simhash Java和Python版本的实现
绍下这个算法主要原理,为了便于理解尽量不使用数学公式,分为这几步:
-
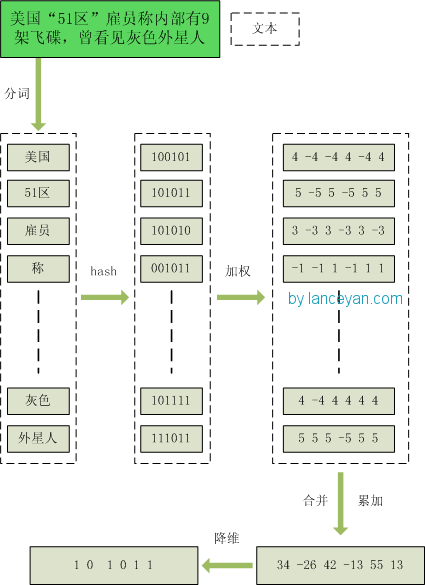
1、分词,把需要判断文本分词形成这个文章的特征单词。最后形成去掉噪音词的单词序列并为每个词加上权重,我们假设权重分为5个级别(1~5)。比如:“ 美国“51区”雇员称内部有9架飞碟,曾看见灰色外星人 ” ==> 分词后为 “ 美国(4) 51区(5) 雇员(3) 称(1) 内部(2) 有(1) 9架(3) 飞碟(5) 曾(1) 看见(3) 灰色(4) 外星人(5)”,括号里是代表单词在整个句子里重要程度,数字越大越重要。
-
2、hash,通过hash算法把每个词变成hash值,比如“美国”通过hash算法计算为 100101,“51区”通过hash算法计算为 101011。这样我们的字符串就变成了一串串数字,还记得文章开头说过的吗,要把文章变为数字计算才能提高相似度计算性能,现在是降维过程进行时。
-
3、加权,通过 2步骤的hash生成结果,需要按照单词的权重形成加权数字串,比如“美国”的hash值为“100101”,通过加权计算为“4 -4 -4 4 -4 4”;“51区”的hash值为“101011”,通过加权计算为 “ 5 -5 5 -5 5 5”。
-
4、合并,把上面各个单词算出来的序列值累加,变成只有一个序列串。比如 “美国”的 “4 -4 -4 4 -4 4”,“51区”的 “ 5 -5 5 -5 5 5”, 把每一位进行累加, “4+5 -4+-5 -4+5 4+-5 -4+5 4+5” ==》 “9 -9 1 -1 1 9”。这里作为示例只算了两个单词的,真实计算需要把所有单词的序列串累加。
-
5、降维,把4步算出来的 “9 -9 1 -1 1 9” 变成 0 1 串,形成我们最终的simhash签名。 如果每一位大于0 记为 1,小于0 记为 0。最后算出结果为:“1 0 1 0 1 1”。
整个过程图为:
大家可能会有疑问,经过这么多步骤搞这么麻烦,不就是为了得到个 0 1 字符串吗?我直接把这个文本作为字符串输入,用hash函数生成 0 1 值更简单。其实不是这样的,传统hash函数解决的是生成唯一值,比如 md5、hashmap等。md5是用于生成唯一签名串,只要稍微多加一个字符md5的两个数字看起来相差甚远;hashmap也是用于键值对查找,便于快速插入和查找的数据结构。不过我们主要解决的是文本相似度计算,要比较的是两个文章是否相识,当然我们降维生成了hashcode也是用于这个目的。看到这里估计大家就明白了,我们使用的simhash就算把文章中的字符串变成 01 串也还是可以用于计算相似度的,而传统的hashcode却不行。我们可以来做个测试,两个相差只有一个字符的文本串,“你妈妈喊你回家吃饭哦,回家罗回家罗” 和 “你妈妈叫你回家吃饭啦,回家罗回家罗”。
通过simhash计算结果为:
1000010010101101111111100000101011010001001111100001001011001011
1000010010101101011111100000101011010001001111100001101010001011
通过 hashcode计算为:
1111111111111111111111111111111110001000001100110100111011011110
1010010001111111110010110011101
大家可以看得出来,相似的文本只有部分 01 串变化了,而普通的hashcode却不能做到,这个就是局部敏感哈希的魅力。目前Broder提出的shingling算法和Charikar的simhash算法应该算是业界公认比较好的算法。在simhash的发明人Charikar的论文中并没有给出具体的simhash算法和证明,“量子图灵”得出的证明simhash是由随机超平面hash算法演变而来的。
simhash是google用来处理海量文本去重的算法。 google出品,你懂的。 simhash最牛逼的一点就是将一个文档,最后转换成一个64位的字节,暂且称之为特征字,然后判断重复只需要判断他们的特征字的距离是不是 大概花三分钟看懂这个图就差不多怎么实现这个simhash算法了。特别简单。谷歌出品嘛,简单实用。 算法过程大概如下: 到此,如何从一个doc到一个simhash值的过程已经讲明白了。 但是还有一个重要的部分没讲, 二进制串A 和 二进制串B 的海明距离 就是 举例如下: 当我们算出所有doc的simhash值之后,需要计算doc A和doc B之间是否相似的条件是: A和B的海明距离是否小于等于n,这个n值根据经验一般取值为3, simhash本质上是局部敏感性的hash,和md5之类的不一样。 