嵌入式Linux驱动笔记(二十五)------Input子系统框架
你好!这里是风筝的博客,
欢迎和我一起交流。
- 一、Input子系统概述
- 二、Input子系统架构
- 三、Input子系统工作机制
- 3.1 核心层(input.c)
- 3.1.1 input_init函数
- 3.1.2 input_dev结构体
- 3.1.3 input_handler结构体
- 3.1.4 input_handle结构体
- 3.1.5 三者结构体关系
- 3.2事件处理层(evdev.c、joydev.c、mousedev.c、input-polldev.c等)
- 3.2.1 input_register_handler函数
- 3.2.2 input_attach_handler函数
- 3.2.3 evdev_connect函数
- 3.2.4 evdev结构体
- 3.2.5 input_register_handle函数
- 3.3设备驱动层(sunxi-keyboard.c)
- 3.3.1 input_allocate_device函数
- 3.3.2 input_register_device函数
- 3.4 上报事件
- 3.4.1 input_pass_values函数
- 3.4.2 evdev_event函数
- 3.4.3 evdev_pass_values函数
- 3.4.4 __pass_event函数
- 3.5 用户空间读取
- 3.5.1 evdev_client结构体
- 3.5.2 evdev_open函数
- 3.5.3 evdev_read函数
- 3.1 核心层(input.c)
- 四、Input子系统整体流程
写在前面的话:
以前也写过一篇关于input的文章,但是当时刚学不就,自己也描述的不好,最近在整理,就参考了大量资料重新发布了这篇文章。
一、Input子系统概述
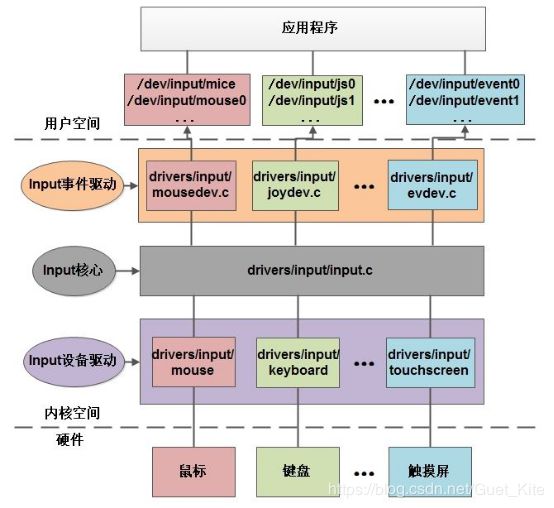
在我们日常的Linux系统中,存在大量的输入设备,例如按键、鼠标、键盘、触摸屏、摇杆等,他们本身就是字符设备,linux内核将这些字符设备的共同性抽象出来,简化驱动开发建立了一个input子系统。二、Input子系统架构
我们知道,Linux 内核驱动可以都是遵循一个逐层抽象的架构: 最上层的抽象层便于系统软件的访问,中间层的实现硬件协议细节,同时提供上下两层连接的接口,对于最下层的 driver 来说就是要定义底层驱动要实现的接口和实际的设备控制,由于 Linux 内核各类驱动的框架支持,driver 可以更加关注设备本身的特性。Linux输入子系统(linux input subsystem)也不例外,从上到下可以分为三层实现,分别为:输入子系统事件处理层(EventHandler)、输入子系统核心层(InputCore)和输入子系统设备驱动层。
事件处理层:接收来自核心层上报的事件,并选择对应的handler(处理程序)去处理。
核心层:负责连接设备驱动层和事件处理层,为设备驱动层提供输入设备驱动的接口(struct input_dev)以及输入设备驱动的注册函数(input_register_device),为事件处理层提供输入事件驱动的接口(struct input_event),还有输入设备驱动的注册函数(input_register_device);通知事件处理层对事件进行处理。
设备驱动层:主要实现对硬件设备的读写访问,来获取硬件设备的数据信息(包括触摸屏被按下、按下位置、鼠标移动、键盘按下等等),并转换为核心层定义的规范后提交给核心层。
三、Input子系统工作机制
3.1 核心层(input.c)
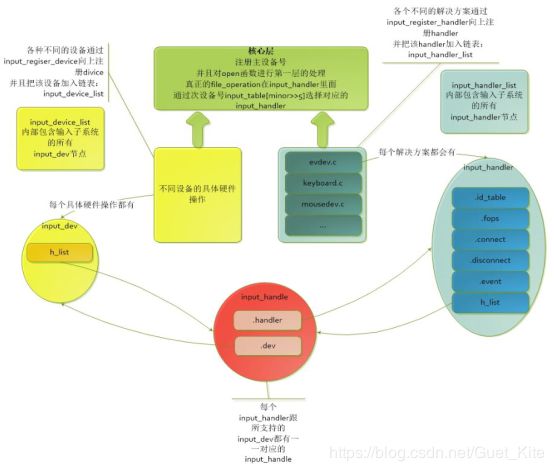
核心层主要实现了大量提供给事件处理层和设备驱动层的接口,Input core的实现代码主要位于driver/input/input.c和include/linux/input.h这两个文件中。3.1.1 input_init函数
输入子系统作为一个模块存在,通过input_init()初始化函数进行初始化。 初始化的工作主要做了: (1)创建一个input_class类,在sysfs中的表现为所有input device都位于/dev/class/input下。 (2)在/proc下创建入口项,即/proc/bus/input目录产生设备信息. (3)注册字符设备input,主设备号为13(#define INPUT_MAJOR13)3.1.2 input_dev结构体
结构体位于include/linux/input.h,属于设备驱动层。每个input_dev都都代表着一个input设备。设备注册的时候会将input_dev链接到input_dev_list这个全局链表里。struct input_dev {
const char *name; //设备的名字
const char *phys; //设备在系统中的物理路径
const char *uniq; //设备的唯一标识名
struct input_id id; //设备ID,与input_handler匹配时会用到。子系统核心是通过他们,将设备驱动与事件处理层联系起来的
/*
struct input_id {
__u16 bustype; //总线类型
__u16 vendor; //生产厂商
__u16 product; //产品类型
__u16 version; //版本
};
*/
unsigned long propbit[BITS_TO_LONGS(INPUT_PROP_CNT)];//设备性质
unsigned long evbit[BITS_TO_LONGS(EV_CNT)]; //设备支持的事件类型
unsigned long keybit[BITS_TO_LONGS(KEY_CNT)];//按键事件:支持的具体按键
unsigned long relbit[BITS_TO_LONGS(REL_CNT)];//相对坐标:具体的相对坐标
unsigned long absbit[BITS_TO_LONGS(ABS_CNT)];//绝对坐标:具体的绝对坐标
unsigned long mscbit[BITS_TO_LONGS(MSC_CNT)];//混杂事件:具体的混杂事件
unsigned long ledbit[BITS_TO_LONGS(LED_CNT)]; //LED事件:具体的动作
