] set];
//设置宽度
CGContextSetLineWidth(ctx, 5);
//3.渲染图层
CGContextStrokePath(ctx);
}
五.绘制带有圆角边框的正方形
#pragma mark - 绘制一个带有圆角边框的正方形
- (void)drawRoundSquare
{
//绘制一个空心的圆角矩形
//1.创建路径 贝塞尔曲线
UIBezierPath *path = [UIBezierPath bezierPathWithRoundedRect:CGRectMake(10, 50, 100, 40) cornerRadius:5];
//设置颜色
[[UIColor redColor] set];
//2.渲染
[path stroke];
//绘制一个实心的圆角正方形
//1.创建路径 贝塞尔曲线
UIBezierPath *path2 = [UIBezierPath bezierPathWithRoundedRect:CGRectMake(10, 140, 100, 100) cornerRadius:5];
//设置颜色
[[UIColor orangeColor] set];
//2.渲染
[path2 fill];
//绘制一个实心的圆
//1.创建路径 贝塞尔曲线
UIBezierPath *path3 = [UIBezierPath bezierPathWithRoundedRect:CGRectMake(10, 290, 100, 100) cornerRadius:50];
//设置颜色
[[UIColor blueColor] set];
//2.渲染
[path3 fill];
}
- 1.
stroke设置边框的颜色,fill填充内部的颜色 - 2.
fill并不是随意使用的,必须是封闭的图形。 - 3.可以通过设置圆角是正方形的高度,生成一个原形,但不是最规范绘制原形的方法,不过也可以使用。
六.绘制一个弧度曲线
#pragma mark - 绘制一个弧度曲线
- (void)drawCurve
{
/**
* 绘制弧度曲线
*
* @param ArcCenter 曲线中心
* @param radius 半径
* @param startAngle 开始的弧度
* @param endAngle 结束的弧度
* @param clockwise YES顺时针,NO逆时针
*/
//绘制一条半圆曲线
//1.创建路径 贝塞尔曲线
UIBezierPath *path = [UIBezierPath bezierPathWithArcCenter:CGPointMake(150, 150) radius:50 startAngle:0 endAngle:M_PI clockwise:YES];
[[UIColor redColor] set];
[path setLineWidth:10];
[path setLineCapStyle:(kCGLineCapRound)];
//2.渲染
[path stroke];
//绘制一条3/4圆曲线
//1.创建路径 贝塞尔曲线
UIBezierPath *path2 = [UIBezierPath bezierPathWithArcCenter:CGPointMake(150, 350) radius:50 startAngle:0 endAngle:270/360.0*(M_PI * 2) clockwise:YES];
[[UIColor yellowColor] set];
[path2 setLineWidth:10];
[path2 setLineCapStyle:(kCGLineCapRound)];
//2.渲染
[path2 stroke];
//绘制一个圆形曲线
//1.创建路径 贝塞尔曲线
UIBezierPath *path3 = [UIBezierPath bezierPathWithArcCenter:CGPointMake(150, 550) radius:50 startAngle:0 endAngle:(M_PI * 2) clockwise:YES];
[[UIColor blueColor] set];
[path3 setLineWidth:10];
[path3 setLineCapStyle:(kCGLineCapRound)];
//2.渲染
[path3 stroke];
}
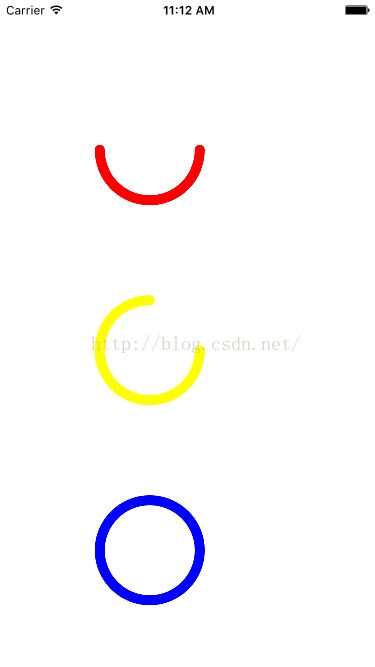
2.这里的角度都是弧度制度,如果我们需要15°,可以用15°/180°*π得到。
3.clockwise这个是顺时针,如果穿1,就是顺时针,穿0,是逆时针
七.绘制一个一个扇形
<span style="font-size:18px;">#pragma mark - 绘制扇形
- (void)drawFanShaped
{
//1.获取图形上下文
CGContextRef ctx = UIGraphicsGetCurrentContext();
//绘制曲线
CGFloat centerX = 100;
CGFloat centerY = 100;
CGFloat radius = 50;
//2.添加一根线