正因为它的局部敏感性,所以我们可以使用海明距离来衡量simhash值的相似度。 由上式这个函数来计算的话,时间复杂度是 O(n); 这里的n默认取值为3。由此可见还是蛮高效的。 百度的去重算法最简单,就是直接找出此文章的最长的n句话,做一遍hash签名。n一般取3。 工程实现巨简单,据说准确率和召回率都能到达80%以上。 shingle原理略复杂,不细说。 shingle算法我认为过于学院派,对于工程实现不够友好,速度太慢,基本上无法处理海量数据。 Python的代码实现如下: Java的代码如下如下: C++的一个大数类如下:C++竟然没有标准的大数类,蛋疼。 https://github.com/CertiVox/MIRACL 原理
simhash值的生成图解如下:
(feature, weight)们。 记为 feature_weight_pairs = [fw1, fw2 ... fwn],其中 fwn = (feature_n, weight_n)。hash_weight_pairs = [ (hash(feature), weight) for feature, weight in feature_weight_pairs ] 生成图中的(hash,weight)们, 此时假设hash生成的位数bits_count = 6(如图);hash_weight_pairs 进行位的纵向累加,如果该位是1,则+weight,如果是0,则-weight,最后生成bits_count个数字,如图所示是[13, 108, -22, -5, -32, 55], 这里产生的值和hash函数所用的算法相关。[13,108,-22,-5,-32,55] -> 110001这个就很简单啦,正1负0。 simhash值的海明距离计算
A xor B 后二进制中1的个数。A = 100111;
B = 101010;
hamming_distance(A, B) = count_1(A xor B) = count_1(001101) = 3;
高效计算二进制序列中1的个数
/* src/Simhasher.hpp */
bool isEqual(uint64_t lhs, uint64_t rhs, unsigned short n = 3)
{
unsigned short cnt = 0;
lhs ^= rhs;
while(lhs && cnt <= n)
{
lhs &= lhs - 1;
cnt++;
}
if(cnt <= n)
{
return true;
}
return false;
}
对比其他算法
百度的去重算法
shingle算法
参考
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
# coding=utf-8
class simhash:
#构造函数
def
__init__(self, tokens=
'', hashbits=
128):
self.hashbits = hashbits
self.
hash = self.simhash(tokens);
#toString函数
def
__str__(self):
return
str(self.
hash)
#生成simhash值
def simhash(self, tokens):
v = [
0] * self.hashbits
for t
in [self._string_hash(x)
for x
in tokens]:
#t为token的普通hash值
for i
in
range(self.hashbits):
bitmask =
1 << i
if t & bitmask :
v[i] +=
1
#查看当前bit位是否为1,是的话将该位+1
else:
v[i] -=
1
#否则的话,该位-1
fingerprint =
0
for i
in
range(self.hashbits):
if v[i] >=
0:
fingerprint +=
1 << i
return fingerprint
#整个文档的fingerprint为最终各个位>=0的和
#求海明距离
def hamming_distance(self, other):
x = (self.
hash ^ other.
hash) & ((
1 << self.hashbits) -
1)
tot =
0;
while x :
tot +=
1
x &= x -
1
return tot
#求相似度
def similarity (self, other):
a =
float(self.
hash)
b =
float(other.
