深入理解nginx chap3 开发一个简单的HTTP模块
1. 如何调用HTTP模块
本质:worker 进程会在一个for 循环里面反复调用事件模块检测网络事件。
2. 基本数据结构
- 命名规则: ngx_http_xxx_module.c
2.1 整形封装
- ngx_int_t 封装了有符号整形, 而 ngx_uint_t 封装了无符号整形
2.2 ngx_str_t
ngx_str_t 封装了字符串
typedef struct { size_t len; u_char * data; }ngx_str_t;可以使用 ngx_strncmp 进行名称比对
2.3 ngx_list_t
这是一个链表容器, 容器内元素为数组
typedef struct ngx_list_part_s ngx_list_part_t; struct ngx_list_part_s{ void * elts; // 指向数组的起始位置 ngx_unit_t nelts; // 标记数组中已经使用的容量 ngx_list_part_t * next; }; typedef struct { ngx_list_part_t * last; // 指向链表的最后一个数组的位置 ngx_list_part_t part; // 指向链表头 size_t size; // 一个链表元素(ie, 数组节点)所包含的元素大小 ngx_uint_t nalloc; // 一个链表元素(ie, 数组节点)所包含的元素个数 ngx_pool_t * pool; // 内存池地址 }ngx_list_t;链表的遍历
可以根据ngx_list_t 的结构类型, (外层链表, 内层数组), 实现结构的遍历操作
2.4 ngx_table_elt_t
本质是一个键值对结构
2.5 ngx_buf_t
缓冲区数据结构ngx_buf_t, 是处理大数据的关键数据结构, 既应用于内存数据也应用于磁盘数据
2.6 ngx_chain_t
一般与ngx_chain_t 配合使用, 用来作为发送包体的数据结构
3. 如何将自己的HTTP模块编译进Nginx
3.1 config
在configure执行的时候, 使用 –add-module=PATH
这里用一个栗子来形象的解释.
在config 文件中写入如下代码:
ngx_addon_name=ngx_http_mytest_module
HTTP_MODULES="$HTTP_MODULES ngx_http_mytest_module"
NGX_ADDON_SRCS="$NGX_ADDON_SRCS $ngx_addon_dir/ngx_http_mytest_module.c"编译生成即可
3.2 configure 脚本
略
3.3 直接修改 makefile
略
4. HTTP模块的数据结构
4.1 ngx_module_t 数据结构
首先, 需要了解的是 ngx_module_t 这个nginx 的模块数据结构, 而在这个数据结构中, 我们最需要关注的是下面 3 个 变量:
- ctx, 用于指向一类模块的上下文结构体 (对于HTTP 模块, ctx 指针必须指向 ngx_http_module_t 接口)
- commands, 用于处理nginx.conf 文件中的配置项
- type, 用来表示模块的类型 (定义HTTP 模块, 这个值应该设置为: NGX_HTTP_MODULE)
4.2 ngx_http_module_t 接口
HTTP 框架在启动的过程中会在每个阶段中调用ngx_http_module_t 中相应的方法
4.3 commands 数组
- 用来定义模块的配置文件参数, 数组中的每个元素都是 ngx_command_t 类型, 数组的结尾使用 ngx_null_command 来标记
- Nginx 解析配置文件的流程:
- 解析每个配置项的时候, 首先会遍历所有的模块
- 对于每个模块而言, 通过遍历commands 数组进行, 查找他所感兴趣的配置项
- 每个ngx_command_t 结构体定义了自己感兴趣的一个配置项
5. 定义自己的HTTP 模块
我们之前写过一篇定义自己的hello world 模块的博文
http://blog.csdn.net/zhyh1435589631/article/details/51638561
里面有写过这部分内容的配置
6. 处理用户请求
- 在出现mytest 配置项的时候, ngx_http_mytest 方法被调用, 这时候, 将ngx_http_core_loc_conf_t 结构的handler 成员指定为ngx_http_mytest_handler。 在HTTP 框架接收完HTTP请求的头部之后, 会调用handler指向的方法, 用来处理用户请求。
6.1 处理方法的返回值
- 主要包含RFC 2616 规范中定义的返回码, 以及Nginx 自身定义的HTTP返回码
- 主要需要了解4个通用的返回码:
- NGX_OK: 表示成功
- NGX_DECLINED: 继续在NGX_HTTP_CONTENT_PHASE 阶段, 寻找感兴趣的HTTP 模块来再次处理这个请求
- NGX_DONE: 表示到此为止, 同时HTTP 框架将暂时不再继续执行这个请求的后续部分。事实上, 如果是keepalive类型的用户请求, 就会保持这个http 连接, 然后把控制权返回给Nginx
- NGX_ERROR: 表示错误, 将终止请求
6.2 获取URI 和 参数
请求的所有信息(方法, URI, 协议版本号和头部等)都可以在传入的ngx_http_request_t 类型的参数 r 中获取。
可以通过r->method 这个整形成员与预定义的几个宏进行比较, 从而获取方法名
- URI, uri 成员指向用户请求的 URI
- args, 指向用户请求中的URI参数