CGContextMoveToPoint(ctx, centerX, centerY);
CGContextAddArc(ctx, centerX, centerY, radius, M_PI, (230 / 360.0)*(M_PI * 2), NO);
//3.关闭线段
CGContextClosePath(ctx);
//4.渲染
CGContextFillPath(ctx);
}</span>

CGContextMoveToPoint2.添加一个圆弧
CGContextAddArc3.闭合绘图
CGContextClosePath4.给路径设置颜色
CGContextStrokePath,或者给图形内部设置颜色CGContextFillPath5.使用贝塞尔曲线,也要设置闭合路径
CGContextClosePath
学有所成,来个小练习~
八.简单下载进度的demo
@interface CustomProgressView : UIView @property (nonatomic,assign) CGFloat progressValue; @end
CustomProgressView.m
@implementation CustomProgressView
- (void)setProgressValue:(CGFloat)progressValue
{
_progressValue = progressValue;
[self setNeedsDisplay];
}
-(void)drawRect:(CGRect)rect
{
UIBezierPath *path = [UIBezierPath bezierPathWithArcCenter:self.center radius:100 startAngle:-M_PI_2 endAngle:(_progressValue / 100.0) *(2 * M_PI) - M_PI_2 clockwise:YES];
[[UIColor redColor] set];
[path setLineWidth:10];
[path setLineCapStyle:(kCGLineCapRound)];
[path stroke];
}
@endViewController.m
@interface ViewController ()
@property (nonatomic,retain) UISlider *slider;
@property (nonatomic,retain) CustomProgressView *progressView;
@property (nonatomic,retain) UILabel *label;
@end
@implementation ViewController
- (void)viewDidLoad {
[super viewDidLoad];
self.progressView = [[CustomProgressView alloc]initWithFrame:CGRectMake(0, 0, self.view.frame.size.width, self.view.frame.size.width)];
self.progressView.backgroundColor = [UIColor whiteColor];
self.label = [[UILabel alloc]initWithFrame:CGRectMake(0, 0, 80, 50)];
self.label.center = self.progressView.center;
self.label.textAlignment = NSTextAlignmentCenter;
[self.progressView addSubview:self.label];
[self.view addSubview:self.progressView];
self.slider = [[UISlider alloc]initWithFrame:CGRectMake(10, 500, self.view.frame.size.width - 20, 50)];
self.slider.minimumValue = 0;
self.slider.maximumValue = 100;
[self.slider addTarget:self action:@selector(changeValue:) forControlEvents:(UIControlEventValueChanged)];
[self.view addSubview:self.slider];
}
- (void)changeValue:(UISlider *)sender
{
self.progressView.progressValue = sender.value;
self.label.text = [NSString stringWithFormat:@"%.f%%",sender.value];
}
- (void)didReceiveMemoryWarning {
[super didReceiveMemoryWarning];
// Dispose of any resources that can be recreated.