hash)
if a > b :
return b / a
else:
return a / b
#针对source生成hash值 (一个可变长度版本的Python的内置散列)
def _string_hash(self, source):
if source ==
"":
return
0
else:
x =
ord(source[
0]) <<
7
m =
1000003
mask =
2 ** self.hashbits -
1
for c
in source:
x = ((x * m) ^
ord(c)) & mask
x ^=
len(source)
if x == -
1:
x = -
2
return x
if __name__ ==
'__main__':
s =
'This is a test string for testing'
hash1 = simhash(s.
split())
s =
'This is a test string for testing also'
hash2 = simhash(s.
split())
s =
'nai nai ge xiong cao'
hash3 = simhash(s.
split())
print(hash1.hamming_distance(hash2) ,
" " , hash1.similarity(hash2))
print(hash1.hamming_distance(hash3) ,
" " , hash1.similarity(hash3))
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
import java.util.StringTokenizer;
public
class SimHash
{
private
String tokens;
private BigInteger strSimHash;
private
int hashbits =
128;
public SimHash(
String tokens)
{
this.tokens = tokens;
this.strSimHash =
this.simHash();
}
public SimHash(
String tokens,
int hashbits)
{
this.tokens = tokens;
this.hashbits = hashbits;
this.strSimHash =
this.simHash();
}
public BigInteger simHash()
{
int[] v =
new
int[
this.hashbits];
StringTokenizer stringTokens =
new StringTokenizer(
this.tokens);
while (stringTokens.hasMoreTokens())
{
String temp = stringTokens.nextToken();
BigInteger t =
this.hash(temp);
for (
int i =
0; i <
this.hashbits; i++)
{
BigInteger bitmask =
new BigInteger(
"1").shiftLeft(i);
if (t.and(bitmask).signum() !=
0)
{
v[i] +=
1;
}
else
{
v[i] -=
1;
}
}
}
BigInteger fingerprint =
new BigInteger(
"0");
for (
int i =
0; i <
this.hashbits; i++)
{
if (v[i] >=
0)
{
fingerprint = fingerprint.add(
new BigInteger(
"1").shiftLeft(i));
}
}
return fingerprint;
}
private BigInteger hash(
String source)
{
if (source == null || source.length() ==
0)
{
return
new BigInteger(
"0");
}
else
{
char[] sourceArray = source.toCharArray();
BigInteger x = BigInteger.valueOf(((
long) sourceArray[
0]) <<
7);
BigInteger m =
new BigInteger(
"1000003");
BigInteger mask =
new BigInteger(
"2").pow(
this.hashbits).subtract(
new BigInteger(
"1"));
for (
char item : sourceArray)
{
BigInteger temp = BigInteger.valueOf((
long) item);
x = x.multiply(m).xor(temp).and(mask);
}
x = x.xor(
new BigInteger(
String.valueOf(source.length())));
if (x.equals(
new BigInteger(
"-1")))
{
x =
new BigInteger(
"-2");
}
return x;
}
}
public
int hammingDistance(SimHash other)
{
BigInteger m =
new BigInteger(
"1").shiftLeft(
this.hashbits).subtract(
new BigInteger(
"1"));
BigInteger x =
this.strSimHash.xor(other.strSimHash).and(m);
int tot =
0;
while (x.signum() !=
0)
{
tot +=
1;
x = x.and(x.subtract(
new BigInteger(
"1")));
}
return tot;
}
public
static
void main(
String[] args)
{
String s =
"This is a test string for testing";
SimHash hash1 =
new SimHash(s,
128);
System.out.println(hash1.strSimHash +
" " + hash1.strSimHash.bitLength());
s =
"This is a test string for testing also";
SimHash hash2 =
new SimHash(s,
128);
System.out.println(hash2.strSimHash +
" " + hash2.strSimHash.bitCount());
s =
"This is a test string for testing als";
SimHash hash3 =
new SimHash(s,
128);
System.out.println(hash3.strSimHash +
" " + hash3.strSimHash.bitCount());
System.out.println(
"============================");
System.out.println(hash1.hammingDistance(hash2));
System.out.println(hash1.hammingDistance(hash3));
}
}
另外说明,位运算只适合整数哦。。。因为浮点的存储方案决定不能位运算,如果非要位运算,就需要Float.floatToIntBits,运算完,再通过Float.intBitsToFloat转化回去。(java默认的float,double的hashcode其实就是对应的floatToIntBits的int值)