unsigned long sndbit[BITS_TO_LONGS(SND_CNT)]; //蜂鸣器事件:具体的动作
unsigned long ffbit[BITS_TO_LONGS(FF_CNT)]; //力反馈事件:具体的动作
unsigned long swbit[BITS_TO_LONGS(SW_CNT)]; //开关事件:具体的动作
unsigned int hint_events_per_packet;
unsigned int keycodemax; //设备支持的最大按键值个数
unsigned int keycodesize; //每个按键的字节大小
void *keycode; //设备的键盘码表
int (*setkeycode)(struct input_dev *dev, //修改键盘码表
const struct input_keymap_entry *ke,
unsigned int *old_keycode);
int (*getkeycode)(struct input_dev *dev, //获取键盘码表
struct input_keymap_entry *ke);
struct ff_device *ff; //如果设备支持力反馈,则该成员将指向力反馈的设备描述结构
unsigned int repeat_key; //保存上一个键值,实现软件自动重复按键
struct timer_list timer; //用于软件自动重复按键的定时器
int rep[REP_CNT]; //记录重复按键的参数值
struct input_mt *mt;
struct input_absinfo *absinfo;
unsigned long key[BITS_TO_LONGS(KEY_CNT)];//反映设备按键按钮的当前状态
unsigned long led[BITS_TO_LONGS(LED_CNT)];//反映设备LED的当前状态
unsigned long snd[BITS_TO_LONGS(SND_CNT)];//反映设备蜂鸣器的当前状态
unsigned long sw[BITS_TO_LONGS(SW_CNT)];//反映设备开关的当前状态
int (*open)(struct input_dev *dev);//输入设备打开函数
void (*close)(struct input_dev *dev);
int (*flush)(struct input_dev *dev, struct file *file);
int (*event)(struct input_dev *dev, unsigned int type, unsigned int code, int value);//发送给事件层handler去处理
struct input_handle __rcu *grab;//类似私有指针,可以直接访问到事件处理接口event
spinlock_t event_lock;
struct mutex mutex;
unsigned int users;
bool going_away;
struct device dev;
struct list_head h_list; //handle的链表
struct list_head node; //通过这个结点,将dev挂到input_dev_list上
unsigned int num_vals;
unsigned int max_vals;
struct input_value *vals;
bool devres_managed;
};
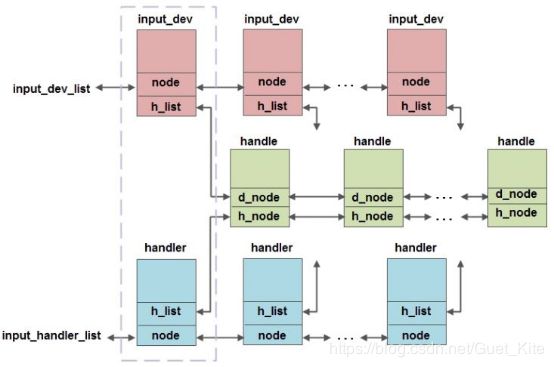
3.1.3 input_handler结构体
结构体位于include/linux/input.h,属于事件处理层。对于不同的handler,都包含有一个名为input_handler的结构体。一个handler就是一个解决方案。事件处理器注册的时候会将它链接到input_handler_list这个全局链表里。struct input_handler {
void *private;
void (*event)(struct input_handle *handle, unsigned int type, unsigned int code, int value);//事件处理函数,让device调用
void (*events)(struct input_handle *handle,
const struct input_value *vals, unsigned int count);
bool (*filter)(struct input_handle *handle, unsigned int type, unsigned int code, int value);
bool (*match)(struct input_handler *handler, struct input_dev *dev);//在将device的id与handler的id_table进行比较之后调用
int (*connect)(struct input_handler *handler, struct input_dev *dev, const struct input_device_id *id);//设备连接
void (*disconnect)(struct input_handle *handle);//断开该连接
void (*start)(struct input_handle *handle);
bool legacy_minors;
int minor;
const char *name;
const struct input_device_id *id_table;//handler支持项,用于匹配设备驱动的数组
struct list_head h_list;//handle的h_node就是挂在input_handler这里的h_list
struct list_head node;//挂在链表input_handler_list上
};
3.1.4 input_handle结构体
结构体位于include/linux/input.h,属于核心层。每一个input_handle结构体就代表一对成功匹配的input_dev和input_handler。它注册的时候将自己分别挂在input_dev和input_handler的h_list上。struct input_handle {
