MapReduce详解
在研究了几天的MapReduce框架后,发现确实是和之前的编程思路不太一样,在此先转一篇供大家学习。
3.3 新的WordCount分析
1)源代码程序
package org.apache.hadoop.examples;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.util.StringTokenizer;
import org.apache.hadoop.conf.Configuration;
import org.apache.hadoop.fs.Path;
import org.apache.hadoop.io.IntWritable;
import org.apache.hadoop.io.Text;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.Job;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.Mapper;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.Reducer;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.lib.input.FileInputFormat;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.lib.output.FileOutputFormat;
import org.apache.hadoop.util.GenericOptionsParser;
public class WordCount {
public static class TokenizerMapper
extends Mapper<Object, Text, Text, IntWritable>{
private final static IntWritable one = new IntWritable(1);
private Text word = new Text();
public void map(Object key, Text value, Context context)
throws IOException, InterruptedException {
StringTokenizer itr = new StringTokenizer(value.toString());
while (itr.hasMoreTokens()) {
word.set(itr.nextToken());
context.write(word, one);
}
}
}
public static class IntSumReducer
extends Reducer<Text,IntWritable,Text,IntWritable> {
private IntWritable result = new IntWritable();
public void reduce(Text key, Iterable<IntWritable> values,Context context)
throws IOException, InterruptedException {
int sum = 0;
for (IntWritable val : values) {
sum += val.get();
}
result.set(sum);
context.write(key, result);
}
}
public static void main (String[] args) throws Exception {
Configuration conf = new Configuration();
String[] otherArgs = new GenericOptionsParser(conf, args).getRemainingArgs();
if (otherArgs.length != 2) {
System.err.println("Usage: wordcount <in> <out>");
System.exit(2);
}
Job job = new Job(conf, "word count");
job.setJarByClass(WordCount.class);
job.setMapperClass(TokenizerMapper.class);
job.setCombinerClass(IntSumReducer.class);
job.setReducerClass(IntSumReducer.class);
job.setOutputKeyClass(Text.class);
job.setOutputValueClass(IntWritable.class);
FileInputFormat.addInputPath(job, new Path(otherArgs[0]));
FileOutputFormat.setOutputPath(job, new Path(otherArgs[1]));
System.exit(job.waitForCompletion(true) ? 0 : 1);
}
}
1)Map过程
public static class TokenizerMapper
extends Mapper<Object, Text, Text, IntWritable>{
private final static IntWritable one = new IntWritable(1);
private Text word = new Text();
public void map(Object key, Text value, Context context)
throws IOException, InterruptedException {
StringTokenizer itr = new StringTokenizer(value.toString());
while (itr.hasMoreTokens()) {
word.set(itr.nextToken());
context.write(word, one);
}
}
Map过程需要继承org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce包中 Mapper 类,并 重写 其map方法。通过在map方法中添加两句把key值和value值输出到控制台的代码,可以发现map方法中value值存储的是文本文件中的一行(以回车符为行结束标记),而key值为该行的首字母相对于文本文件的首地址的偏移量。然后StringTokenizer类将每一行拆分成为一个个的单词,并将<word,1>作为map方法的结果输出,其余的工作都交有 MapReduce框架 处理。
2)Reduce过程
public static class IntSumReducer
extends Reducer<Text,IntWritable,Text,IntWritable> {
private IntWritable result = new IntWritable();
public void reduce(Text key, Iterable<IntWritable> values,Context context)
throws IOException, InterruptedException {
int sum = 0;
for (IntWritable val : values) {
sum += val.get();
}
result.set(sum);
context.write(key, result);
}
}
Reduce过程需要继承org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce包中 Reducer 类,并 重写 其reduce方法。Map过程输出<key,values>中key为单个单词,而values是对应单词的计数值所组成的列表,Map的输出就是Reduce的输入,所以reduce方法只要遍历values并求和,即可得到某个单词的总次数。
3)执行MapReduce任务
public static void main (String[] args) throws Exception {
Configuration conf = new Configuration();
String[] otherArgs = new GenericOptionsParser(conf, args).getRemainingArgs();
if (otherArgs.length != 2) {
System.err.println("Usage: wordcount <in> <out>");
System.exit(2);
}
Job job = new Job(conf, "word count");
job.setJarByClass(WordCount.class);
job.setMapperClass(TokenizerMapper.class);
job.setCombinerClass(IntSumReducer.class);
job.setReducerClass(IntSumReducer.class);
job.setOutputKeyClass(Text.class);
job.setOutputValueClass(IntWritable.class);
FileInputFormat.addInputPath(job, new Path(otherArgs[0]));
FileOutputFormat.setOutputPath(job, new Path(otherArgs[1]));
System.exit(job.waitForCompletion(true) ? 0 : 1);
}
在MapReduce中,由Job对象负责管理和运行一个计算任务,并通过Job的一些方法对任务的参数进行相关的设置。此处设置了使用TokenizerMapper完成Map过程中的处理和使用IntSumReducer完成Combine和Reduce过程中的处理。还设置了Map过程和Reduce过程的输出类型:key的类型为Text,value的类型为IntWritable。任务的输出和输入 路径 则由命令行参数指定,并由FileInputFormat和FileOutputFormat分别设定。完成相应任务的参数设定后,即可调用 job.waitForCompletion() 方法执行任务。
WordCount处理过程
本节将对WordCount进行更详细的讲解。详细执行步骤如下:
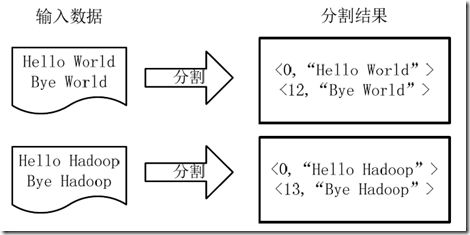
1)将文件拆分成splits,由于测试用的文件较小,所以每个文件为一个split,并将文件按行分割形成<key,value>对,如图4-1所示。这一步由MapReduce框架自动完成,其中偏移量(即key值)包括了回车所占的字符数(Windows和Linux环境会不同)。
分割过程
2)将分割好的<key,value>对交给用户定义的map方法进行处理,生成新的<key,value>对,如图4-2所示。
执行map方法
3)得到map方法输出的<key,value>对后,Mapper会将它们按照key值进行排序,并执行Combine过程,将key至相同value值累加,得到Mapper的最终输出结果。如图4-3所示。
Map端排序及Combine过程
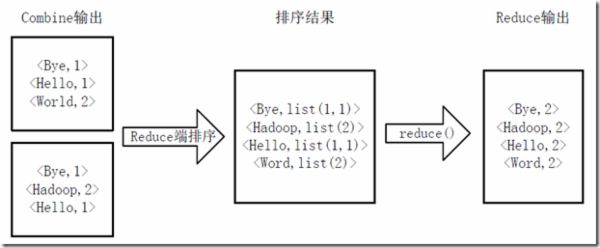
4)Reducer先对从Mapper接收的数据进行排序,再交由用户自定义的reduce方法进行处理,得到新的<key,value>对,并作为WordCount的输出结果,如图4-4所示。
Reduce端排序及输出结果