- http_protocol 的data 成员指向用户请求中HTTP 协议版本字符串的起始地址, len 成员为其字符串长度
6.3 获取HTTP 头部
ngx_http_headers_in_t 类型的headers_in存储已经解析过的HTTP 头部
6.4 获取HTTP 包体
- 由于HTTP 包体的长度有可能非常大, 如果试图一次性调用并读完所有的包体, 可能导致nginx 的阻塞
- nginx 提供一个叫做 ngx_http_read_client_request_body的异步方法, 调用它只是说明要求Nginx开始连接请求的包体, 并不表示是否已经接收完毕。
- 如果 ngx_http_read_client_request_body是在ngx_http_mytest_handler处理方法中调用的话, 一般后者需要返回 NGX_DONE
- 而如果不想处理请求中的包体的时候, 可以调用 ngx_http_discard_request_body 方法将接收自客户端的HTTP 包体丢弃掉
7. 发送响应
- HTTP响应主要包括 3 个部分: 响应行, 响应头部, 包体
7.1 发送HTTP头部
- 使用api: ngx_http_send_header 即可
- 只需要在发送之前, 预先指定一下 headers_out 中的成员即可
7.2 将内存中的字符串作为包体发送
- 调用 ngx_http_output_filter 可以实现向客户端发送HTTP 响应包体
- 发送的内容放在 ngx_buf_t 结构中, 并使用 ngx_chain_t 传递给 ngx_http_output_filter 方法
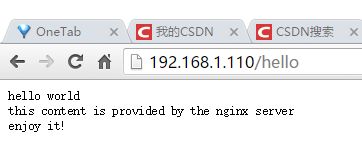
7.3 hello world 演示
http://blog.csdn.net/zhyh1435589631/article/details/51638561
8. 发送磁盘文件
8.1 如何发送磁盘中的文件
- 发送文件的接口和上面发送内存中数据的接口类似, 不同的是如何设置 缓冲区 ngx_buf_t
- 需要设置 ngx_buf_t 中的 in_file 标志
- 设置ngx_file_t 数据结构

- 设置ngx_buf_t 中的 file_pos 和 file_last
8.2 清理文件句柄
- nginx 通过异步方式将整个文件高效的发送给用户, 但是需要在发送完毕之后, 关闭打开的文件句柄, 避免句柄泄露
- ngx_pool_cleanup_file 用于关闭文件句柄
- ngx_pool_cleanup_t 结构

- ngx_pool_cleanup_file_t 结构

- 使用ngx_pool_cleanup_add 添加, 并设置完上面两个结构即可
8.3 支持用户多线程下载和断点续传
r->allow_ranges = 1;
8.4 文件传输效果
8.5 文件传输的整体代码
#include <ngx_config.h>
#include <ngx_core.h>
#include <ngx_http.h>
static char *
ngx_http_mytest(ngx_conf_t *cf, ngx_command_t *cmd, void *conf);
static ngx_int_t ngx_http_mytest_handler(ngx_http_request_t *r);
static ngx_command_t ngx_http_mytest_commands[] =
{
{
ngx_string("mytest"),
NGX_HTTP_MAIN_CONF | NGX_HTTP_SRV_CONF | NGX_HTTP_LOC_CONF | NGX_HTTP_LMT_CONF | NGX_CONF_NOARGS,
ngx_http_mytest,
NGX_HTTP_LOC_CONF_OFFSET,
0,
NULL
},
ngx_null_command
};
static ngx_http_module_t ngx_http_mytest_module_ctx =
{
NULL, /* preconfiguration */
NULL, /* postconfiguration */
NULL, /* create main configuration */
NULL, /* init main configuration */
NULL, /* create server configuration */
NULL, /* merge server configuration */
NULL, /* create location configuration */
NULL /* merge location configuration */
};
ngx_module_t ngx_http_mytest_module =
{
NGX_MODULE_V1,
&ngx_http_mytest_module_ctx, /* module context */
ngx_http_mytest_commands, /* module directives */
NGX_HTTP_MODULE, /* module type */
NULL, /* init master */
NULL, /* init module */
NULL, /* init process */
NULL, /* init thread */
NULL, /* exit thread */
NULL, /* exit process */
NULL, /* exit master */
NGX_MODULE_V1_PADDING
};
static char *
ngx_http_mytest(ngx_conf_t *cf, ngx_command_t *cmd, void *conf)