}
@end

drawRect:(CGRect)rect,必须要使用setNeedsDisplay,其他的无效。九.饼状图
@interface PieView ()
@property (nonatomic,retain) NSArray *nums;
@property (nonatomic,assign) NSInteger total;
@end
@implementation PieView
- (NSInteger)total
{
if (_total == 0) {
for (int i = 0; i < self.nums.count ; i ++) {
_total += [self.nums[i] integerValue];
}
}
return _total;
}
- (NSArray *)nums
{
if (!_nums) {
self.nums = @[@"10",@"20",@"30",@"40"];
}
return _nums;
}
- (void)drawRect:(CGRect)rect
{
//绘制一个饼图
CGFloat radius = 150;
CGFloat startA = 0;
CGFloat endA = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < self.nums.count; i++) {
NSNumber *num = self.nums[i];
startA = endA;
endA = startA + [num floatValue]/self.total * (2 * M_PI);
UIBezierPath *path = [UIBezierPath bezierPathWithArcCenter:self.center radius:radius startAngle:startA endAngle:endA clockwise:YES];
[path addLineToPoint:self.center];
CGFloat randRed = arc4random_uniform(256)/255.0;
CGFloat randGreen = arc4random_uniform(256)/255.0;
CGFloat randBlue = arc4random_uniform(256)/255.0;
UIColor *randomColor = [UIColor colorWithRed:randRed green:randGreen blue:randBlue alpha:1];
[randomColor set];
[path fill];
}
}
@end
ViewController.m
PieView *pie = [[PieView alloc]initWithFrame:[UIScreen mainScreen].bounds];
pie.backgroundColor = [UIColor whiteColor];
[self.view addSubview:pie];

十.柱状图
@interface BarChartView()
@property (nonatomic,retain) NSArray *nums;
@end
@implementation BarChartView
- (NSArray *)nums
{
if (!_nums) {
self.nums = @[@"10",@"20",@"30",@"40",@"50",@"60",@"70",@"80"];
}
return _nums;
}
- (void)drawRect:(CGRect)rect
{
//1.获取图形上下文
CGContextRef ctz = UIGraphicsGetCurrentContext();
//2.绘制图像
//设置间距
CGFloat margin = 30;
//当柱状图的数量多于5的时候缩小它们的间距
if (self.nums.count > 5) {
margin = 10;
}
//柱状图的宽度 = ( view的宽度 - 间隔的总宽度 )/ 柱状图的个数
CGFloat width = (rect.size.width - (self.nums.count + 1) *margin) / self.nums.count;
for (int i = 0; i < self.nums.count; i++) {
//求出 每一个数字所占的比例
CGFloat num = [self.nums[i] floatValue]/100;
//起点位置
CGFloat x = margin + (width + margin) * i ;
CGFloat y = rect.size.height * (1 - num);
CGFloat height = rect.size.height * num;
CGRect rectA = CGRectMake(x, y, width, height);
CGContextAddRect(ctz, rectA);
CGFloat randRed = arc4random_uniform(256)/255.0;
CGFloat randGreen = arc4random_uniform(256)/255.0;
CGFloat randBlue = arc4random_uniform(256)/255.0;
UIColor *randomColor = [UIColor colorWithRed:randRed green:randGreen blue:randBlue alpha:1];
[randomColor set];
//渲染
CGContextFillPath(ctz);
}
}
/*
// Only override drawRect: if you perform custom drawing.
// An empty implementation adversely affects performance during animation.
- (void)drawRect:(CGRect)rect {
// Drawing code
}
*/
@end
ViewController.m
BarChartView *view = [[BarChartView alloc]initWithFrame:[UIScreen mainScreen].bounds];
view.backgroundColor = [UIColor whiteColor];
