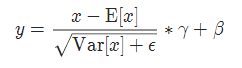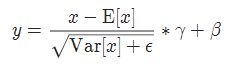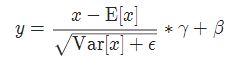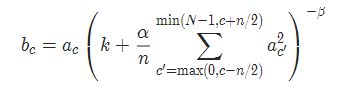PyTorch学习之归一化层(BatchNorm、LayerNorm、InstanceNorm、GroupNorm)
原文:https://blog.csdn.net/shanglianlm/article/details/85075706
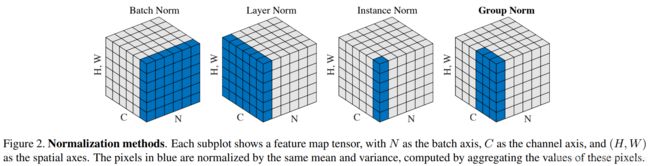
BN,LN,IN,GN从学术化上解释差异:
BatchNorm:batch方向做归一化,算NHW的均值,对小batchsize效果不好;BN主要缺点是对batchsize的大小比较敏感,由于每次计算均值和方差是在一个batch上,所以如果batchsize太小,则计算的均值、方差不足以代表整个数据分布
LayerNorm:channel方向做归一化,算CHW的均值,主要对RNN作用明显;
InstanceNorm:一个channel内做归一化,算H*W的均值,用在风格化迁移;因为在图像风格化中,生成结果主要依赖于某个图像实例,所以对整个batch归一化不适合图像风格化中,因而对HW做归一化。可以加速模型收敛,并且保持每个图像实例之间的独立。
GroupNorm:将channel方向分group,然后每个group内做归一化,算(C//G)HW的均值;这样与batchsize无关,不受其约束。
SwitchableNorm是将BN、LN、IN结合,赋予权重,让网络自己去学习归一化层应该使用什么方法。
目录
1 BatchNorm
2 GroupNorm
3 InstanceNorm
4 LayerNorm
5 LocalResponseNorm
1 BatchNorm
-
torch.nn.BatchNorm1d(num_features, eps=
1e-05, momentum=
0.1, affine=
True, track_running_stats=
True)
-
torch.nn.BatchNorm2d(num_features, eps=
1e-05, momentum=
0.1, affine=
True, track_running_stats=
True)
-
torch.nn.BatchNorm3d(num_features, eps=
1e-05, momentum=
0.1, affine=
True, track_running_stats=
True)
参数:
- num_features: 来自期望输入的特征数,该期望输入的大小为’batch_size x num_features [x width]’
- eps: 为保证数值稳定性(分母不能趋近或取0),给分母加上的值。默认为1e-5。
- momentum: 动态均值和动态方差所使用的动量。默认为0.1。
- affine: 布尔值,当设为true,给该层添加可学习的仿射变换参数。
- track_running_stats:布尔值,当设为true,记录训练过程中的均值和方差;
实现公式:
2 GroupNorm
torch.nn.GroupNorm(num_groups, num_channels, eps=1e-05, affine=True)
参数:
- num_groups:需要划分为的groups
- num_features: 来自期望输入的特征数,该期望输入的大小为’batch_size x num_features [x width]’
- eps: 为保证数值稳定性(分母不能趋近或取0),给分母加上的值。默认为1e-5。
- momentum: 动态均值和动态方差所使用的动量。默认为0.1。
- affine: 布尔值,当设为true,给该层添加可学习的仿射变换参数。
实现公式:
3 InstanceNorm
-
torch.nn.InstanceNorm1d(num_features, eps=
1e-05, momentum=
0.1, affine=
False, track_running_stats=
False)
-
torch.nn.InstanceNorm2d(num_features, eps=
1e-05, momentum=
0.1, affine=
False, track_running_stats=
False)
-
torch.nn.InstanceNorm3d(num_features, eps=
1e-05, momentum=
0.1, affine=
False, track_running_stats=
False)
参数:
- num_features: 来自期望输入的特征数,该期望输入的大小为’batch_size x num_features [x width]’
- eps: 为保证数值稳定性(分母不能趋近或取0),给分母加上的值。默认为1e-5。
- momentum: 动态均值和动态方差所使用的动量。默认为0.1。
- affine: 布尔值,当设为true,给该层添加可学习的仿射变换参数。
- track_running_stats:布尔值,当设为true,记录训练过程中的均值和方差;
实现公式:
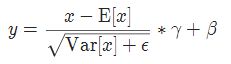
4 LayerNorm
torch.nn.LayerNorm(normalized_shape, eps=1e-05, elementwise_affine=True)
参数:
- normalized_shape: 输入尺寸
[∗×normalized_shape[0]×normalized_shape[1]×…×normalized_shape[−1]]
- eps: 为保证数值稳定性(分母不能趋近或取0),给分母加上的值。默认为1e-5。
- elementwise_affine: 布尔值,当设为true,给该层添加可学习的仿射变换参数。
实现公式:
5 LocalResponseNorm
torch.nn.LocalResponseNorm(size, alpha=0.0001, beta=0.75, k=1.0)
参数:
- size:用于归一化的邻居通道数
- alpha:乘积因子,Default: 0.0001
- beta :指数,Default: 0.75
- k:附加因子,Default: 1