void *private;//表示handler的特定数据
int open;//表示handler的特定数据
const char *name;//表示handler的特定数据
struct input_dev *dev;//与handle相连的input_dev
struct input_handler *handler;//与handle相连的input_handler
struct list_head d_node;//handle结构体的该节点将与input_dev相连
struct list_head h_node;//handle结构体的该节点将与input_handler相连
};
3.1.5 三者结构体关系
input子系统维护两条全局的链表input_dev_list和input_handler_list,每当调用input_register_device函数时会将Input设备加入到input_dev_list链表的尾部;每当调用input_register_handler函数时会将handler加入到input_handler_list链表的尾部;每当调用input_register_handle函数时会将handle加入到其对应的Input设备的h_list链表的尾部,并且还会该handle加入到其对应的handler的h_list链表的尾部。
3.2事件处理层(evdev.c、joydev.c、mousedev.c、input-polldev.c等)
事件处理程序负责和应用程序的接口,事件处理层包含:通用事件处理器(evdev)、鼠标事件处理器(mousedev)、摇杆事件处理器(joydev)等,每个事件处理器也都实例化了input_handler对象:evdev_handler、mousedev_handler、joydev_handler等。在input子系统中,输入事件驱动是标准的,对所有的输入类都是可以用的,所以我们也不会去开发输入事件驱动,我们更可能的是去利用已存在的输入事件驱动,把事件反馈到相应的设备文件中来。 事件处理层的函数调用非常简单,当需要加入新的handler时,需要先构建input_handler结构体,然后调用input_register_handler对该handler进行注册。 以通用事件处理层来解析,代码放在driver/input/evdev.c:
每个handler都会实例化一个input_handler:
static struct input_handler evdev_handler = {
.event = evdev_event,
.events = evdev_events,
.connect = evdev_connect,
.disconnect = evdev_disconnect,
.legacy_minors = true,
.minor = EVDEV_MINOR_BASE,
.name = "evdev",
.id_table = evdev_ids,
};
3.2.1 input_register_handler函数
int input_register_handler(struct input_handler *handler)
{
struct input_dev *dev;
int error;
error = mutex_lock_interruptible(&input_mutex);
if (error)
return error;
INIT_LIST_HEAD(&handler->h_list);//初始化handler结构体的h_list
list_add_tail(&handler->node, &input_handler_list);//将它挂在input_handler_list全局链表上
list_for_each_entry(dev, &input_dev_list, node)//遍历全局链表input_dev_list
input_attach_handler(dev, handler);//连接匹配的双方
input_wakeup_procfs_readers();
mutex_unlock(&input_mutex);
return 0;
}
3.2.2 input_attach_handler函数
static int input_attach_handler(struct input_dev *dev, struct input_handler *handler)
{
const struct input_device_id *id;
int error;
id = input_match_device(handler, dev); //两边开始匹配
if (!id)
return -ENODEV;
error = handler->connect(handler, dev, id); //调用handler的connect,关键之处
if (error && error != -ENODEV)
pr_err("failed to attach handler %s to device %s, error: %d\n",
handler->name, kobject_name(&dev->dev.kobj), error);
return error;
}
函数里会开始match,通过input_handler结构体的id_table字段匹配,确认过眼神,寻找对的“人”。对于evdev来分析:
static const struct input_device_id evdev_ids[] = {
{ .driver_info = 1 }, /* Matches all devices */
{ }, /* Terminating zero entry */
};
Evdev作为通用的handler,会和所有的device match。
最后即调用evdev的connect函数:evdev_connect->input_register_handle
3.2.3 evdev_connect函数
static int evdev_connect(struct input_handler *handler, struct input_dev *dev,
