机器学习实战笔记——KNN算法
KNN算法是监督学习分类方法。何为监督学习?我们用来训练的数据集应当包括数据特征和标签两个部分,通过训练建立数据特征和标签之间关系的算法模型,这样的话,将测试数据集套用算法模型,可以得到测试数据的标签。
一 KNN算法原理
在训练样本集中每个数据都存在标签,即我们知道样本集中每一数据与所属分类的对应关系。输人没有标签的新数据后,将新数据的每个特征与样本集中数据对应的特征进行比较,然后算法提取样本集中特征最相似数据(最近邻)的分类标签。选择k个最相似数据中出现次数最多的分类,作为新数据的分类。在KNN中,通过计算对象间距离作为各个对象之间的相似性指标,代替对象之间的匹配度计算。
对于训练样本数为m,特征数为n的训练样本集,计算测试样本x与m个训练样本的欧氏距离
其中i=1,2,……,m。对d(x,yi)进行降序排列,选择前k个值,出现次数最多的分类作为测试样本x的分类。
形象地理解,将训练样本和测试样本投影到n维空间上,以某个测试样本为中心,距离其最近的k个训练样本点采用投票原则,投出该训练样本的标签。
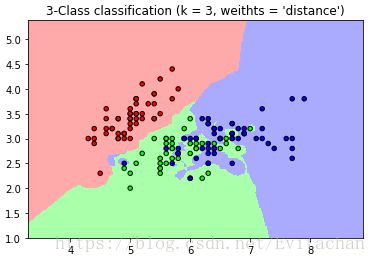
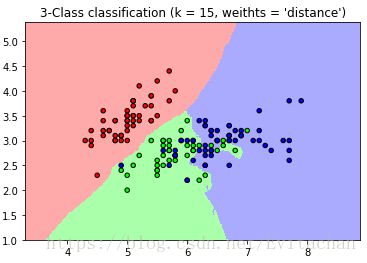
由此可见,k值的选择会影响到标签的决策。以iris数据集为例。
数据集中共150个样本点,四个特征,为了绘制散点图,选取前两个特征进行分类。
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from sklearn import neighbors
# import some data to play with
from sklearn import datasets
iris = datasets.load_iris()
# only take the first two features.
# we could avoid this ugly slicing by using a two-dim dataset
x = iris.data[:, :2]
y = iris.target
# k
n_neighbors = 3
# create color maps
from matplotlib.colors import ListedColormap
cmap_light = ListedColormap(['#FFAAAA', '#AAFFAA', '#AAAAFF'])
cmap_bold = ListedColormap(['#FF0000', '#00FF00', '#0000FF'])
# knn
n_neighbors = 3
for weights in ['uniform', 'distance']:
# we create an instance of Neighbors classifier and fit the data
clf = neighbors.KNeighborsClassifier(n_neighbors, weights = weights)
clf.fit(x, y)
# plot the decision boundary.
# For that, we will assign a color to each point in the mesh[x_min, x_max] * [y_min, y_max]
x_min, x_max = x[:, 0].min() - 1, x[:, 0].max() + 1
y_min, y_max = x[:, 1].min() - 1, x[:, 1].max() + 1
xx, yy = np.meshgrid(np.arange(x_min, x_max, .02), np.arange(y_min, y_max, .02))
# predict
z = clf.predict(np.c_[xx.ravel(), yy.ravel()])
# put the result into a color plot
z = z.reshape(xx.shape)
plt.figure()
plt.pcolormesh(xx, yy, z, cmap = cmap_light)
# plot also the training points
plt.scatter(x[:, 0], x[:, 1], c = y, cmap = cmap_bold, edgecolor = 'k', s = 20)
plt.xlim(xx.min(), xx.max())
plt.ylim(yy.min(), yy.max())
plt.title("3-Class classification (k = %i, weithts = '%s')" % (n_neighbors, weights))
plt.show() 比较两个图,可以很明显看出,当k取值不同时,分类的效果不同。
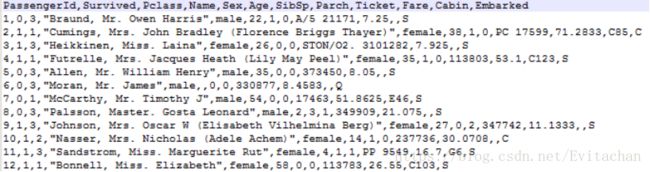
二 KNN算法预测泰坦尼克沉船遇难情况
原始数据有10个特征,选取特征:‘Pclass’,‘Sex’,‘Age’,‘SibSp’,‘Parch’ 5个作为决策树特征向量。
数据预处理
>训练集中共有891位乘客的数据信息,其中277位乘客的年龄数据缺失,余下数据年龄平均值为29.7,用30补全缺失项。