{
ngx_http_core_loc_conf_t *clcf;
//首先找到mytest配置项所属的配置块,clcf貌似是location块内的数据
//结构,其实不然,它可以是main、srv或者loc级别配置项,也就是说在每个
//http{}和server{}内也都有一个ngx_http_core_loc_conf_t结构体
clcf = ngx_http_conf_get_module_loc_conf(cf, ngx_http_core_module);
//http框架在处理用户请求进行到NGX_HTTP_CONTENT_PHASE阶段时,如果
//请求的主机域名、URI与mytest配置项所在的配置块相匹配,就将调用我们
//实现的ngx_http_mytest_handler方法处理这个请求
clcf->handler = ngx_http_mytest_handler;
return NGX_CONF_OK;
}
static ngx_int_t ngx_http_mytest_handler(ngx_http_request_t *r)
{
//必须是GET或者HEAD方法,否则返回405 Not Allowed
if (!(r->method & (NGX_HTTP_GET | NGX_HTTP_HEAD)))
{
return NGX_HTTP_NOT_ALLOWED;
}
//丢弃请求中的包体
ngx_int_t rc = ngx_http_discard_request_body(r);
if (rc != NGX_OK)
{
return rc;
}
ngx_buf_t *b;
b = ngx_palloc(r->pool, sizeof(ngx_buf_t));
//要打开的文件
u_char* filename = (u_char*)"/tmp/test.txt";
b->in_file = 1;
b->file = ngx_pcalloc(r->pool, sizeof(ngx_file_t));
b->file->fd = ngx_open_file(filename, NGX_FILE_RDONLY | NGX_FILE_NONBLOCK, NGX_FILE_OPEN, 0);
b->file->log = r->connection->log;
b->file->name.data = filename;
b->file->name.len = sizeof(filename) - 1;
if (b->file->fd <= 0)
{
return NGX_HTTP_NOT_FOUND;
}
//支持断点续传
r->allow_ranges = 1;
//获取文件长度
if (ngx_file_info(filename, &b->file->info) == NGX_FILE_ERROR)
{
return NGX_HTTP_INTERNAL_SERVER_ERROR;
}
//设置缓冲区指向的文件块
b->file_pos = 0;
b->file_last = b->file->info.st_size;
ngx_pool_cleanup_t* cln = ngx_pool_cleanup_add(r->pool, sizeof(ngx_pool_cleanup_file_t));
if (cln == NULL)
{
return NGX_ERROR;
}
cln->handler = ngx_pool_cleanup_file;
ngx_pool_cleanup_file_t *clnf = cln->data;
clnf->fd = b->file->fd;
clnf->name = b->file->name.data;
clnf->log = r->pool->log;
//设置返回的Content-Type。注意,ngx_str_t有一个很方便的初始化宏
//ngx_string,它可以把ngx_str_t的data和len成员都设置好
ngx_str_t type = ngx_string("text/plain");
//设置返回状态码
r->headers_out.status = NGX_HTTP_OK;
//响应包是有包体内容的,所以需要设置Content-Length长度
r->headers_out.content_length_n = b->file->info.st_size;
//设置Content-Type
r->headers_out.content_type = type;
//发送http头部
rc = ngx_http_send_header(r);
if (rc == NGX_ERROR || rc > NGX_OK || r->header_only)
{
return rc;
}
//构造发送时的ngx_chain_t结构体
ngx_chain_t out;
//赋值ngx_buf_t
out.buf = b;
//设置next为NULL
out.next = NULL;
//最后一步发送包体,http框架会调用ngx_http_finalize_request方法
//结束请求
return ngx_http_output_filter(r, &out);
}
9. 用C++ 语言编写HTTP 模块
- 使用G++ 编译C++ 代码, 用 GCC 编译nginx 代码, 使用 C++ 编译器链接
9.1 编译方式修改
- 直接修改makefile
- LINK = $(CXX) 使用 g++ 链接
- C++ 文件使用 $(CXX) 编译
9.2 程序中的符号转换
extern “C”{
}
10. 小结
ps: 处理方法必须是快速, 无阻塞的, ngx_http_mytest_handler 或者类似的处理方法中是不可以有耗时很长的操作的