const struct input_device_id *id)
{
minor = input_get_new_minor(EVDEV_MINOR_BASE, EVDEV_MINORS, true);//索引值
if (minor < 0) {
error = minor;
pr_err("failed to reserve new minor: %d\n", error);
return error;
evdev = kzalloc(sizeof(struct evdev), GFP_KERNEL);//分配结构体空间
if (!evdev) {
error = -ENOMEM;
goto err_free_minor;
}
INIT_LIST_HEAD(&evdev->client_list);
spin_lock_init(&evdev->client_lock);
mutex_init(&evdev->mutex);
init_waitqueue_head(&evdev->wait);//初始化等待队列waitqueue
evdev->exist = true;
dev_no = minor;
if (dev_no < EVDEV_MINOR_BASE + EVDEV_MINORS)
dev_no -= EVDEV_MINOR_BASE;
dev_set_name(&evdev->dev, "event%d", dev_no);
evdev->handle.dev = input_get_device(dev);//得到input_dev
evdev->handle.name = dev_name(&evdev->dev);
evdev->handle.handler = handler;//得到input_handler
evdev->handle.private = evdev;
evdev->dev.devt = MKDEV(INPUT_MAJOR, minor);
evdev->dev.class = &input_class;//得到class
evdev->dev.parent = &dev->dev;
evdev->dev.release = evdev_free;
device_initialize(&evdev->dev);
error = input_register_handle(&evdev->handle);//注册input_handle
if (error)
goto err_free_evdev;
cdev_init(&evdev->cdev, &evdev_fops);//文件操作
evdev->cdev.kobj.parent = &evdev->dev.kobj;
error = cdev_add(&evdev->cdev, evdev->dev.devt, 1);//对应设备文件为/class/input/event(dev_no)。
if (error)
goto err_unregister_handle;
error = device_add(&evdev->dev);
if (error)
goto err_cleanup_evdev;
return 0;
}
如触摸屏驱动的event0,这个设备是用户空间要访问的设备,可以理解它是一个虚拟设备,因为没有对应的硬件,但是通过handle->dev 就可以找到input_dev结构,而它对应着触摸屏,设备文件为/class/input/input0。这个设备索引值是minor。
3.2.4 evdev结构体
struct evdev {
int open;//打开标志
struct input_handle handle;//关联的input_handle
wait_queue_head_t wait;//等待队列,当进程读取设备,而没有事件产生的时候,进程就会睡在其上面
struct evdev_client __rcu *grab;//强制绑定的evdev_client结构
struct list_head client_list;//evdev_client 链表,这说明一个evdev设备可以处理多个evdev_client,可以有多个进程访问evdev设备
spinlock_t client_lock; /* protects client_list */
struct mutex mutex;
struct device dev;//device结构,说明这是一个设备结构
struct cdev cdev;
bool exist;
};
evdev结构体在配对成功的时候生成,由handler->connect生成,对应设备文件为sys/class/input/event(n)。
注:需要注意evdev结构体------->sys/class/input/event(n)。input_dev结构-------->sys/class/input/input(n)
3.2.5 input_register_handle函数
注册一个新的input_handle,代表一对input_dev和input_handler匹配了。int input_register_handle(struct input_handle *handle)
{
struct input_handler *handler = handle->handler;
struct input_dev *dev = handle->dev;
int error;
error = mutex_lock_interruptible(&dev->mutex);
if (error)
return error;
if (handler->filter)
list_add_rcu(&handle->d_node, &dev->h_list);//将handle的d_node,链接到其相关的input_dev的h_list链表中
else
list_add_tail_rcu(&handle->d_node, &dev->h_list);
mutex_unlock(&dev->mutex);
list_add_tail_rcu(&handle->h_node, &handler->h_list);//将handle的h_node,链接到其相关的input_handler的h_list链表中
if (handler->start)
handler->start(handle);
return 0;