>性别男/女用1/0表示。from numpy import *
import operator
from os import listdir
def classify0(inX, dataSet, labels, k):
dataSetSize = dataSet.shape[0]
diffMat = tile(inX, (dataSetSize,1)) - dataSet
sqDiffMat = diffMat**2
sqDistances = sqDiffMat.sum(axis=1)
distances = sqDistances**0.5
sortedDistIndicies = distances.argsort()
classCount={}
for i in range(k):
voteIlabel = labels[sortedDistIndicies[i]]
classCount[voteIlabel] = classCount.get(voteIlabel,0) + 1
sortedClassCount = sorted(classCount.items(), key=operator.itemgetter(1), reverse=True)
return sortedClassCount[0][0]
def createDataSet():
group = array([[1.0,1.1],[1.0,1.0],[0,0],[0,0.1]])
labels = ['A','A','B','B']
return group, labels
def file2matrix(filename):
file = open(filename)
arraylines = file.readlines()
numberoflines = len(arraylines) - 1
returnMat = zeros((numberoflines,3)) #创建行数为numberoflines,列数为2的矩阵
classLabel = []
index = 0
for line in arraylines[1:]:
line = line.strip()
lis = line.split(' ')
returnMat[index,:] = lis[0:3]
classLabel.append(int(lis[-1])) #是为1类,否为0类
index += 1
return returnMat,classLabel
def autoNorm(dataSet):
minVals = dataSet.min(0)
maxVals = dataSet.max(0)
ranges = maxVals - minVals
normDataSet = zeros(shape(dataSet))
m = dataSet.shape[0]
normDataSet = dataSet - tile(minVals, (m,1))
normDataSet = normDataSet/tile(ranges, (m,1)) #element wise divide
return normDataSet, ranges, minVals
def datingClassTest():
hoRatio = 0.1 #hold out 10%
datingDataMat,datingLabels = file2matrix('datingTestSet2.txt')
normMat, ranges, minVals = autoNorm(datingDataMat)
m = normMat.shape[0]
numTestVecs = int(m*hoRatio)
errorCount = 0.0
for i in range(numTestVecs):
classifierResult = classify0(normMat[i,:],normMat[numTestVecs:m,:],\
datingLabels[numTestVecs:m],3)
str= "the classifier came back with: %d, the real answer is: %d"\
% (classifierResult, datingLabels[i])
print(str)
if (classifierResult != datingLabels[i]): errorCount += 1.0
str= "the total error rate is: %f" % (errorCount/float(numTestVecs))
print(str)使用交叉验证方法,选取一定比例数据作为测试集,比较利用KNN算法分类所得标签与真实标签结果是否一致,若不一致,则错误样本数加一。最终利用错误样本数除以总验证样本数得到错误率。
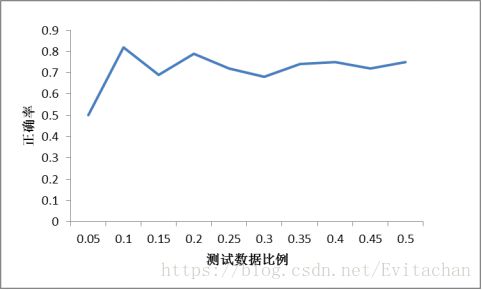
经验证,测试数据比例与正确率关系如下。在选取10%数据作为测试数据时分类效果最好,这与最常用的十折交叉验证相符合。
三 总结
1. 在选取10%数据作为测试数据时分类效果最好,这与最常用的十折交叉验证相符合。
2. k值选择过大或过小都会影响正确率,在使用KNN模型时,我们需要不断调整k值,直到找到局部最优解,这也是KNN算法需要解决的问题。