[self.view addSubview:view];
十一.绘制图片
绘制文字和图片的时候,是不用去获取图像上下文的
-(void)drawRect:(CGRect)rect
{
//剪切图片,超出的图片位置都要剪切掉!必须要在绘制之前写,否则无效
// UIRectClip(CGRectMake(0, 0, 100, 50));
UIImage *image = [UIImage imageNamed:@"image"];
//独立
//在什么范围内(原图大小)
[image drawInRect:rect];
//在哪个位置开始画
[image drawAtPoint:CGPointMake(10, 10)];
//平铺
[image drawAsPatternInRect:rect];
}

[image drawInRect:rect]; //拉伸效果
[image drawAtPoint:CGPointMake(10, 10)];//适应效果
[image drawAsPatternInRect:rect];//平铺效果
十二.绘制富文本
- (void)drawRect:(CGRect)rect
{
NSString *str = @"不管开心与否\n每天都要努力生活\n爱自己\n爱家人";
//设置文字的属性
NSMutableDictionary * paras = [NSMutableDictionary dictionary];
//设置字体大小
paras[NSFontAttributeName] = [UIFont systemFontOfSize:40];
//设置字体颜色
paras[NSForegroundColorAttributeName] = [UIColor blackColor];
//设置镂空渲染颜色
paras[NSStrokeColorAttributeName] = [UIColor orangeColor];
//设置镂空渲染宽度
paras[NSStrokeWidthAttributeName] = @3;
//创建阴影对象
NSShadow *shodow = [[NSShadow alloc] init];
//阴影颜色
shodow.shadowColor = [UIColor yellowColor];
//阴影偏移量
shodow.shadowOffset = CGSizeMake(5, 6);
//阴影的模糊半径
shodow.shadowBlurRadius = 4;
//苹果的富文本就是这样搞出来的
paras[NSShadowAttributeName] = shodow;
[str drawAtPoint:CGPointZero withAttributes:paras];
}

十三.雪花飘动
//只有在drawRect方法中才能拿到图形上下文,才可以画图
- (void)drawRect:(CGRect)rect {
//设置下雪的动画
UIImage *image = [UIImage imageNamed:@"snow"];
_snowY += 10;
[image drawAtPoint:CGPointMake(0, _snowY)];
if (_snowY >= rect.size.height) {
_snowY = 0;
}
}
// 如果在绘图的时候需要用到定时器,通常使用CADisplayLink
// NSTimer很少用于绘图,因为调度优先级比较低,并不会准时调用
- (void)awakeFromNib
{
// 创建定时器
CADisplayLink *link = [CADisplayLink displayLinkWithTarget:self selector:@selector(timeChange)];
// 添加主运行循环
[link addToRunLoop:[NSRunLoop mainRunLoop] forMode:NSDefaultRunLoopMode];
}
// CADisplayLink:每次屏幕刷新的时候就会调用,屏幕一般一秒刷新60次
- (void)timeChange{
[self setNeedsDisplay];
}1.本质就是调用
drawRect方法,一直刷新雪花的y值
2.每一次调用drawRect,都创建大量的对象,有人说可能性能不好,不过你可能多虑了,没吃都是在内存加载,不会创建新的UIImage
十四.图形上下文栈
我自己详细的介绍了一下,上下文栈,可以看一下~
图形上下文详解
十五.图形上下文矩阵
到底是个啥?
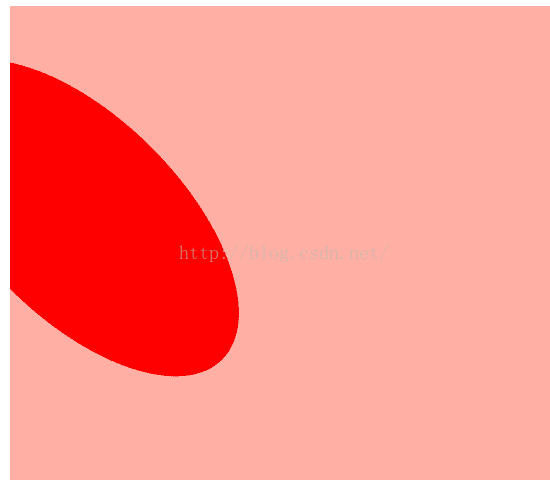
就是图形上下文画出的东西永远是方方正正的,你要是想画个偏离的矩形,按照过去的方法画不出来,只能使用矩阵的方式。分别有偏移,缩放,旋转
- (void)drawRect:(CGRect)rect {
//图形上下文矩阵
//1.画一个椭圆
CGContextRef ctx = UIGraphicsGetCurrentContext();
// CGContextAddEllipseInRect(ctx, CGRectMake(100, 100, 100, 100));
CGPathRef path = CGPathCreateWithEllipseInRect(CGRectMake(0, 0, 200, 100),nil);
[[UIColor redColor] set];
//1.偏移
// CGContextTranslateCTM(ctx, 10, 10);
//2.旋转
// CGContextRotateCTM(ctx, M_PI_4);
//3.缩放
CGContextScaleCTM(ctx, 0.25, 2);
CGContextAddPath(ctx, path);
CGContextFillPath(ctx);
}1.绘制变化的图形的步骤
- 先绘制path
- 设置图形上下文矩阵
- 将path添加到图形上下文(这一步很重要,一定按照步骤来)
- 渲染
2.绘图的时候,我们要使用底层的 CGPathRef,或者贝塞尔,然后 CGContextRef+path的方式。
如不这样,我注释的CGContextAddEllipseInRect(ctx, CGRectMake(100, 100, 100, 100))方法,这个方法中已经先去添加了path到图形上下文,即使我们在去添加图形上下文矩阵,也是无效
3.可以和图形上下文栈一起使用,给特定的一些图案设置一些属性,还有一些不会受到影响