}
3.3设备驱动层(sunxi-keyboard.c)
设备驱动程序负责和底层输入设备的通信,一个输入事件,如按键,是通过驱动层到系统核心层到事件处理层到用户空间的顺序到达用户空间并传给应用程序使用。事件驱动程序是标准的,对所有的输入设备都是可用的,所以要实现的是设备驱动程序而不是事件驱动程序。 在输入子系统框架下,我们一般的编写驱动也就是对device部分进行编写,当需要加入新的device时,需要先构建input_dev结构体,然后设置支持的事件、中断等参数,最后调用input_register_device对该input_dev进行注册。static int sunxi_keyboard_probe(struct platform_device *pdev)
{
static struct input_dev *sunxikbd_dev;//input_dev结构体
struct sunxi_key_data *key_data;
key_data = kzalloc(sizeof(*key_data), GFP_KERNEL);
if (IS_ERR_OR_NULL(key_data)) {
pr_err("key_data: not enough memory for key data\n");
return -ENOMEM;
if (sunxikbd_key_init(key_data, pdev)) {
err = -EFAULT;
goto fail1;
}
sunxikbd_dev = input_allocate_device();//分配空间
if (!sunxikbd_dev) {
pr_err("sunxikbd: not enough memory for input device\n");
err = -ENOMEM;
goto fail1;
}
sunxikbd_dev->name = INPUT_DEV_NAME;
sunxikbd_dev->phys = "sunxikbd/input0";
sunxikbd_dev->id.bustype = BUS_HOST;//总线类型
sunxikbd_dev->id.vendor = 0x0001;//生产厂商
sunxikbd_dev->id.product = 0x0001;//产品类型
sunxikbd_dev->id.version = 0x0100;//版本
#ifdef REPORT_REPEAT_KEY_BY_INPUT_CORE
sunxikbd_dev->evbit[0] = BIT_MASK(EV_KEY)|BIT_MASK(EV_REP);//支持的事件
pr_info("support report repeat key value.\n");
#else
sunxikbd_dev->evbit[0] = BIT_MASK(EV_KEY);
#endif
for (i = 0; i < KEY_MAX_CNT; i++)
set_bit(key_data->scankeycodes[i], sunxikbd_dev->keybit);
key_data->input_dev = sunxikbd_dev;
platform_set_drvdata(pdev, key_data);
if (request_irq(key_data->irq_num, sunxi_isr_key, 0,//中断设置
"sunxikbd", key_data)) {
err = -EBUSY;
pr_err("request irq failure.\n");
goto fail2;
}
err = input_register_device(key_data->input_dev);
if (err)
goto fail3;
pr_debug("sunxikbd_init end\n");
return 0;
}
常用的事件类型有:
#define EV_SYN 0x00 //同步事件
#define EV_KEY 0x01 //按键事件
#define EV_REL 0x02 //相对坐标(如:鼠标移动,报告相对最后一次位置的偏移)
#define EV_ABS 0x03 //绝对坐标(如:触摸屏或操作杆,报告绝对的坐标位置)
#define EV_MSC 0x04 //其它
#define EV_SW 0x05 //开关
#define EV_LED 0x11 //按键/设备灯
#define EV_SND 0x12 //声音/警报
#define EV_REP 0x14 //重复
#define EV_FF 0x15 //力反馈
#define EV_PWR 0x16 //电源
#define EV_FF_STATUS 0x17 //力反馈状态
#define EV_MAX 0x1f //事件类型最大个数和提供位掩码支持
#define EV_CNT (EV_MAX+1)
3.3.1 input_allocate_device函数
input_allocate_device函数在driver/input/input.c实现,主要是为构建新的input device分配内存空间,分配kobject,并指定为/sys/class跟sys/devices,以便后面再sysfs创建目录和文件节点,方便开发和调试,最后是初始化设备的handle链表和node。struct input_dev *input_allocate_device(void)
{
struct input_dev *dev;
dev = kzalloc(sizeof(struct input_dev), GFP_KERNEL);//为结构体分配内存
if (dev) {
dev->dev.type = &input_dev_type;// 设备类型
dev->dev.class = &input_class;// 设置生成在sys/class/input里面添加设备名文件
device_initialize(&dev->dev);//主要是指定kset(/sys/devices/)跟kobject_init
mutex_init(&dev->mutex);
spin_lock_init(&dev->event_lock);
INIT_LIST_HEAD(&dev->h_list);//初始化handle的链表
INIT_LIST_HEAD(&dev->node);//初始化node
__module_get(THIS_MODULE);
}
return dev;
}
3.3.2 input_register_device函数
input_register_device函数在driver/input/input.c实现,这样一个新的设备就诞生了。int input_register_device(struct input_dev *dev)
{
static atomic_t input_no = ATOMIC_INIT(0);//这个原子变量,代表总共注册的input设备,每注册一个加1,因为是静态变量,所以每次调用都不会清零的
__set_bit(EV_SYN, dev->evbit);//默认每个设备都支持同步事件类型
__clear_bit(KEY_RESERVED, dev->keybit);//按键保留事件动作不允许发给应用层
input_cleanse_bitmasks(dev);//确保没有选中支持的事件类型和动作都清零
init_timer(&dev->timer);//初始化定时器,用于软件连击按键
if (!dev->rep[REP_DELAY] && !dev->rep[REP_PERIOD]) {//没有设置默认的定时时间,则默认赋值
dev->timer.data = (long) dev;
dev->timer.function = input_repeat_key;
dev->rep[REP_DELAY] = 250;
dev->rep[REP_PERIOD] = 33;
}
if (!dev->getkeycode)//如果设备驱动没有设置自己获取键值的函数,系统默认
dev->getkeycode = input_default_getkeycode;
if (!dev->setkeycode)//如果设备驱动没有指定按键重置函数,系统默认
dev->setkeycode = input_default_setkeycode;
dev_set_name(&dev->dev,"input%ld",(unsignedlong)atomic_inc_return(&input_no) - 1);//设备名字为input0、input1等
error = device_add(&dev->dev);//device_add首先会调用kobject_add往sys/device添加相应的设备文件,然后再创建uevent 等各种文件和目录,接下来会调用 device_add_class_symlinks来sys/class/input相关的文件 软链接到sys/devices这里面的东西
list_add_tail(&dev->node, &input_dev_list);//将设备挂到input_dev_list链表上
list_for_each_entry(handler, &input_handler_list, node)//遍历input_handler_list链表
input_attach_handler(dev, handler);//然后调用input_attach_handler函数进行id匹配
}
在input_register_handler函数里,handler会去寻找input_dev去match,同理,在input_register_device函数里,input_dev也会去寻找input_handler来match,真是千里姻缘一线牵啊。
3.4 上报事件
输入事件的传递以input_event为基本单位:struct input_event {
struct timeval time; // 时间戳
__u16 type; // 事件总类型
__u16 code; // 事件子类型
__s32 value; // 事件值
};
设备驱动程序上报事件的函数有:
input_report_key//上报按键事件
input_report_rel//上报相对坐标事件
input_report_abs//上报绝对坐标事件
input_report_ff_status
input_report_switch
input_sync//上报完成后需要调用这些函数来通知系统处理完整事件
input_mt_sync//上报完成后需要调用这些函数来通知系统处理完整事件
这些函数其实是input_event函数的封装,调用的都是input_event函数,在输入设备驱动(input_dev)中,一般通过轮询或中断方式获取输入事件的原始值(raw value),经过处理后再使用input_event()函数上报;核心层将事件数据(type、code、value)打包、分发至事件处理器;
调用关系为:input_event->input_handle_event->input_pass_values,这一函数在input.c中实现。
3.4.1 input_pass_values函数
static void input_pass_values(struct input_dev *dev,
struct input_value *vals, unsigned int count)
{
struct input_handle *handle;
struct input_value *v;
if (!count)
return;
rcu_read_lock();
handle = rcu_dereference(dev->grab);//如果是绑定的handle,则调用绑定的handler->event函数
if (handle) {
count = input_to_handler(handle, vals, count);// 调用相关的事件处理器的event函数,进行事件的处理,即handler->event
} else {
list_for_each_entry_rcu(handle, &dev->h_list, d_node) //如果没有绑定,则遍历dev的h_list链表,寻找handle,如果handle已经打开,说明有进程读取设备关联的evdev
if (handle->open)
count = input_to_handler(handle, vals, count);// 调用相关的事件处理器的event函数,进行事件的处理,即handler->event
}
rcu_read_unlock();
add_input_randomness(vals->type, vals->code, vals->value);
}
函数最终就会调用到handler->event,对事件进行处理。
3.4.2 evdev_event函数
static void evdev_event(struct input_handle *handle,
unsigned int type, unsigned int code, int value)
{
struct input_value vals[] = { { type, code, value } };
evdev_events(handle, vals, 1);//count为1的evdev_events
}
函数调用关系为:evdev_event->evdev_events->evdev_pass_values
3.4.3 evdev_pass_values函数
static void evdev_pass_values(struct evdev_client *client,
const struct input_value *vals, unsigned int count,
ktime_t mono, ktime_t real)
{
struct evdev *evdev = client->evdev;
const struct input_value *v;
struct input_event event;//以input_event结构体为基本单位
bool wakeup = false;
event.time = ktime_to_timeval(client->clkid == CLOCK_MONOTONIC ?
mono : real);
/* Interrupts are disabled, just acquire the lock. */
spin_lock(&client->buffer_lock);
for (v = vals; v != vals + count; v++) {
event.type = v->type;//将传过来的事件,赋值给input_event结构
event.code = v->code;
event.value = v->value;
__pass_event(client, &event);//里面做消息传递
if (v->type == EV_SYN && v->code == SYN_REPORT)
wakeup = true;
}
spin_unlock(&client->buffer_lock);
if (wakeup)
wake_up_interruptible(&evdev->wait);//唤醒等待的进程
}
3.4.4 __pass_event函数
设备驱动上报事件并不是直接传递给用户程序,在通用事件处理器(evdev)中,事件被缓存在缓冲区中。__pass_event函数里会将input_event放到client结构结构体的环形缓冲区里,即evdev_client结构体的buffer,用户程序通过read()函数从环形缓冲区中获取input_event事件。static void __pass_event(struct evdev_client *client,
const struct input_event *event)
{
client->buffer[client->head++] = *event;//将事件赋值给客户端的input_event 缓冲区数组
client->head &= client->bufsize - 1;//队头head自增指向下一个元素空间
if (unlikely(client->head == client->tail)) {// 当队头head与队尾tail相等时,说明缓冲区空间已满
client->tail = (client->head - 2) & (client->bufsize - 1);
client->buffer[client->tail].time = event->time;
client->buffer[client->tail].type = EV_SYN;
client->buffer[client->tail].code = SYN_DROPPED;
client->buffer[client->tail].value = 0;
client->packet_head = client->tail;
if (client->use_wake_lock)
wake_unlock(&client->wake_lock);
}
// 当遇到EV_SYN/SYN_REPORT同步事件时,packet_head移动到队头head位置
if (event->type == EV_SYN && event->code == SYN_REPORT) {
client->packet_head = client->head;
if (client->use_wake_lock)
wake_lock(&client->wake_lock);
kill_fasync(&client->fasync, SIGIO, POLL_IN);
}
}
3.5 用户空间读取
在input_handler->connect函数里,会调用cdev_init(&evdev->cdev, &evdev_fops);static const struct file_operations evdev_fops = {
.owner = THIS_MODULE,
.read = evdev_read,
.write = evdev_write,
.poll = evdev_poll,
.open = evdev_open,
.release = evdev_release,
.unlocked_ioctl = evdev_ioctl,
#ifdef CONFIG_COMPAT
.compat_ioctl = evdev_ioctl_compat,
#endif
.fasync = evdev_fasync,
.flush = evdev_flush,
.llseek = no_llseek,
};
3.5.1 evdev_client结构体
struct evdev_client {
unsigned int head;//针对buffer数组的索引
unsigned int tail;//针对buffer数组的索引,当head与tail相等的时候,说明没有事件
unsigned int packet_head; /* [future] position of the first element of next packet */
spinlock_t buffer_lock; /* protects access to buffer, head and tail */
struct wake_lock wake_lock;
bool use_wake_lock;
char name[28];
struct fasync_struct *fasync;//异步通知函数
struct evdev *evdev;//evdev设备
struct list_head node;// evdev_client 链表项
int clkid;
unsigned int bufsize;
struct input_event buffer[];//这个是一个input_event数据结构的数组,input_event代表一个事件
};
这个结构在进程打开event0设备的时候调用evdev的open方法,在open中创建这个结构,并初始化。在关闭设备文件的时候释放这个结构。
3.5.2 evdev_open函数
static int evdev_open(struct inode *inode, struct file *file)
{
struct evdev *evdev = container_of(inode->i_cdev, struct evdev, cdev);
unsigned int bufsize = evdev_compute_buffer_size(evdev->handle.dev);// 1.计算环形缓冲区大小bufsize以及evdev_client对象大小size
unsigned int size = sizeof(struct evdev_client) +
bufsize * sizeof(struct input_event);
struct evdev_client *client;
int error;
client = kzalloc(size, GFP_KERNEL | __GFP_NOWARN);// 2. 分配内核空间
if (!client)
client = vzalloc(size);
if (!client)
return -ENOMEM;
client->bufsize = bufsize;
spin_lock_init(&client->buffer_lock);
snprintf(client->name, sizeof(client->name), "%s-%d",
dev_name(&evdev->dev), task_tgid_vnr(current));
client->evdev = evdev;
evdev_attach_client(evdev, client);// 3. 注册client到内核evdev->client_list链表
error = evdev_open_device(evdev);
if (error)
goto err_free_client;
file->private_data = client;
nonseekable_open(inode, file);
return 0;
}
在evdev_open()函数中,分配并注册了evdev_dev结构体,就可以使用client读取数据了。每个打开设备节点(/dev/input/eventN)的用户程序,在建立client连接的同时,也构建了自己的缓冲区用以获取事件,不同的client之间互不干涉。
3.5.3 evdev_read函数
static ssize_t evdev_read(struct file *file, char __user *buffer,
size_t count, loff_t *ppos)
{
struct evdev_client *client = file->private_data;
struct evdev *evdev = client->evdev;
struct input_event event;
size_t read = 0;
int error;
if (count != 0 && count < input_event_size())//长度至少要满足一个input_event的大小
return -EINVAL;
for (;;) {
if (!evdev->exist)
return -ENODEV;
if (client->packet_head == client->tail &&
(file->f_flags & O_NONBLOCK))//当client缓冲区无数据;evdev不存在;文件非阻塞打开,那个read直接返回错误
return -EAGAIN;
if (count == 0)
break;
while (read + input_event_size() <= count &&//当要读取的数据大于struct input_event且client里面的buffer有数据
evdev_fetch_next_event(client, &event)) {//取出event数据
if (input_event_to_user(buffer + read, &event))//把数据拷贝到用户空间,对copy_to_user的封装
return -EFAULT;
read += input_event_size();
}
if (read)
break;
if (!(file->f_flags & O_NONBLOCK)) {
error = wait_event_interruptible(evdev->wait,//当client里面没有数据时,将应用程序请到evdev->wait等待队列休息
client->packet_head != client->tail ||
!evdev->exist);
if (error)
return error;
}
}
return read;
}
evdev_read函数里最终会调用evdev_fetch_next_event函数从buffer取出事件了,如果buffer里没有数据而且是O_NONBLOCK读取,则会暂时休眠,当有数据时,会在evdev_pass_values函数里唤醒。
如图所示: